Mayevsky crane
- a device for releasing air from central water heating radiators, opened using a special key or screwdriver.
Another name for the Mayevsky crane is the air release valve STD 7073V (according to TU 36-710-82).
During the process of replenishing coolant, a certain amount of air dissolved in water penetrates into the heating system (sometimes more than 30 /), which can be released in the form of bubbles in places with low water speed and low pressure, which, accumulating, can create air jams, preventing the circulation of coolant [1 ]. The presence of certain metals (for example, aluminum) in the heating system promotes the release of hydrogen from water. As a rule, the system is filled with air during long periods of inactivity, and during the filling process it must be displaced with water. In all cases, air or accumulated gases are removed through air vents installed at the highest points of the system, including in heating devices.
Conventional water taps were often used to remove air from radiators, but consumers (especially those without hot water supply) are very tempted to use them to draw water for domestic needs, which is unacceptable in closed heating systems. The Mayevsky tap is designed in such a way that it is difficult to open it without special tools, and taking water from it is inconvenient.
The name “Mayevsky tap” is commonly used, but is not enshrined in GOST or SNIP (from official documents it is used only in some estimate standards [2]), therefore in textbooks this device is usually called simply a radiator needle air valve [1].
Mode of application
The presence of air in the radiator is indicated by a decrease in its temperature at high temperatures in the network and, accordingly, cooling in the room. Air from the radiator can sometimes be removed without opening the air valve if the water flow rate is sufficient to remove it (for example, you can try to set the maximum temperature on the thermostat, if there is one). If this does not help, turn the valve until the hiss of escaping air becomes clearly audible. When all the air has been removed as much as possible, water will flow from the tap; To collect it, you can use a rag or a special vessel combined with a key. [4] [5]
How is the faucet used?
In order to bring the water circulation into the required working condition, you need to do some actions. Prepare a screwdriver with a basin and remove all valuables away. After this, insert a screwdriver into the thread on the faucet and very slowly begin to rotate it counterclockwise. If after such manipulations you hear the hiss of air coming from the pipe, stop rotating immediately. Perhaps the air will come out with a characteristic loud whistle. Don't be scared or worried, this is how it should be. When water starts flowing from the tap itself (place a basin), you need to immediately turn the tap in the opposite direction (clockwise). It also happens that air will come out along with water. It's okay, just wait until the air stops coming out.
Source
Share the news on social networks
- Related Posts
- Do-it-yourself room renovation or how I spent the summer
- How to avoid mistakes in bathroom design
- Do-it-yourself electrical wiring in a wooden house. Step-by-step methodology for performing work
« Previous entry
Alternative
Water taps
Advantages: easier to find on the farm, including in rural areas. When used in the process of filling a heating system, it makes it easy to localize water leakage into the vessel, which eliminates the need to constantly monitor each tap.
Disadvantage: water is often collected through taps by consumers. Water in closed heating systems is of unacceptably low quality according to sanitary standards (unsuitable for domestic needs), and in the case of increased coolant consumption, its quality can decrease even more significantly, contributing to the rapid overgrowth of pipes with scale and increased corrosion.
Bleeding air through threads
With some skill, you can bleed air from a radiator that is not equipped with an air vent device through the thread of the upper connection. However, the procedure is quite complicated and labor-intensive. [5]
Mayevsky taps and water taps are not automatic devices: a person must activate them and monitor the moment when they need to be closed. When starting up large heating systems or on devices where air constantly accumulates, the operation of such devices is inconvenient. Options without such disadvantages:
The use of heating systems that eliminate air accumulation in the radiator
Heating systems always have devices for removing air from the lines - automatic vents or open expansion tanks. If you supply water to the top radiator plug from above [P 1], air will be able to escape through this angle. However, if the water speed exceeds 0.2-0.25 m/s, bubbles do not float up against the flow even in a vertical pipe (riser) [1], and the presence of a tap on the radiator will be useful. In addition, with bottom wiring (water supply through risers from below), the risers can extend beyond the radiators of the upper floor with special air pipes
, going to centralized air collectors. This design is quite effective, but the cost of pipes increases greatly.
