Ventilation and air conditioning in a production workshop
Ventilation in a workshop is a multi-level, complex system that is calculated and always designed for a specific production, taking into account the specifics of working conditions and manufactured products. Allows you to adjust microclimatic parameters during the work process.
Ventilation can be natural and forced (mechanical), as well as supply, exhaust and mixed. The most commonly used supply and exhaust unit is with mechanical drive. In this case, local exhaust devices are additionally installed to remove heat from the air flow saturated with hazardous substances. The necessary equipment is provided for by the workshop ventilation design.
Ventilation standards are provided for by SNiP, and for each individual production there are a number of specific requirements that must be met. Also, the heating of the workshop is interconnected with the ventilation system, and air conditioning allows, if necessary, to maintain precise temperature parameters.
Ventilation of galvanizing shop
The danger is posed by alkaline, acidic, electrolyte vapors, hydrogen cyanide, and excessive heat and humidity levels. The ventilation system must meet fire safety standards, be made of stainless materials, or be coated with anti-corrosion protection.
Ventilation standards determine the air exchange rate of the galvanizing shop to be 3 (rooms for the production of cyanide salts and other solutions). The inflow is supplied from above, 5% of it should go to nearby compartments. The air flow removed by the general ventilation system is necessarily filtered from harmful impurities.
Onboard suction for tanks with acid and cyanide solution are used as local ventilation. The hoods are equipped with explosion-proof fans with an additional backup mechanism. Exhaust air must be cleaned before being released outside.
Determining the height of the pipe
To organize the natural ventilation system of a private house with your own hands, you should have a good understanding of the principle of its operation. So, as the basis for such communication in living rooms, channels that are located vertically can be used. They start in a ventilated area and end under the roof.
The main condition when creating an organized natural ventilation system in a country cottage with your own hands is the correct selection of the height of the pipes. This is an important parameter on which the quality of the ventilation system depends.
So, the pipe should be of such a height that it exceeds the roof ridge by an average of 1.5 - 2 m in an area where the wind is highly active.
The air duct should be located:
- somewhere at the level of 0.5 m above the roof from the ridge, provided that the distance from it and to the ventilated duct is less than 1.5 m;
- in the same vertical with the ridge, if the ventilation duct is located at a distance of 1.5 - 3 m;
- at an angle of 10°, provided that the specified distance exceeds 3 m;
- if the installation of pipes needs to be done on a flat floor, then the minimum distance is 30 cm, and on a sloping roof the height of the shaft must be at least 50 cm.
Welding shop ventilation
Ventilation of welding shops is aimed at removing air flow containing nitrogen oxide, carbon, ozone, and fluoride compounds. For this purpose, local hoods are provided.
Ventilation standards determine the supply-exhaust ratio of 2/3 in the lower tier, 1/3 in the upper. The calculation of ventilation for welding production is carried out taking into account the weight of the electrodes used in 1 hour:
- manual welding – 1500-4500 m³ h/kg;
- semi-automatic on carbon dioxide – 1700-2000 m³ h/kg;
- welding with flux-cored wire – 2500-5400 m³ h/kg.
Calculation of ventilation for welding production is carried out to an acceptable level.
Sanitary standards
Another option for calculating ventilation is according to sanitary standards. Similar calculations are carried out for public and administrative facilities. To make correct calculations, you need to know the average number of people who will constantly be inside the building. If we talk about regular consumers of indoor air, they need about 60 cubic meters per hour per person. But since public facilities are also visited by temporary persons, they must also be taken into account. The amount of air consumed by such a person is about 20 cubic meters per hour.
If you carry out all the calculations based on the initial data from the tables, then when you receive the final results, it will become clearly visible that the amount of air coming from the street is much greater than that consumed inside the building. In such situations, they most often resort to the simplest solution - installing a ventilation hood at approximately 195 cubic meters per hour. In most cases, adding such a network will create an acceptable balance for the existence of the entire ventilation system.
