Basic modes and functions of air conditioners
Depending on the functions provided by the manufacturer, the complexity of the system and power consumption vary. Air conditioners and block systems perform the following functions:
- cooling and heating of enclosed spaces;
- ventilation for the purpose of uniform distribution of air in the room;
- air dehumidification is an inevitable accompanying option, associated with the extraction of water from cooled air;
- air purification with coarse, fine and electrostatic filters;
- maintaining the temperature within the specified parameters;
- change in speed and direction of air flow.
Please note the lack of ventilation. The influx of fresh air occurs naturally, through leaks in door and window openings.
kW consumption calculations
Let's take an air conditioner (07) with a power of 2000 Watts, which means that it consumes 700 - 800 W/hour depending on the mode: heating or cooling the air, but if the air conditioner has an inverter compressor, then the consumption will decrease by another 30-50% and will be 350- 500 W/hour.
We recommend: What is SOI (ODN) in a housing and communal services receipt
Calculation of consumption for 1 minute: 500 (device power) / 60 (minutes in an hour) = 8.3 Watts/minute.
Let's say that you turn it on for 9 hours a day: 500(consumption per hour) * 9(number of operating hours) = 4500 W (4.5 kW/day).
Electricity consumption per month: 30 (days of operation) * 4.5 (consumption per day) = 135 kW/month.
The amount of payment for the electricity spent by the air conditioner: 135 * 3.5 rubles (for example, the tariff for 1 kW/hour, there are different tariffs in each region, district, city and village) = 472.5 rubles.
Attention, we calculated the consumption of a type 07 air conditioner with an inverter compressor for a 9-hour working day (in hot weather it can work for 18 hours and then the consumption will increase by 2 times), if you have the same type, but without an inverter, then the consumption will be 5, 85 kW per day, 175.5 kW per month.
Air conditioner power consumption
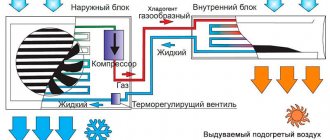
All network devices, including air conditioners, are consumers of electrical energy. It is converted into mechanical, and is spent on overcoming air resistance as it moves, to reproduce associated functions associated with energy consumption.
The power consumption of the air conditioner, measured in kW, is several times less than the cooling power. This is due to the characteristics of climate control equipment. Energy is spent only on moving air masses, and the efficiency of the installation in terms of power consumption is 250-300%. This means that for a household air conditioner with a cooling power of 2 kW, a motor with a power consumption of 700 W is used, which is connected to a household single-phase network.
The power of the air conditioner is indicated in the passport data and on the body of the device; during cooling, it is about 3 times more than consumed. When choosing an air conditioner, proceed from the need for cooling power. For a room up to 3 m high, 10 square meters requires 1 kW. The indicator is basic when calculating the choice of climate system. Depending on the complexity of the design, glass area, doors, greater cooling power will be required.
If the air conditioner can operate for cooling/heating, the design uses additional equipment. In this case, heat is taken from the outside air and supplied to the room. That is, when heating a room, the units perform the opposite work; the power consumption of the air conditioner is not spent on the heating element. Such systems are more expensive because a heat pump is included in the system.
Saving tips
There are several ways to save energy:
- Choose an inverter type of air conditioner or with an inverter compressor.
- Keep an eye on the filters and heat exchanger; if they are dirty, it takes longer for air to enter the room.
- After use, turn it off and unplug it from the socket (since even in this state it consumes electricity).
- If you don't need it, turn it off.
- Do not open windows and doors so that the converted (cooled or heated) air does not escape into the street.
We recommend: How much electricity does a multicooker (steamer) consume?
Air conditioner power factor
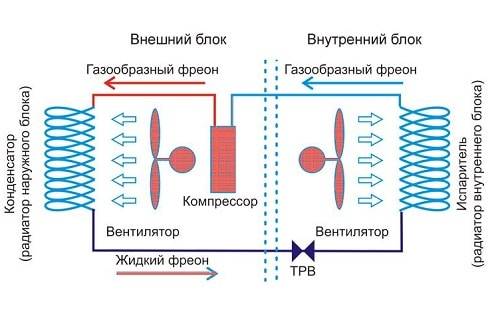
When calculating how much power an air conditioner of any type consumes, a developed calculation methodology is used. Basic conditions include:
- main wall;
- complete sealing;
- standard difference between outside and inside temperatures.
The calculation of cooling power under such conditions is taken as one. The presence of a large glazing area, ceiling heights, and doorways change the ability of the circuit to retain heat, and a coefficient is introduced for the cooling power. Power consumption depends on the energy efficiency of the equipment. An inverter air conditioner will have greater efficiency due to the absence of starting peak loads of the compressor.