Automatic air vent
It is similar to other automatic vents, but differs from devices usually installed on main pipelines in its angular design (the inlet is horizontal, and the hole must look strictly vertical). [2] [6]
Story
According to research by amateur historians of heating engineering [7], in 1931, Gosplan Resolution No. 13 determined: “For downstream wiring, do not make air pipes, but install air valves at the radiators.” Through these taps, the population of the houses actively dispensed water, which in most cases is unacceptable for sanitary and technical reasons. The Ch. B. Mayevsky tap, which complicates unplanned water withdrawal, was developed and implemented in 1933. By deeper research [ Whose?
] it was established that before this, at the end of 1931, fitter (plumber) S. A. Roev (Minsk) developed and implemented air valves of his own design.
They consisted of two parts with a gasket between them. During the heating season of 1932 they were tested and received recognition. The crane of Ch. B. Mayevsky differed from this device in the way it sealed parts: Mayevsky used a “cone to cone” connection, Mayevsky’s (Roev?) key was cross-shaped, but otherwise it was a similar device. [ source not specified 354 days
]
Mayevsky crane - what is it?
Regardless of what water treatment measures were applied before the coolant was supplied to the network, a certain amount of air dissolved in it enters the system along with the liquid. In areas of low pressure and movement, it forms bubbles, which can accumulate and create blood clots, preventing normal water circulation. The Mayevsky valve is designed to bleed this air, preventing the formation of blood clots in the system.
The Mayevsky crane itself has very compact dimensions and an extremely simple principle of operation. For a better understanding of what it is, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the photo of this device:
Picture 1 -
Various types of Mayevsky cranes:

Figure 2 –
Mayevsky tap installed on the radiator:

Design of various models of Mayevsky crane
Mayevsky's air vent is a device in the center of which there is a needle shut-off valve. The movement of the valve is controlled by a special tetrahedral screw. The outside has a standard thread size: ½, ¾ or 1 inch. The control screw is equipped with a head with a slot for a Phillips screwdriver. In addition, it can be rotated using a special key or regular pliers. There are several models of the Mayevsky air vent. Interesting information about this useful device is contained in the following video:
Manual model
This is the simplest and most reliable device that allows you to control the amount of air in the heating system. The simplest Mayevsky crane consists of:
- durable brass body;
- steel needle valve;
- plastic casing.
The design of the device may vary: in some models the plastic casing moves in a horizontal plane, in others there is a special hole on the edge of the valve nut. In addition to the usual Mayevsky manual tap, two more varieties are produced: an automatic tap and a model with a built-in safety valve.

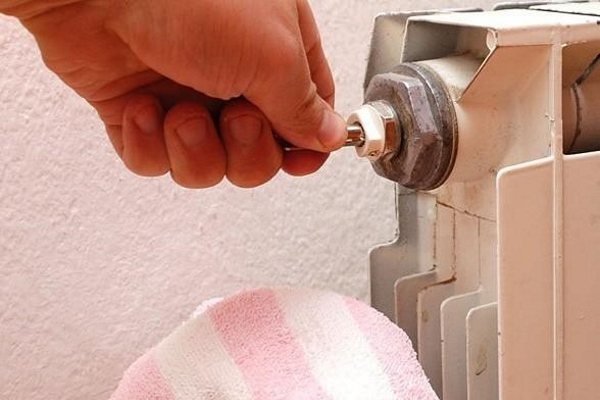
Mayevsky's manual tap can be installed on almost any radiator. To open it, you can use a special key, as well as a screwdriver or pliers
Design of the Mayevsky automatic crane
This device looks like a small metal cylinder with a hole in the top. Inside, in addition to the needle valve, there is also a sensor that operates on the float principle. The sensor responds to changes in the volume of air inside the tap. When a critical value is reached, the valve opens and releases the accumulated air, and then closes. For the operation of such a device, practically no human intervention is required; it is enough to simply install it in a suitable place.
Automated models are sensitive to the condition of the coolant. A narrow opening can easily become clogged, causing the valve to operate unnecessarily. You can remove such a blockage using a regular sewing needle.
What are the benefits of using a safety valve?
