Warm floors, which some time ago were an unaffordable luxury for most of the country's population, are becoming more and more accessible to the general population from year to year.
What is a heated floor? In general terms, this is a heating system that heats the floor from below. There are a lot of different coverings for them (carpet, laminate, linoleum), but the best of them is tile - practical, durable and with good thermal conductivity.
Kinds
There are many different types of heated floors, differing both in their operating principle and in their design. Moreover, some of them are better suited to certain types of flooring and have different costs. As a result, it’s worth taking a closer look at the types of floors.
Mermen
As the name implies, the heat source will be water circulating in the system. In turn, it will be heated by a gas boiler or central heating system. Naturally, a system with a gas boiler will be more reliable, not dependent on heating shutdowns, scheduled work or accidents on heating mains.
In addition, in some houses with an old layout, it is impossible to install such a system, because in this case, your neighbors will be able to forget about hot water from the tap. Therefore, water heating systems are often installed in cottages or new buildings.
Advantages:
- Low installation cost.
- Compatible with any floor covering.
- Can act as a substitute for traditional heating.
- Economical (saves 30-50% of thermal energy, depending on the type of room).
- When working with a gas boiler, it is completely autonomous.
Flaws:
- It cannot be installed in any room (for the reasons stated above).
- Extremely limited ability to regulate the heating temperature (with gas boiler heating, adjustment is difficult; with central heating, it is impossible).
- If a system breaks down and is not detected in a timely manner, flooding is possible and, as a result, repairs of not only heating, but also coatings are possible.
- Raising floors. Since the pipes used in the installation cannot be called thin, you should expect a serious rise in the floors.
- More difficult to install than electric flooring.
Electrical
Compared to their water counterparts, electric floors have much greater design variability , namely, they can use single-core, two-core or ultra-thin cable, etc. (we’ll talk about this in the “Classification” section) and can be installed wherever there is electricity.
In addition, they are often produced in the form of special “rolls”, so their installation will be much more convenient and simpler.
Advantages:
- Unlike heaters, it does not dry out the air.
- Prevents the appearance of mold and fungi.
- The thermostat allows you to fine-tune the temperature (water floors are not capable of this).
- Does not depend on a centralized heating system (when installed in apartments).
- Does not require installation of additional equipment.
Flaws:
- Consumes a lot of energy (about 150 watts per square meter).
- Installation can only be carried out in areas free of cabinets and household appliances, so you will have to plan the floors in advance, and purchasing a new cabinet can turn into a serious headache.
Classification
As mentioned above, there are a lot of options for electric floors, but the main ones are:
- Cable.
- Infrared.
- Heating.
Let's take a closer look at them:
Cable
Cable electrical floors can have single-core, double-core or ultra-thin cable. During installation, a single-core cable will require its return to the thermostat, while a two-core cable can be laid regardless of the layout, without returning to the thermostat, but it also costs more.
These cables must be laid in a cement-sand screed, and it, in turn, will raise the floor level by 4-6 cm.
Advantages:
- Does not require maintenance.
- Can be installed over an old screed (using ultra-thin cable).
- Relative cheapness of components.
Flaws:
- If the cable is damaged, the entire system fails.
- Low floor heating efficiency compared to other types of electric heated floors.
Heating
Being one of the varieties of cable underfloor heating, a heating mat made from ultra-thin cable has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Does not require installation in a screed.
- Can be laid directly into a layer of tile adhesive.
- Installation is easier than with a regular cable.
Flaws:
- Higher price.
- Comes with fixed power.
- As in the case of a cable, a break even in one place disables the entire system.
Infrared
One of the “youngest” representatives of the heated floor market , infrared floor embodies the pinnacle of progress achieved in this area. Possessing ease of installation of the film mat, it differs both in the heating principle and in some design features. Infrared floors can be either with a carbon heating element or with a bimetallic one.
Advantages:
- Easy to install.
- Modularity. If one of the heating sections fails, it will not affect the operation of the others.
- The infrared floor roll can be easily cut and laid in any way that is convenient, which simplifies the installation procedure.
- If necessary, it is easy to dismantle and move.
Flaws:
- High price.
- A floor with a bimetallic heating element requires connection to a circuit breaker to turn off the differential current.
- Cannot be used with tiles.
Types of electric heated floors
Laying schemes for heated floors.