When selecting equipment, energy efficiency characteristics COP and ERR are used. COP is an indicator of the ratio of heating power to air conditioner power consumption. The coefficient is in the range of 2.8-4.0. The ERR indicator is the ratio of heating power to the power consumption of the air conditioner in W. The coefficient is in the range of 2.5 – 3.5. The ratio indicates that the air conditioning process is adiabatic and produces more heat than cold.
According to the ICO5151 standard, it is customary to measure the energy efficiency of an air conditioner under temperature conditions outside of +35 0 C, indoors up to +27 0 C. Changing conditions affects the efficiency of the system, power consumption in kW per hour.
When choosing an air conditioner, the main attention is paid to its technical characteristics:
- Cooling power
- Power consumption
- Air heating option
- Refrigerant type
- Inverter type
- Possibility of ventilation (fresh air supply)
- Noise produced
- Basic consumer functions
- Distance between outdoor and indoor unit
- Influence of outside temperature on operation
- Additional devices (all-weather unit, drainage pump, etc.)
Air conditioner power
This is the most important characteristic of any split system. The area for which it is designed, as well as its cost, depends on this value. The calculation consists of several stages:
1. It is very easy to determine the approximate electrical power - for every 10 sq.m. refrigerated space requires 1 kW. with a ceiling height of 2.8 - 3.0 m. Using this simplified method, the required power is determined to compensate for heat inflows from walls, floors, ceilings and windows.
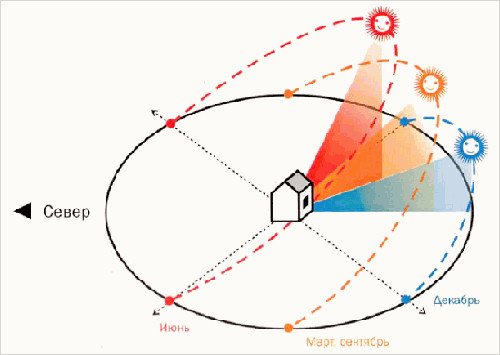
2. Taking into account the sides on which the windows face.
If the room has a large glass area or the windows face the sunny side, then the heat gain will be greater and the electrical power must be increased by 15 - 20%.
You can calculate heat inflows using the following formula: Q = S * h * q, where Q is heat inflows (W); S—room area (sq.m); h—room height (m); q - coefficient equal to 30 - 40 W/kb.m (for the south side - 40, for the north - 30, average value - 35 W/kb.m).
Note that these calculations are applicable only for permanent buildings, since it is almost impossible to air condition an iron stall or a store with a transparent roof - on a sunny day, the heat gain from the walls and ceiling will be too large.
3. Accounting for heat generated by people and electrical appliances.
It is believed that in a calm state a person emits 0.1 kW of heat; computer or copy machine - 0.3 kW; for other devices, we can assume that they emit 1/3 of their rated power as heat. Having summed up all heat releases and heat inflows, we obtain the required value.
Example: let’s make a calculation for a typical living room with an area of 26.0 sq.m (ceiling height 3.0 m) in which there are two people and a computer.
To compensate for heat inflows from walls, windows, floors and ceilings, it is necessary: 26.0 sq.m * 3.0 m * 35 W/kb.m = 2.73 kW. To compensate for the heat generated by people and the computer, it is necessary: 0.1 kW * 2 = 0.2 kW (from people) and 0.3 kW (from the computer) In total, we sum up all heat emissions and heat inflows: 2.73 kW + 0.2 kW + 0.3 kW = 3.23 kW.
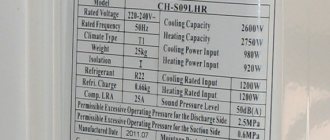
Now all that remains is to choose an air conditioner model that is close in power from the standard range - 3.5 kW (most manufacturers produce air conditioners with powers close to the standard range: 2.0; 2.5; 3.5; 5.0; 7.0 kW). By the way, models from this series are usually called “seven”, “nine”... “twenty-four”. These numbers are present in the names of air conditioners from most manufacturers and indicate their power not in the usual kilowatts, but in thousands of BTU (British Thermal Unit). 1 BTU is equal to 0.3 W (more precisely 0.2931 W). Accordingly, an air conditioner with a capacity of about 7000 BTU or 7000 * 0.3 = 2.1 kW will have the number 7 in its name, etc. But for example Daikin, the name of the models is tied to the typical power in watts (the Daikin FTY35 air conditioner has a power of 3.5 kW).
Although this calculation is approximate, for domestic premises its error is small. However, before choosing an air conditioner, be sure to invite our engineer, who will help you accurately calculate the power and select equipment, and also agree with you on the location of the units and inter-unit communications (the cost of installation will depend on this). Let us only add that this service is free for you.
Accurate selection of air conditioner power is very important. Insufficient power may only appear in hot weather, and if the air conditioner is installed at the end of summer, you may only feel it a year later, when it will be too late to make a claim. Excessive power also does not lead to anything good. Firstly, an air conditioner that is too powerful creates a strong flow of cold air - if you are in close proximity to the air conditioner, you can catch a cold. Secondly, the air conditioner will turn on and off more often, which will lead to increased wear on the compressor. Thirdly, it will be more expensive.