Mayevsky's air vent with a safety valve is a somewhat more complicated version of the manually operated model. The safety valve is sensitive to the coolant pressure in the system. If this indicator exceeds 15 atmospheres, the safety valve will open and begin draining the coolant from the heating circuit. This situation may occur due to a sudden water hammer, in which case the valve will prevent damage to system elements.
Whatever option you choose, we recommend that you buy all heating equipment from the Gipostroy online store - this is a time-tested supplier. So, at the link https://www.gipostroy.ru/catalog/category/klimat-i-otoplenie you can get acquainted with the current prices for heating devices and components.
Design and principle of operation
Manufacturers offer many modifications of Mayevsky cranes - they differ in their shape, number of components, etc. However, their operating principle remains unchanged.
Initially, the now classic design of the Mayevsky crane involved two structural elements:
- conical screw;
- metal case.
Both elements fit tightly to each other, which was achieved by high-precision calibration and made it possible to reliably hold the coolant inside. The hole for bleeding air was usually located on the side.
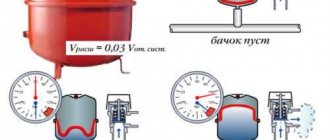
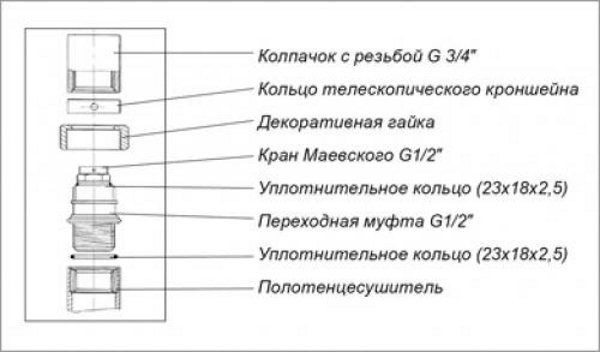
Of course, modern versions of the Mayevsky tap have a more complex design, which is due to the presence of gaskets, decorative trims and plugs. Schematically, the element can be represented in the following form (the figure shows a tap that is used on a heated towel rail):
The operating principle of the Mayevsky crane is quite simple:
- The conical screw is turned, the head of which comes out;
- The bleeder hole opens through which the air is released.
Due to the fact that the Mayevsky valve or radiator needle air valve is a standardized product, there are also certificates that confirm its satisfaction of all established standards. In accordance with technical regulatory documentation, the product must meet the following requirements:
- Working environment
. The Mayevsky crane should be divided into types depending on the system in which it is installed. Accordingly, there are valves designed to work with drinking and technical liquids, as well as valves working with steam and compressed air. - Temperature
. The operating temperature for the Mayevsky tap should be 100-120 degrees, although some modern devices can easily function at 150 degrees. - Pressure
. In accordance with GOSTs, namely GOST 356-80, Mayevsky taps must withstand pressures of 1.0 and 1.6 MPa. This indicator indicates what operating pressure of the environment the element can withstand throughout the entire period of its operation. - Thread type
. This characteristic is very important when installing a faucet, because all pipeline elements must fit together clearly and not leak. This is why thread standards were introduced. Typically, products are found with 1, 1/2 or 3/4 inch external threads. If we talk about metric threads, then they are 10 mm in increments of 1 mm. - Material
. As a rule, brass or steel 20 is used to make a Mayevsky tap, because these materials are sufficiently resistant to corrosion. The tightness class is directly related to this parameter. Typically, manufacturers do not indicate such information on the product, so it is worth remembering that the valve must have an A-class tightness, which is also specified in GOST 9544-93.
When choosing a product, the main thing to remember is that the faucet must meet all the characteristics of the system itself. Otherwise, it may fail or will not perform its intended functions.
How does this device work?
A small cylinder is installed at the top of the radiator or in another suitable location. There is a special valve inside the cylinder, which is controlled by a screw.

The Mayevsky crane is a small device that is easy to install and operate. To service the manual model, you will need some space in the radiator niche.