Foundry ventilation
A distinctive feature of foundries is the excessive amount of heat generated during the metal casting process, which is accompanied by vapors of ammonia, carbon monoxide, and sulfur dioxide. Therefore, for the technological equipment of foundries, local exhaust hoods with high productive capacity and resistance to high temperatures are required.
The calculation of the ventilation system for foundries is carried out carefully, taking into account all parameters. Local exhaust ventilation in the workshop complements the general one with forced ventilation. Natural ventilation and ventilation of the work area directly near the hot equipment is also organized.
The supply ventilation of the workshop is general, the flow is directed from top to bottom. Heating is combined with a ventilation system.
What you need to know about bakery ventilation >>>>
Calculation of ventilation system elements
To calculate the ventilation system and select all its elements, you need to find out:
- air flow (for more information on determining air flow, see below)
- aerodynamic resistance of the system (in this case, the resistance of all elements of the ventilation system is summed up, as well as the resistance of the air ducts depending on their length and size)
- the power of the air heater is determined by the formula N heat = G pr ⋅ρ air ⋅c air ⋅(t room - t air), where G pr - Supply air flow
- ρ air - Air density
- c air — Heat capacity of air
- t room - Temperature maintained in the room
- t out — Outside air temperature
- G pr — Supply air flow
- d uvl - The amount of water that must be added to the air,
Paint shop ventilation
Installation of supply and exhaust type workshop ventilation is carried out both locally and generally. The calculation of workshop exhaust ventilation is made based on the characteristics of paint and varnish production. Local hoods with a centrifugal fan are installed above paint baths, in spray painting compartments, etc.
In rooms with a height of 5 m above the local one, a mechanical exhaust is installed to remove toxic fumes that were not captured by the lower exhaust system.
The supply air flow is uniformly supplied from above and heated in winter. The design of workshop ventilation determines the percentage of inflow up to 80% of the drawn-out harmful flow, which creates a rarefied pressure.
Ventilation of a car service paint shop
The tasks that the ventilation of a paint shop should perform are the removal of contaminated air along with fumes and drops of paint, its filtration before being discharged outside. They will be performed by exhaust ventilation in the paint booth of the car service center. In addition to the exhaust system, an influx of fresh air is also necessary, pre-cleaned from dust particles and subsequently heated to a certain temperature, ensuring comfortable working conditions for personnel. Air supply is carried out by supply systems. They create conditions for carrying out work on applying paintwork in accordance with the standards. Since paint is heavier than air, air intake should be done from below, therefore exhaust grilles and air ducts, as a rule, are located in the lower part of the workshop along the walls, and air supply, accordingly, should occur from above. To prevent heavy paint mist from spreading throughout the room and to improve coating application to the surface, it is necessary that the room temperature is at least 20°C.
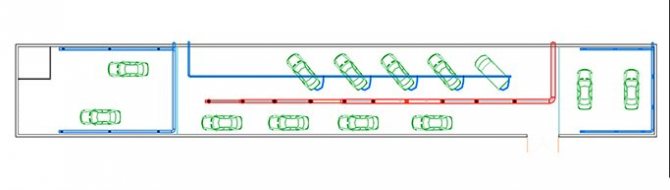
Ventilation diagram in a car service center To calculate the ventilation in a paint booth, it is necessary to take into account all the features of the technological process, the size of the room, the equipment available, the number of personnel, etc.
Read more about paint shop ventilation.
You can get a free draft design and cost of ventilation for your car service
Go
Ventilation of metallurgical workshop
The calculation of workshop exhaust ventilation is based on the removal of excess heat from blast furnaces. In addition, aspiration devices are designed to remove excess dust generated, for example, when using solid fuel (coal). The aspiration system is equipped with electric precipitators and bag filter devices, which are characterized by high productivity. Fuel supply departments for blast furnaces are equipped with heating, air conditioning, and ventilation systems.
Examples of calculating air flow are based on factors:
- the use of fans with a power of several hundred kW;
- excessive dustiness of the air;
- fire hazard in some areas;
- the need to ensure acceptable working conditions for personnel;
- maintaining specified temperature parameters;
- ensuring simple, low-cost maintenance.
