Vacuum tube for solar collectors
The vacuum tube is the main design element of solar collectors, using which it becomes possible to obtain cheap thermal energy that is used by humans for their needs.
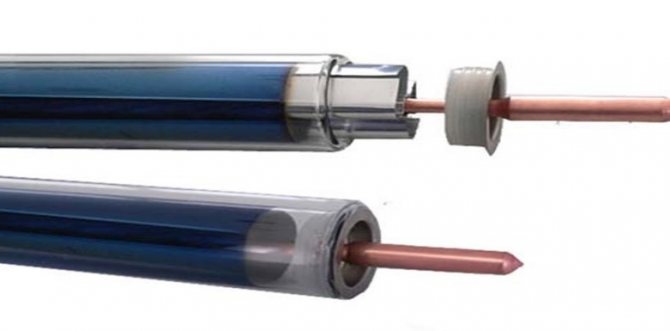
Structurally, the vacuum tube looks like this:
At its core, a vacuum tube is a heat exchanger consisting of two tubes placed one inside the other. The outer tube is made of durable glass, the inner tube is made of copper. To enhance the absorption of solar energy, a heat-absorbing layer, an adsorber made of a multilayer coating, is placed in the inner space of the glass flask. Also, air has been evacuated from the interior of the glass flask, thereby creating a vacuum that has better thermal conductivity and ability to retain heat than air.
The resulting thermal energy is transferred to a copper heat pipe, inside of which a refrigerant is placed, which, when heated, rises upward, where it evaporates in the condenser. The heat generated during the evaporation of the refrigerant is transferred to the coolant of the heating or hot water supply system.
Solar technology

The water tank must be adjacent to the collector itself. Connecting the solar collector to the system can be done in several ways; this directly depends on the type of water circulation. One of the simplest types of connections is a connection with natural circulation. In this type, the main and most important thing is the heating of water in the system, which will subsequently heat the room.
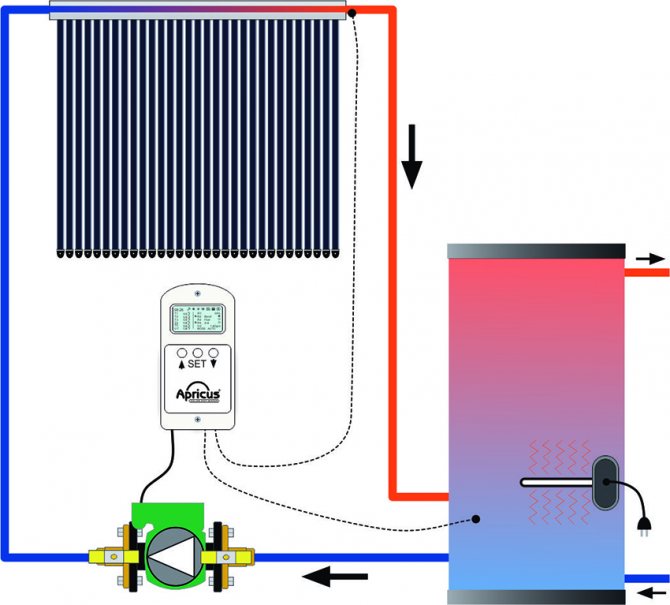
Traffic jams often occur at the entrance to the collector, which is explained by the lower cost of such a system. If desired, you can connect pumps to the solar collector that will force water to circulate through the heating system. The main advantages of such pumps are control, namely heating stops when the required temperature is reached. With such a heating system for a private house, it is best to use heating boilers in parallel, for example, those powered by gas.

Before installing the solar collector, it is necessary to choose the best possible place where it will stand. It is advantageous to install collectors so that they are exposed to direct sunlight most of the day. On average, the size of a water tank should not exceed 40 cm3, since in the cold season and cloudy and sunny weather, heating of the house may come to naught. This is the case if autonomous heating using only a solar collector is not planned.
Before purchasing a solar collector for your home, you should definitely consult with a specialist who is well versed in this area and can advise and give practical advice on choosing a collector.
Without the help of a specialist, you can make a mistake in choosing a collector and thereby not only spend a small amount of money, but also be left without heating your home during the cold season.

Recently, a lot of different solar collectors have appeared on the market, which differ in their shape, characteristics, as well as manufacturers. When purchasing, you should definitely pay attention to the performance of a particular collector; it is different for each collector, so you need to decide which performance will be most useful for your home.
Advantages of a solar collector