If you need to bleed air from the system, simply open the valve and then close it. This is the first thing to do if the radiator or some part of the heating system warms up less than the rest. If the heating temperature in the problem area soon increases, the problem can be considered solved. If the radiator does not heat up after bleeding the air, it is most likely clogged. You will have to dismantle the radiator, wash it and install it again.
If the system operates in forced circulation mode, the circulation pump must be turned off before bleeding the air. If this is not done, some of the air will be entrained by the coolant flow and remain in the system. After turning off the pump, you need to wait at least five minutes, and only then open the air vent. During this time, air bubbles will rise up.
After the air leaves the system, water will flow from the tap. This will be a thin stream with a diameter of approximately 1.5 mm. Therefore, even before you start bleeding air, you should remove things from the radiator that can get wet, and also stock up on a suitable container for water. To use the Mayevsky tap, it is not necessary to drain the coolant or dismantle the radiators. Having studied the principle of operation of the Mayevsky crane, you should pay attention to the design of individual models.
Mayevsky tap for cast iron radiators
The question of whether Mayevsky taps can be installed on cast iron batteries is controversial even among experienced plumbers. This is due to the fact that such elements are not suitable for use in radiators of this design. Of course, from the technical side, it is possible to install a crane on a cast iron battery. To do this, you need to cut a hole in the top of the plug, make a thread and insert the air valve itself. But even the most accurate work will not allow the device to work with high efficiency.
How to install a Mayevsky crane
The installation of the tap must be carried out in the upper part of the radiator device on the side opposite to the flow of coolant, since it is in this place that air collects. The specifics of each system should be taken into account. If a vertical heating system is installed in the house, then Mayevsky taps are installed on the radiators of the upper floor. In addition, air vents are installed on all heating devices that are connected to the riser below the upper connection axis.
When using a horizontal system, the taps are mounted on all heating devices without exception that can be connected to them.
If the Mayevsky tap is installed on a floor radiator located horizontally and parallel to the floor surface, then it is placed in the upper part of the highest point of the radiator. The adjusting screw points upward.
Many bathrooms have heated towel rails, which are heated by the coolant circulating inside them. On such devices a Mayevsky tap is installed for a heated towel rail. Installation has some peculiarities. If the heated towel rail has a bottom connection, then there is already a place for screwing in the tap. But for models with a side connection, it is necessary to modify it. A tee is cut into the supply pipe, into which the tap is screwed. The air outlet should be directed away from the wall. It is advisable to equip some models of heated towel rails with even two air vents.
Procedure for installing a tap on a radiator
1. Before installing the faucet, it is necessary to drain the water from the system.
2. Unscrew the plug located in the upper part of the radiator.
3. Screw the tap into place of the plug. The standard equipment of the faucet includes a rubber gasket that ensures the tightness of its installation. For a more reliable seal, it is recommended to screw FUM tape or oiled flax fibers onto the threads of the tap.
Tip: When installing the faucet, it is recommended to direct the air outlet hole slightly downwards. In this position, it will be more convenient to collect the water leaving the system, which will begin to follow the air.
If a tap is installed on an old cast iron battery that does not have a hole, then the following modification is performed. A hole is drilled in the cast iron plug, which has a slightly smaller diameter than the tap thread. The thread is cut inside the cast iron plug. After this, the air vent valve is fitted and screwed in.
In our separate article you will find photos of installing wall-mounted heated towel rails in the bathroom, as well as video instructions for installing it yourself.
You can read about making your own drainage well here.
Mayevsky tap for heated towel rail
Many people have encountered this problem when part of the heated towel rail remains cold. This is possible provided that the coolant cannot penetrate into certain areas of the plumbing fixture due to air “locks”. Their occurrence in “snake” heated towel rails is a fairly common phenomenon, arising due to the rather narrow passage diameter. A similar problem can be solved using a Mayevsky crane.
As a rule, in modern heated towel rails this element is included in the kit, but if it is not available, then it can be purchased separately. The main thing is to consult with a specialist who will tell you which faucet you need to take so that it fits specifically to your device.