Ventilation of the meat industry
Examples of ventilation system calculations are based on the specifics of the functioning of various departments:
- raw materials, machine, extrusion, separation of semi-finished products: general forced exhaust from the upper tier, there is also an influx of fresh air supplied down evenly throughout the room;
- ventilation of the sausage shop (hard smoked sausages, smoked pork meats), thermal and offal departments: general mechanical with additional local ventilation, in summer the influx into the upper zone is natural (in winter - with mechanical stimulation);
- dumpling compartment: local exhaust hoods are used, air supply units in the upper zone supply the flow evenly, the movement speed is low;
- smoke generating zones: general exhaust ventilation from the upper tier, the inflow is supplied directly to the work area mechanically in winter and in the off-season, natural supply in summer.
Ventilation in the workshop
Home > Blogs > Ventilation in the workshop
As a rule, the workshop is equipped with supply and exhaust ventilation, which can be either natural or forced. Ventilation ducts are provided at the stage of wall construction. Why is a vertical void with a cross-section of 260x130mm left in the brickwork? One such channel is made in the upper corner (as close as possible to the ceiling), and the other in the opposite lower corner (as close to the floor as possible). Thus, we get the simplest supply and exhaust ventilation, which without fans is called natural.
If the walls are already ready, but there are no channels in them, then they are made from pipes with a diameter of at least 100 mm. Just like in the case discussed above, the inner end of one pipe should be as close to the ceiling as possible, and that of the second pipe as close to the floor as possible (300-500mm). The outer ends of the pipes are brought out and protected by special caps of a pyramidal, conical or cylindrical shape. For forced ventilation, pipes or wall ducts are equipped with fans. In addition, it is recommended to paint the exhaust pipe facing the street black, since it attracts the sun, and when the duct (pipe) is heated, the exhaust performance improves significantly. For the same reasons, the exhaust pipe must be insulated, since at sub-zero temperatures ventilation may stop altogether. For heating in winter and improving functional qualities, an electric light bulb of medium power is lowered into the exhaust pipe (or wall channel) and left there in the on state.
Also, to ensure forced ventilation, a rotary diffuser-vane is installed on the top of the supply pipe, the work of which is to use the speed of air flows. The weather vane catches the air flow and redirects it indoors, thus providing a powerful flow of fresh air.
The biggest mistake when creating ventilation in a workshop is neglecting the supply duct. That is, they simply “forget” to do it. In the summer, of course, this issue is resolved by opening windows and doors, but in winter everything is much more complicated. After all, along with poor-quality air, heat from the room also evaporates, which accordingly affects the comfortable sensations during the work process.
Ventilation of fish production
The production process is characterized by the presence of a sharp, specific odor that accumulates at the bottom of the premises. The ventilation system device provides:
- acceptable working conditions for personnel, removing the air flow filled with a specific odor;
- quality of fish products. The preparation of fish products is accompanied by culinary and heat treatment. In this case, particles of fat, burning, and associated odors enter the working air environment. To remove them, local exhaust is used;
- required storage period. Removing excess water vapor, odor, and along with them various microorganisms allows you to adhere to standards for shelf life of products.
Ventilation of a repair shop
A special feature is the uneven, intense release of welding aerosols in certain areas. When repairing large-sized equipment and machines, it is impossible to organize local exhaust hoods. There may also be restrictions on the heat supply of the repair and technical unit.
The workshop ventilation drawing is drawn up in accordance with all related factors. It is possible to organize local climatic zones of a certain structure. At the height of the welding fume accumulation, air ducts are installed through which the air flow is diverted and filtered. On the other hand, an inflow (purified with the addition of fresh air mass) is supplied above the working area, thus creating air circulation.

Hot shop ventilation: installation features >>>>
Calculation of mechanical ventilation
The variant number corresponds to the sum of the last two digits of the cipher.
One of the effective means of normalizing the air environment of industrial premises is ventilation.
The main document regulating the use of ventilation is SNiP II-33-75.
Equipment for installing ventilation systems should be selected taking into account the category of explosion and fire hazard in accordance with building codes and electrical installation rules.
Mechanical ventilation is the most widespread.