Also, if you have available materials, it is possible to make this kind of collector with your own hands. The second significant advantage of the collector, in contrast to solar panels, is that they are capable of absorbing 90% of the sun's rays. The solar collector is capable of receiving the sun's rays not only on a maximally sunny day, but also in slightly cloudy weather.
Disadvantages of solar collectors
In windy weather, even if the sun shines strongly, the collector will not heat at full strength. If, when heating your house, you did not install a pump to force water through the heating pipes, then with even the slightest frost, the ice that forms in the pipes can break them.
Compared to other heating devices, the collector is significantly inferior to them in heating water. Boilers are capable of heating water in pipes up to 100 degrees, and the solar collector up to no more than 60 degrees.
Properties
Common properties, regardless of design, for all types of vacuum tubes are the presence of a light-absorbing layer, an adsorber, placed in a glass tube made of durable glass. Depending on the design, the properties characteristic of a particular type of tube also differ.
Vacuum tubes are:
- Simple - used in water heating installations with an open circulation circuit. In this design, the coolant circulates directly in the “body” of the glass tube.
- U-shaped - is an improved version of a simple design. A U-shaped copper channel and a heat-absorbing plate are placed in the body of the glass bulb. This design can be used in networks with excess pressure and allows you to repair the manifold (replace the tube) without stopping the operation of the system in which it operates.
- With a heat rod “HEAT PIPE” - differs from the U-shaped design in that a copper rod is placed in the inner space of the glass flask, inside of which, in turn, a lightly boiling liquid, a refrigerant, is pumped. Properties and usability are similar to U-shaped structures.
- With increased absorption area (“SUPER HEAT PIPE”) – is a one-piece design with an enlarged thermal plate. The possibility of use and properties are similar to the properties of the above-considered structures.