Mayevsky automatic crane
Mayevsky's automatic faucet in appearance is practically no different from a standard device with manual adjustment. Its main feature is hidden inside the body itself. In addition to the needle valve, the device contains a float sensor. It moves inside depending on the pressure that is applied to it. When it reaches a certain level, it moves, opening a hole through which air escapes. After this, the sensor returns to its original position.
The key advantage of such devices is that they require virtually no human intervention, but it is worth considering that they are more sensitive to blockages. Therefore, if Mayevsky’s automatic tap does not operate correctly, it should be cleaned. Even a regular sewing needle is suitable for this.
Varieties
There are three types of air vents, differing in operating principle and design:
1. Mayevsky manual tap . This is the simplest device that is controlled manually. If uneven heating of the radiator is detected, the tap can be opened with a key or any screwdriver, and then, as air leaves the radiator, turn the tap in the opposite direction.

The photo shows a Mayevsky manual type crane
2. Automatic tap . The difference between an automatic crane is the absence of manual control of its operation. Its design and operating principle are somewhat different from the functioning of a manual crane. An automatic faucet is made of brass in the form of a cylinder, but there is no needle valve in its design. Instead, a plastic float is used. How does an automatically controlled Mayevsky crane work? A plastic float, depending on the presence of air in the system, moves inside the tap and controls the opening and closing of the valve. Everything happens without human intervention.
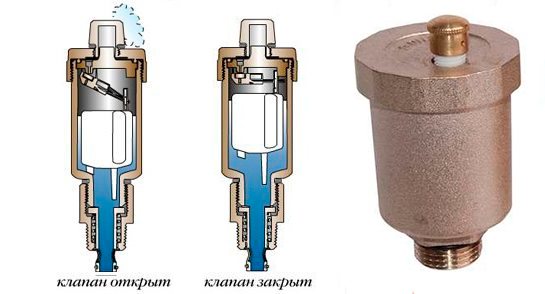
The principle of operation of the Mayevsky automatic crane is visually demonstrated in the photo above.
All automatic taps have the ability to be manually controlled, which can be used when the passage opening becomes clogged.
3. Crane with built-in safety device . For this type of Mayevsky crane, the principle of its operation is somewhat different from the usual bleeding of air. The safety valve is able to control the coolant pressure in the system. If the coolant pressure exceeds the limit value, reaching 15 atmospheres, the valve will operate and begin to forcibly bleed the coolant from the heating system. This prevents damage to individual elements of the system in the event of sudden water hammer.
It is especially important to install air vents with safety valves in heating systems made of polypropylene and metal-plastic pipes, which may not withstand high pressure.
Key for Mayevsky crane
Some models of the Mayevsky crane cannot be activated without using a special key. On the one hand, this is a little inconvenient, because if you lose it, you will have to run to the store to buy a new one. On the other hand, this method of opening the tap has a number of advantages:
- The presence of a four-sided key allows you to restrict access to plumbing fixtures without your knowledge.
- The key has very compact dimensions, which allows you to use the crane even if it is difficult to access.
- The key fits precisely into the seat, allowing you to open the tap without difficulty.
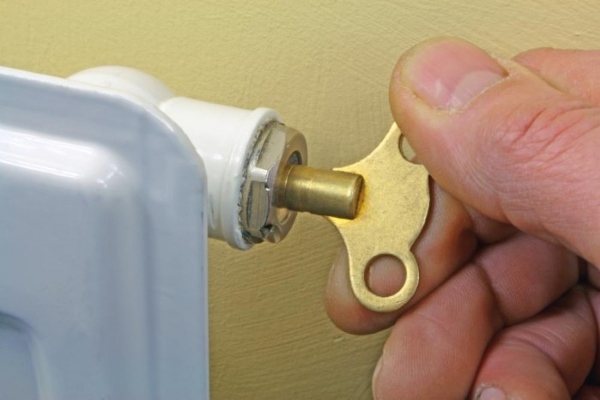

It is worth noting that there are models that can be opened without using a special key. Instead, a regular Phillips screwdriver or hexagon can be used. Mayevsky cranes are also quite widely used, which do not require the use of any extraneous tools at all. In them, a rotary tap is initially provided in the design.