The calculation of mechanical ventilation comes down to solving the following two key problems:
1) determining the required amount of air;
2) aerodynamic calculation of the ventilation network, as a result of which the required fan pressure to supply the calculated amount of air and the diameters of the air ducts are found. Knowing the amount of air and pressure, a fan is selected from the catalog so that its efficiency is at least 0.6.
The initial data for calculating ventilation are given in table. 2.
During general ventilation, the required amount of air is determined based on the requirements of SNiP II-33-75.
In the absence of harmful emissions in a production room with a volume per worker of less than 20 m3, the air exchange should be at least 30 m3/h, and in rooms with a volume of 20 to 40 m3 - at least 20 m3/h. In rooms with a volume per worker of more than 40 m3 and the presence of natural ventilation, air exchange is not calculated.
If there is no natural ventilation, the air flow per worker should be at least 60 m3/h.
When gaseous pollutants are released, the necessary air exchange is determined based on the dilution of their permissible concentrations according to the formula
(3)
where L
– volume of supply or exhaust air, m3/h;
z
– amount of harmful substances entering the indoor air, mg/h;
Cud
,
Cpr
- concentration of harmful substances in the exhaust and supply air, respectively, mg/m3.
The content of harmful substances in the removed air, as a rule, should not exceed the maximum permissible concentration. The concentration of harmful substances in the supply air should not exceed 0.3 MAC. If the main hazard is heat, then air exchange is calculated based on the removal of excess heat using the formula:
(4)
where Lpr
– volume of supply air, m3/h;
tsp
,
tpr
– temperature of exhaust and supply air, respectively;
Qs
is the amount of sensible heat released in the room, kcal/h.
table 2
Mechanical shop ventilation
A general ventilation system for the workshop is used with additional local exhaust hoods over roughing and grinding machines, non-cooled equipment, tanks for technical fluids, etc.
General ventilation in a machine shop is designed at a ventilation rate of 30 m³/person or more. It is necessary to remove residual heat, toxic vapors of emulsions, oils, aerosols, and technical liquids. Supply air is supplied from top to bottom.
The workshop is heated by air, combined with a ventilation system.
Need for ventilation
Firstly, it is immediately worth noting that without fresh air, a person’s lungs begin to function worse. It is also possible that a variety of diseases will appear, which with a high percentage of probability will develop into chronic ones. Secondly, if the building is a residential building in which there are children, then the need for ventilation increases even more, since some ailments that can infect a child are likely to remain with him for life. In order to avoid such problems, it is best to arrange ventilation. There are several options worth considering. For example, you can start calculating the supply ventilation system and installing it. It is also worth adding that diseases are not the only problem.

In a room or building where there is no constant exchange of air, all furniture and walls will become covered with a coating from any substance that is sprayed into the air. Let's say, if this is a kitchen, then everything that is fried, boiled, etc. will leave its sediment. In addition, dust is a terrible enemy. Even cleaning products that are designed to clean will still leave a residue that will negatively impact the occupants.
Paint shop ventilation
Toxic vapors of solvents, paints, and coatings are removed by local installations located above degreasing apparatus, painting chambers, jet spraying, drying, and dipping tanks.
The design standards for a paint shop determine a one-time exhaust flow from the upper tier and a one-time influx that compensates for the work of local suction.
The heating of the paint shop can be central or combined with a ventilation system.

Ventilation of thermal shops
The calculation of exhaust ventilation for the heat treatment shop is made taking into account water, oil vapor, convection, and radiant heat generated by the technological equipment. Carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide generated as a result of the combustion of solid fuel are hazardous to the health of personnel.
All technological installations are equipped with a local exhaust hood that removes excess heat, carbon dioxide, and hydrocyanic acid (formed by the interaction of cyanide salts and carbon dioxide).
Also, the installation of ventilation in a work area with intense heat generation works on the influx, supplying fresh air directly to the person. In addition, aeration devices are additionally installed as an economical method of ventilation.
What is industrial ventilation?