Note that without visiting the site it is difficult to accurately calculate the required power of the air conditioner and, most importantly, determine the features and cost of installation. Therefore, do not trust companies that are ready to do all the necessary calculations “over the phone” and immediately send a team of installers. The visit of a company representative before the start of installation work is also necessary to agree on the exact location of the units and communications.
Air conditioner power calculator
You can independently calculate which split system to buy and choose one that meets your requirements by using the air conditioner power calculator. The most energy-consuming process ERR is taken as the base one - the energy consumed to obtain cooling performance.
Information you need to enter into the calculator:
- Area of the room, ceiling height, whether to take ventilation into account, if so, what is the air exchange rate.
- The room is sunny or darkened, an attic or a permanent room.
- How many people work or live?
- Number of computers, televisions, total power of equipment in the room.
As a result of the calculation based on the provided information, the system will display the parameters - estimated cooling power - Q in kW and the range in which it is optimal to select the Q range air conditioner.
Using the table of power distribution of air conditioners, select the type of device, the power of the household air conditioner that is most suitable for the stated conditions.
How to calculate the power consumption of an air conditioner for a room
You can calculate the power of the air conditioner both for a room and for any household premises yourself.
Let's take a room: area 20 sq. m, ceiling height 3 m, accommodates 1 person, has a computer, TV and refrigerator. The room is sunny, office equipment works alternately.
Calculation:
- Heat inflows into the room are the sum of the walls and ceiling Q1, from the person Q2 and from the equipment that produces heat Q3.
- In the solar room, to determine Q1, q 20x3x40/1000 = 2.4 kW is used. Q2 is assumed to be 0.1 kW in a quiet state. Q3 is determined by the sum of the heat emission of a computer, as the most expensive - 0.3 kW and a refrigerator 30% of the power of 150 W - 0.05 kW. Heat dissipation – 2.4 kW + 0.1 kW + 0.35 kW = 2.85 kW.
- Using Q range (-5~+15)% you need to look for an air conditioner with a cooling capacity of 2.7 - 3.3 kW.
- We select a model of suitable power from the table.
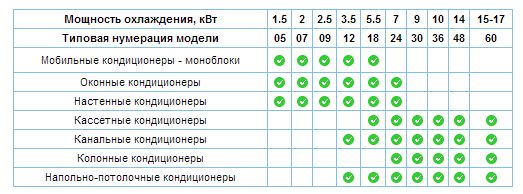
When independently choosing a climate system based on cooling power, you must take into account that the power of the air conditioner may not be in kilowatts, but in units of BTU/hour, this indicator corresponds to the British inch/pound measurement system. You can use a plate that connects the model range with the power of the air conditioner, according to the British and international systems.
| Row | BTU | kW | Row | BTU | kW |
| 7 | 7000 | 2,1 | 36 | 36000 | 10,6 |
| 9 | 9000 | 2,6 | 42 | 42000 | 12,3 |
| 12 | 12000 | 3,5 | 48 | 48000 | 14,0 |
| 18 | 18000 | 5,3 | 54 | 54000 | 15,8 |
| 24 | 24000 | 7,0 | 56 | 56000 | 16,4 |
| 28 | 28000 | 8,2 | 60 | 60000 | 17,6 |
Knowing the cooling capacity, you can always determine how much power the air conditioner consumes in units of measurement.
It is important to choose the right split system, window or floor air conditioner. Excessive power consumption can lead to disruption. Thus, calculations for a small room allow you to select a mobile unit, wall and window air conditioners. Floor-ceiling and duct fggfhfns are used if the area is more than 26 square meters. meters.
Detailed universal formula for calculating the power level for a specific room
If you decide to independently measure the power of the air conditioner, you can use the formula: Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3, where
Q1 - heat inflows from the window, walls, floor and ceiling.
Q1 = S * h * q / 1000, where
S—room area (m²); h—room height (m);
q - coefficient equal to 30 - 40 W/m³:
- q = 30 for a room located on the shadow side;
- q = 35 at medium illumination;
- q = 40 for rooms located on the sunny side of the world.
Q2 is the sum of heat inflows from people.
The heat inflows emanating from an adult are equal to:
- 0.1 kW - at rest;
- 0.13 kW - with light movement;
- 0.2 kW - for heavy physical activity.
Q3 is the sum of heat inflows from the use of household appliances.
Heat gains generated by everyday appliances:
0.3 kW - computer;
0.2 kW - TV.
Most experts highly recommend hanging blinds or light curtains on the window openings of the sunniest areas. In the bedroom, blackout curtains would be an ideal option.
The air conditioning system functions properly and at full capacity only when it is in perfect condition and correctly installed. The warranty for an air conditioner is issued not by the manufacturer of the device, but by the company that installed it.