Specifications
Many parameters of the crane can be changed in accordance with the stated requirements and installation location. For example, when used in central heating systems, special Mayevsky taps are used, which can withstand impacts of up to several atmospheres. The domestic market produces taps with a special coating that protects them from strong mechanical stress, water and vapors, and they can also operate at temperatures of +150°C.
Its installation, as described above, is carried out in the hole of the central heating system, which does not always have the required dimensions. In order to install a faucet, you must either replace the plug with the desired size, or use gaskets to create the optimal design.
Its installation does not require much time and is quite simple, which makes it quite popular in this area.
To open and install it, you can use an S-shaped key, which is standard and available from every service department. To facilitate installation, this faucet is designed with a left-hand thread, which allows you to not hold the faucet during installation. In this case, it is very important to determine the angle of inclination of the hole. If you install this hole with a downward view, it will make it easier to collect water from the tap when air is removed.
It should be remembered that draining large amounts of water from the system using a tap is almost impossible and is not recommended. This is due to the fact that its air outlet hole is extremely small. Moreover, it is made of brass or polymer materials, and cleaning of such an outlet is usually carried out using a pin or needle when the tap is open. Today, the Mayevsky tap is the most accessible, cheap and easy-to-use method of removing air from a water heating system.
How to bleed air?
Before bleeding air through the Mayevsky tap, it is necessary to carry out some preparatory manipulations. These include:
- Remove all valuables that could be damaged by contact with water away from the radiator from which air will be released.
- Prepare a container in advance in which you will collect the water coming out of the tap.
- If you are bleeding air from a forced circulation system, you must first turn off the pump. Otherwise, the air will not be able to rise to a level sufficient to exit.
- Carefully and slowly turn the tap counterclockwise.
- When air comes out of the hole and a hiss is heard, you can stop rotating.
- Leave the tap open until water starts coming out of it. If the liquid comes out intermittently and with bubbles, this means that there is still a certain amount of air in the system. Wait until the stream flows continuously.
After completing all the above procedures, you can begin bleeding air from the radiator:
Features of operation
Let's look at how to use the Mayevsky crane. To do this, it is advisable to place some kind of container under the battery and stock up on a dry cloth. Using a wrench or screwdriver, turn the locking screw counterclockwise a quarter or half a turn. Air will begin to hiss out of the system. When it comes out completely, water will flow from the tap. You must wait until the water starts flowing continuously. After this, the locking screw can be tightened.
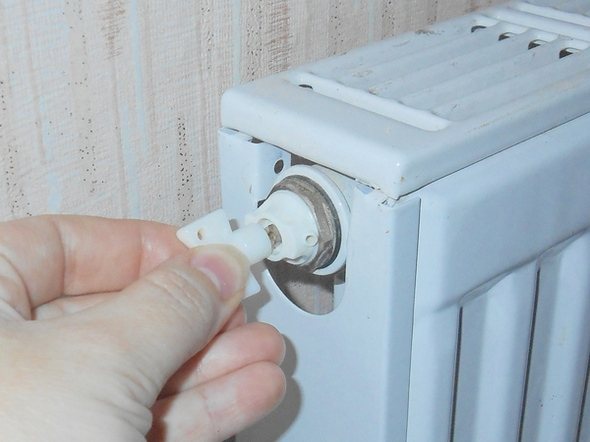

Knowing what to do, bleeding air from the radiator is very simple.
If the air was successfully bled out, but the battery remained cold, then this is a sign of clogging. To clean a clogged battery, you will have to resort to the help of plumbers.
Tip: If the heating system includes pumps that force the coolant to circulate, they must be turned off 10 minutes before bleeding the air. When the pumps are turned on, air will not accumulate at the top point of the radiator, but will be carried throughout the system by the flow of water.
If the tap hole is clogged, it can be cleaned with a needle or other sharp object.
If the faucet has not been used for a long time, the rotation of the adjusting screw may be difficult due to the formation of corrosion on it. If this situation occurs, use WD-40 lubricant spray. Within a few minutes after applying it to the screw thread, it can be easily unscrewed. At the end of the heating season, it is advisable to lubricate the adjusting screw with silicone grease. In this case, the thread will not be destroyed by the influence of the coolant on it.