Air exchange standards for parking lots, car service stations, gas stations
In vehicle storage rooms, supply and exhaust ventilation is designed to dilute and remove harmful gas emissions, ensuring sanitary and hygienic conditions. According to the technological task, the amount of emitted harmful substances is taken; according to the design task, the time of people’s stay (duration of work) in the room is taken.
Air exchange rates
| General ventilation | Exhaust from the upper zone, inflow into the working zone and ditches. In inspection ditches – 125 m3/h, in pits – 100 m3/h, in tunnels 5 times. |
| Local blowjobs | Local suction (f100-200 mm) from the exhaust pipe. 10% of the exhaust enters the room. |
| Hood: | |
| Up to 120 hp – 350 m3/h | |
| 120-180 hp – 500 m3/h | |
| 180-240 hp – 650 m3/h | |
| More than 240 hp – 800 m3/h. | |
| Local suction from washing units and parts. |
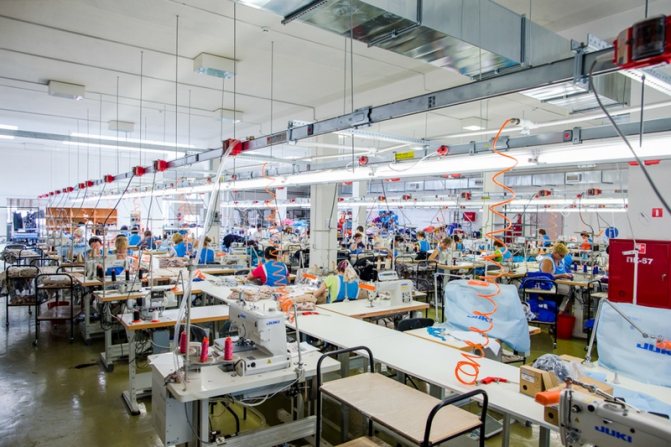
Ventilation of the sewing workshop
The exhaust ventilation of the workshop is designed for dust removal, cleaning, and humidification of air masses. As a rule, roof fans are used to draw air through ventilation shafts and air ducts. Cleaning is carried out using mesh or fabric filters.
The supply ventilation of the workshop is built from above, uniformly supplying fresh air throughout the entire room. If the ceiling height is insufficient, the inflow is directed upward or equipped with protective screens.
If air pollution exceeds permissible levels, local hoods with a filtration system to humidify the removed air flow are additionally installed.

Consequences of poor ventilation
If the fresh air supply system is not properly organized, the rooms will experience a lack of oxygen and increased humidity. Errors in the design of the hood are fraught with the appearance of soot on the walls of the kitchen, fogging of the windows and the appearance of fungus on the surface of the walls.
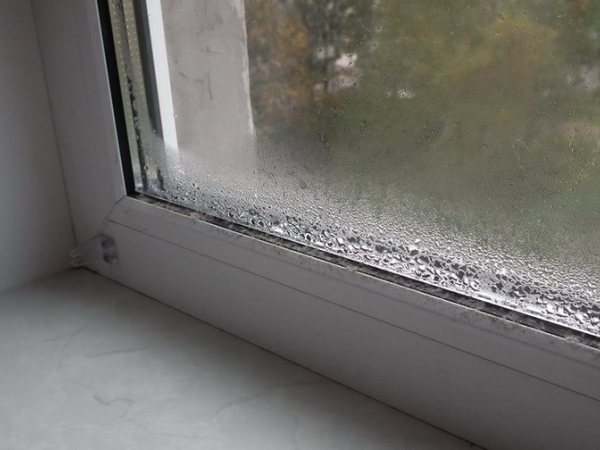

Fogging of windows due to insufficient exhaust
It should be taken into account that round or square pipes can be used to install the ventilation system. When removing air without the use of special devices, it is advisable to install round air ducts, since they are stronger, more airtight and have good aerodynamic characteristics. Square pipes are best used for forced ventilation.
Ventilation production workshop
Refers to industrial premises, ventilated in accordance with the standards and requirements of sanitary and hygienic control. It is equipped with a general ventilation system that removes waste air masses from the upper tiers of the working room. If necessary, local hoods are installed.