Design and principle of operation
The simplest solar collector is black metal plates enclosed in a glass or plastic housing, which are usually mounted on the roof of a house. In essence, a solar collector is a miniature greenhouse that stores solar energy. This energy warms the water circulating through pipes hidden under the plate. The more energy transferred to the coolant, the higher its efficiency. But, although the operating principle is the same for all collectors, their design differs somewhat depending on the type of collector and its scope of application.
Unused cooled water from the reservoir gradually falls down, making room for heated water from the collector. Cold water enters the heat exchanger, where it is heated and returned to the tank. In practice, this means that the water in the storage tank always remains hot - on clear sunny days its temperature can reach up to 70 o C.
Types and characteristics of domestic collectors for water heating and heating
The described scheme of operation of the collector is very simplified, but in reality solar systems are somewhat more complicated. There are several types of solar collectors with their own design features.
Flat highly selective
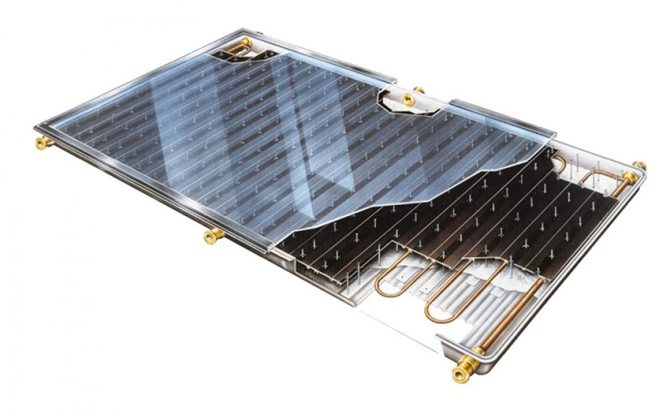
Flat-plate collector is one of the most common types. Their advantage is their low price, but compared to other models they lose more heat. Flat-plate solar collectors consist of a planar absorber, a clear glass cover, thermal insulation on the reverse side and a frame, which is generally made of aluminum or steel.
A planar absorber is a dark-colored metal sheet connected to heat-conducting pipes. The absorber layer accumulates solar rays and transforms solar energy into thermal energy, which is then transferred to the coolant fluid (a mixture of water and glycol). This liquid “channels” heat into the solar battery. The glass covering of the collector protects the absorber from environmental influences and reduces heat loss, creating a greenhouse effect. Mineral fiber thermal insulation also performs the same function.
Vacuum tubular
Solar collectors of this type consist of glass tubes, each of which contains a device that absorbs sunlight. Vacuum is an ideal heat insulator, and therefore the heat loss of such collectors is much less. There are two types of vacuum collectors, differing in the heating method - with indirect heat transfer and direct flow. The first type of device is intended for all-season use, and the second - for the warm season, from April to September.
Materials
Regardless of the design of the vacuum tube, the main material used in all types of devices is borosilicate glass, which can withstand significant external loads without damaging the body of the glass bulb (rain, snow, hail, etc.).
Another material used in almost all designs is copper, from which the inner tube is made. Copper was not chosen by chance, because this particular metal has good thermal conductivity and practically does not corrode during operation.
Antifreeze (refrigerant), a substance placed inside the copper tube, has the ability to evaporate at a relatively low temperature.
An adsorber is a heat-absorbing layer that can be made of various compositions capable of absorbing heat. The type of composition is chosen individually by each manufacturer.
The heat absorption plate is made of copper and is attached to the heat rod.
Solar collector power calculation
As an example, reservoir calculations for the Moscow region will be given.
Data for calculations:
- Place of application - Moscow region Absorption area - 2.35 m2 (based on the table on the average amount of solar energy received for the regions of the Russian Federation)
- The amount of insolation in the Moscow region is 1173.7 kW*hour/m2
- Efficiency – from 67% to 80% (minimum indicators relevant for outdated collectors will be used, so the results will be slightly underestimated).
- Collector inclination angle – the optimal inclination angle data will be used in the calculations.
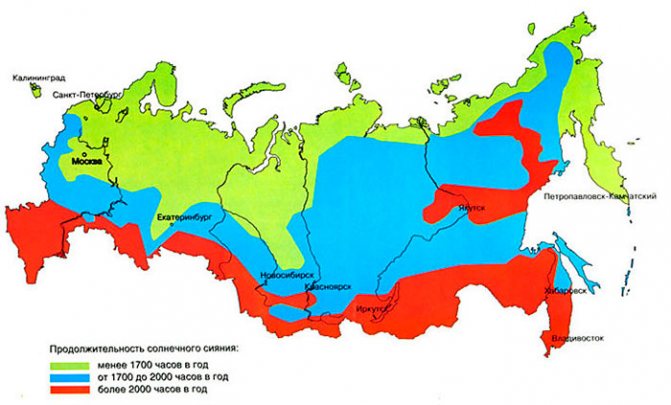
insolation map of Russia
We calculate the absorption area for one tube:
15 tubes = 2.35 sq. m.; 1 tube = 2.35 / 15 = 0.15 sq. m.
Now that the area absorbed by one tube is known, let’s determine the number of tubes equal to 1 square meter. collector surface: 1 / 0.15 = 6.66. In other words, 7 collector tubes are required per meter of absorption surface.
Next, we calculate the thermal power of one collector tube. This will make it possible to calculate the number of tubes required to obtain sufficient thermal energy for periods of one day and one year:
The resulting power per day is calculated as follows: 0.15 (S absorption of 1 tube) x 1173.7 (insolation value in the Moscow region) x 0.67 (solar collector efficiency) = 117.95 kW*h/m. sq .
To calculate the annual efficiency of one tube in a selected region, annual insolation data should be used in the formula for calculating daily power. In other words, in place of 1173.7 it is necessary to put the regional insolation values.
The power generated using one tube in Moscow ranges from 117.95 (using an efficiency of 67%) to 140 kW*hour/sq.m. (using an efficiency of 80%).
On average, one vacuum tube of a heat collector produces 0.325 kW*hour per day.
In the sunniest months (June, July), one tube will produce 0.545 kWh.
It is impossible to operate a solar collector without light; for this reason, the indicated indicators must be used when calculating daylight hours.
How much electricity can you save in Moscow by using one sq. m. manifold (as we found out, these are 7 vacuum tubes)?
Annual energy savings will be:
117.95 kW*hour/m2 * 7 = 825.6 kW*hour/sq.m.
Accordingly, the solar collector will generate the greatest power in the summer months. For example, in June, when using 1 sq.m. collector, electricity generation will be about 115–117 kW*hour/sq.m.
In other words, the energy benefit when using a solar collector with 15 vacuum tubes, where S = 2.35 sq. m. for the period from March to August with a total insolation value for the entire specified period of 874.2 kW*hour/sq.m. will be: 874.2 * 2.35 * 0.67 = 1376 kW, that is, almost 1.4 MegaW. energy, which is approximately 8 kW per day.
Let us recall the statistical information given in the first part of the article - a household uses from 2 to 4 kW of energy when consuming hot water by one person daily. These indicators imply the use of a collector for heating hot water and, in particular, such needs as taking a shower, washing dishes, etc.
Calculations of a solar collector consisting of 15 vacuum tubes allow us to conclude that during the gardening season this device will be enough to provide hot water to a family of three people. As a result, taking into account all unfavorable circumstances, such as cloudy or rainy weather, you can save a lot of money on electricity used to heat water.
If we talk about optimal conditions (sunny weather and no rain), then in this case the generation of thermal energy by a solar collector will completely avoid the need to pay for electricity.
Average prices
Depending on the technical characteristics, design and company of the manufacturer, the cost of such products may differ, but in order to understand the order of the numbers, below are the retail prices for the models of the companies that are most popular in our country.
The cost of the model will be:
- Simple type (“Andi-Group”) – from 1000.00 rubles.
Technical characteristics: outer diameter - 58±0.7mm; length - 1800±5mm.
- Heat pipe type (“Andi-Group”) – from 2400.00 rubles.
Technical characteristics: outer diameter - 58±0.7mm; length - 1800±5mm.
- Simple type (“WESWEN”) – from 1400.00 rubles.
Technical characteristics: length - 1800 mm; diameter - 58 mm.
- Type heat pipe (“WESWEN”) – from 3400.00 rubles.
Technical characteristics: length - 1800 mm; diameter - 58 mm.
- Simple type (“TEPLOPEN”) - from 1800.00 rubles.
Technical characteristics: length - 1800 mm; diameter - 58 mm.
- Type heat pipe (“TEPLOPEN”) – from 2200.00 rubles.
Technical characteristics: length - 1800 mm; diameter - 58 mm.