If you need to replace the Mayevsky tap, use two adjustable wrenches. Use one key to hold the cap on the radiator, and the other to unscrew the tap. If this is not done, then unscrewing the tap can weaken the plug and lead to loss of its tightness.
We looked at how to bleed air from the system using a Mayevsky valve yourself and how to operate an automatically controlled device. If you provide the necessary care to this device, check it and clean it in a timely manner, the device will serve for a long time without causing any problems to its owners.
Video: What is a Mayevsky crane and where is it used?
More details about how it is used and why, on what principle it works, can be seen in the video:

Mayevsky crane
- a device for releasing air from central water heating radiators, opened using a special key or screwdriver.
Another name for the Mayevsky crane is the air release valve STD 7073V (according to TU 36-710-82).
During the process of replenishing coolant, a certain amount of air dissolved in water (sometimes more than 30 g/t) penetrates into the heating system, which can be released in the form of bubbles in places with low water speed and low pressure, which, accumulating, can create air locks, preventing coolant circulation [1] . The presence of certain metals (for example, aluminum) in the heating system promotes the release of hydrogen from water. As a rule, the system is filled with air during long periods of inactivity, and during the filling process it must be displaced with water. In all cases, air or accumulated gases are removed through air vents installed at the highest points of the system, including in heating devices.
Conventional water taps were often used to remove air from radiators, but consumers (especially those without hot water supply) are very tempted to use them to draw water for domestic needs, which is unacceptable in closed heating systems. The Mayevsky tap is designed in such a way that it is difficult to open it without special tools, and taking water from it is inconvenient.
The name “Mayevsky tap” is commonly used, but is not enshrined in GOST or SNIP (from official documents it is used only in some estimate standards [2]), therefore in textbooks this device is usually called a “radiator needle air valve” [1].
Mayevsky crane - principle of operation, types, device
The coolant circulating in the heating radiators provides us with heat during the cold season. However, situations often arise in which the battery does not warm up completely. They arise due to the accumulation of air in the far part of the radiator, which prevents the radiator from filling with hot water. Therefore, it needs to be removed somehow. For this purpose, a Mayevsky valve is used, the operating principle of which is based on bleeding air pockets when the shut-off cone valve is loosened. The Mayevsky tap is installed at the top point of the heating radiator. It can be controlled automatically or manually. When the valve is opened just half a turn, the air in the system comes out of it, freeing up space for the coolant. This device is used on all types of radiators, including old ones.
Construction [edit | edit code]
The basis of the Mayevsky tap is a needle-type shut-off valve. The valve working body is moved by a screw with a square head (for a special key) with a slot for a slotted screwdriver. The plug with the valve, in turn, is screwed into a hole with a diameter of ½" (DN 15) in the upper part of the radiator (opposite the upper water connection and/or thermal head). Between the head of the screw and the area around the valve stem, from where liquid can flow out when the tap is opened, a plastic casing with an outlet hole of ⌀ 2 mm is installed, which can rotate around a horizontal axis (in other designs, the hole is made directly into the face of the brass valve nut) [1].
How to choose the right device?
To choose the appropriate model of the Mayevsky crane, you need to assess the condition and capabilities of your heating system, as well as the features of the placement of radiators. Simple manual models are suitable almost everywhere. It should be remembered that some space will be needed to rotate the control screw: more - for working with a screwdriver or pliers, less - if the valve is opened using a special key. In radiator niches, space can be very limited.
Directions for use [edit | edit code]
The presence of air in the radiator is indicated by a decrease in its temperature at high temperatures in the network and, accordingly, cooling in the room. Air from the radiator can sometimes be removed without opening the air valve if the water flow rate is sufficient to remove it (for example, you can try to set the maximum temperature on the thermostat, if there is one). If this does not help, turn the valve until the hiss of escaping air becomes clearly audible. When all the air has been removed as much as possible, water will flow from the tap; to collect it, you can use a rag or a special vessel combined with a key [3] [4] .
Alternative [edit | edit code]
Water taps [ edit | edit code]
Advantages: water taps are easier to find on the farm [ what?