The influx is also supplied to the upper layers, evenly distributed downwards to the working areas of the personnel.
Heating is combined with a ventilation system and supplied by air.
Confectionary shop
It is divided into zones, the air exchange of which depends on the specifics of the product being manufactured. The exhaust ventilation of the workshop is installed from above in the cooking zones, areas with biscuit, caramel, and waffle ovens. Additionally, stoves, boilers, and ovens are equipped with a local exhaust hood to remove the hot air flow.
Departments for processing cocoa beans, areas in which flour and other bulk products are sifted (starch, powdered sugar, etc.) are equipped with local aspiration units that remove fine dust, they clean the air flow and return it back to the room.
In the final design area, the workshop ventilation project provides for the use of an air conditioner for detailed regulation of the temperature of the working environment.
The supply ventilation of the workshop is supplied from above; in winter it can be heated when supplied to the zone of increased steam formation in order to eliminate foggy condensate.

Supply and exhaust mechanical ventilation
A mechanical supply system is designed to supply fresh air into the building. Mechanical exhaust ventilation pulls air out of a building.
The mechanical supply ventilation scheme is a combination of an intake device, filters, air ducts, fans and air blowing mechanisms (air curtains, showers, air-thermal curtains).
The exhaust ventilation circuit consists of an air intake mechanism, a fan, air ducts, filters of varying degrees of purification, and an exhaust mechanism.
Woodworking shop
A special feature is the presence of fine wood dust, shavings, and sawdust. The equipment generates heat during operation; solvents and glue are also used.
The workshop ventilation system is organized using bag filters and cyclones. Exhaust hoods are located in the floor and under it to remove wood dust and small shavings. There should be local suction above the machines to prevent the spread of small particles throughout the workshop.
General ventilation is carried out by dispersed supply of air supply masses to the upper part of the room. As a rule, perforated type air ducts are installed.
The woodworking shop is heated by an air heating system combined with a ventilation system.

Oh! There are no materials yet(((. Browse the site again!
General network calculation
As mentioned above, simply selecting and installing a specific type will not be enough. It is necessary to clearly determine exactly how much air needs to be removed from the room and how much needs to be pumped back in. Experts call this air exchange, which needs to be calculated. Depending on the data obtained when calculating the ventilation system, it is necessary to make a starting point when choosing the type of device.
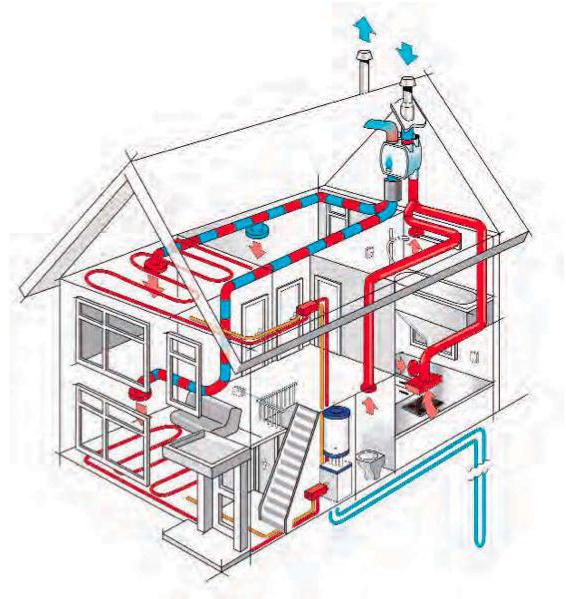
Today, a large number of different calculation methods are known. They are aimed at determining various parameters. For some systems, calculations are carried out to find out how much warm air or evaporation needs to be removed. Some are carried out in order to find out how much air is needed to dilute contaminants, if this is an industrial building. However, the disadvantage of all these methods is the requirement of professional knowledge and skills.
What to do if it is necessary to calculate the ventilation system, but there is no such experience? The very first thing that is recommended to do is to familiarize yourself with the various regulatory documents available in each state or even region (GOST, SNiP, etc.). These papers contain all the indications that any type of system must comply with.