], including in rural areas. The use of such taps in the process of filling the heating system makes it possible to easily localize water leakage into the vessel, which eliminates the need to constantly monitor each tap.
Disadvantage: consumers often collect water through such taps. Water in closed heating systems is of unacceptably low quality according to sanitary standards (unsuitable for domestic needs), and in the case of increased coolant consumption, its quality can decrease even more significantly, contributing to the rapid overgrowth of pipes with scale and increased corrosion.
Removing air through the thread [edit | edit code]
With some skill, you can bleed air from a radiator that is not equipped with an air vent device through the thread of the upper connection. However, the procedure is quite complex and labor-intensive [4].
Maintenance-free alternatives [ edit | edit code]
Mayevsky taps and water taps are not automatic devices: a person must activate them and monitor the moment when they need to be closed. When starting up large heating systems or on devices where air constantly accumulates, the operation of such devices is inconvenient. In such cases the following applies:
Heating systems that eliminate air accumulation in the radiator [ edit | edit code]
Heating systems always have devices for removing air from the lines - automatic vents or open expansion tanks. If you supply water to the top radiator plug from above [P 1], air will be able to escape through this angle. However, if the water speed exceeds 0.2-0.25 m/s, bubbles do not float up against the flow even in a vertical pipe (riser) [1], and the presence of a tap on the radiator will be useful. In addition, with bottom wiring (water supply through risers from below), the risers can extend beyond the radiators of the upper floor with special air pipes
, going to centralized air collectors. This design is quite effective, but the financial costs of pipes increase greatly.
Automatic air vent [ edit | edit code]
It is similar to other automatic vents, but differs from devices usually installed on main pipelines in its angular design (the inlet is horizontal, and the hole must look strictly vertical).
History [edit | edit code]
According to research by amateur historians of heating engineering [5], in 1931, Gosplan Resolution No. 13 determined: “For downstream wiring, do not make air pipes, but install air valves at the radiators.” Through these taps, the population of the houses actively dispensed water, which in most cases is unacceptable for sanitary and technical reasons. The Ch. B. Mayevsky tap, [P 2] complicating unplanned water withdrawal, was developed and introduced in 1933. More in-depth research [ whose?
] it was established that before this, at the end of 1931, fitter (plumber) S. A. Roev (Minsk) developed and implemented air valves of his own design.
They consisted of two parts with a gasket between them. During the heating season of 1932 they were tested and received recognition. The crane of Ch. B. Mayevsky differed from this device in the way it sealed parts: Mayevsky used a “cone to cone” connection, Mayevsky’s (Roev?) key was cross-shaped, but otherwise it was a similar device [ source not specified 2766 days
].
To come in
MAEVSKY CRANE
Well, it looks like Indian summer in Kyiv is over today. The day was sunny, 22-23 degrees. Then the thunder started to rumble and now it's raining decently. By the way, it is believed that thunder in October foreshadows a short and mild winter. Let's see. But for tomorrow they are broadcasting only +11. This means it’s time to think about the warmth of our slums. They hung this notice on the front door, the meaning of which is this: move. I just wonder why the residents of the 9th floor need such technical details of the planned work. To my shame, I just learned what a Mayevsky crane is from Wikipedia - I live much below the 9th floor. Warmth to your home and a short and mild winter!
Mayevsky crane
– manual air vent for releasing air from central heating radiators. The Mayevsky crane is distinguished by its reliability and ease of use.
In 1931, Gosplan Resolution No. 13 said the following: “When laying downstream, do not make air pipes, but install air taps at the radiators.” The installation of conventional taps led to the withdrawal of water from heating systems by the population. The crane of engineer Ch.B. Mayevsky, developed and implemented by him in 1933 and which later became widely known, was supposed to resist this. However, deeper research revealed the following: at the end of 1931, fitter S.A. Roev developed and implemented air valves of his design consisting of two parts, with a gasket between them. In the 1932 season they were tested and received universal acclaim. The C.B. Mayevsky crane differed from this device in the way it sealed parts. Mayevsky’s device used a “cone to cone” connection; otherwise it was a similar device, with the exception that Mayevsky’s key was cruciform.