Cable underfloor heating is a heating cable with one or more cores. Under the influence of electric current, the cable heats up and transfers heat to the floor laid on top. Please note that the cable in such a system can be different and have different properties. The most technologically advanced and convenient option would be to use heated floors based on a self-regulating cable. A self-regulating cable consists of two cores placed in a polymer that changes its electrical conductivity depending on its own temperature. Overheating of such a cable, if it is in good condition, is impossible. Any cutting of the heating cord is acceptable.
A more budget-friendly option would be to use a resistive cable in a heated floor system. The effect of heat generation in it is achieved due to the high resistance of the conductors inside it, but it cannot be cut, and the power supply of such a floor must be adjusted in terms of power.
- Cable with a reinforcing mesh is the same cable heated floor, but already mounted for ease of installation on a mesh and sold in the form of rolled mats, divided into cutting sections.
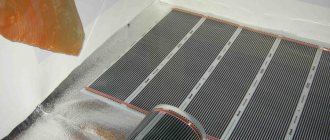
- An infrared (film) floor is a layer of electrically conductive material with high resistance enclosed between two layers of durable heat-resistant film. Heating here occurs in the same way as in previous versions, that is, by the movement of current through a material with high resistance.
The peculiarity of this type of floor lies in its design. These floors are sold in rolls, divided into sections that can be cut. Along the edges of the roll there are conductive wires that supply current to the heating element between them. This type of flooring is intended for laying directly under the decorative floor covering without pouring a concrete screed. Infrared floors can be of 2 subtypes: carbon and bimetallic. The difference in their operation is that a coal floor can be laid under tiles and tiles, but a bimetallic floor cannot. You should check with the seller for more details.
Laying and installation
Laying and installing electric heated floors is quite simple, while installing a water floor, although possible with your own hands, will require serious skills and a separate descriptive article.
Therefore, we will describe the installation of electric floors in general terms:
- Level the surface on which the floor will be laid.
- Install a non-heat-conducting underlay on the ceiling.
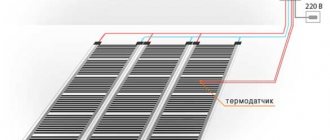
- Lay the cable, mat or infrared heated floor on the substrate, insulating the ends and installing a temperature sensor.
- Secure the heated floor with tape to the substrate so that it does not move during installation.
- (Cable floor) lay cement-sand screed.
- (Heating mat with tiles) lay the mat in a layer of tile adhesive.
- (Infrared floor and heating mat with other coatings) lay the coating on top of the heated floor.
- Mount the thermostat near the wiring.
- Connect the wires of the thermostat, floor and electrical network according to the connection diagram.

Warm floor GREEN BOX is ideal for rooms with a complex configuration of the area, where it is necessary to “bypass” furniture and plumbing fixtures. That is, it is used in cases where the heating area has a complex geometric shape.
Warm floor GREEN BOX is a universal solution: it is easily installed from a convenient plastic reel, does not require a screed (the heating cable is laid directly under the tiles in tile adhesive), and can also be laid under a screed if a heat-storage system is needed.
GREEN BOX is an environmentally friendly heated floor, it is made of high-quality, environmentally friendly materials and fully complies with international sanitary standards.
Features of Green Box heating sections:
- A continuous foil shielding shell provides a 100% guarantee of electrical safety and absence of electromagnetic radiation;
- Miniature cable diameter (only 3 mm) - allows you to install the heating section in a layer of tile adhesive without a screed device;
- Reliable protection of the heating core is ensured by several layers of insulation;
- Additional protection against overheating is provided by heat-resistant, ultra-reliable fluoroplastic insulation, which can withstand temperatures up to +180°C;
- The two-core design of the section is convenient for connecting to the network.
Economical
- From an economic point of view, it is especially profitable to purchase a heated floor on a coil for those rooms that have small heating areas
- Green Box heated floors are not an energy-intensive system. To create a comfortable heated floor using Green Box, a power density of 120 W per sq.m is sufficient.
- Modern thermostats significantly reduce energy consumption of the Green Box underfloor heating system. Thanks to the electronic thermostat TP 715, the Green Box heated floor consumes up to 50% of the installed power. And the use of a programmable thermostat TP 725 allows you to save up to 70% of electricity.
Environmental friendliness
- In the production of Green Box heating cables, high-quality materials from the world's leading plastic manufacturers are used, which do not contain components harmful to human health (for example, lead).
- The modern design of the Green Box heating cable makes it completely safe. The two-core design and the presence of a continuous screen provide reliable protection against electromagnetic radiation.
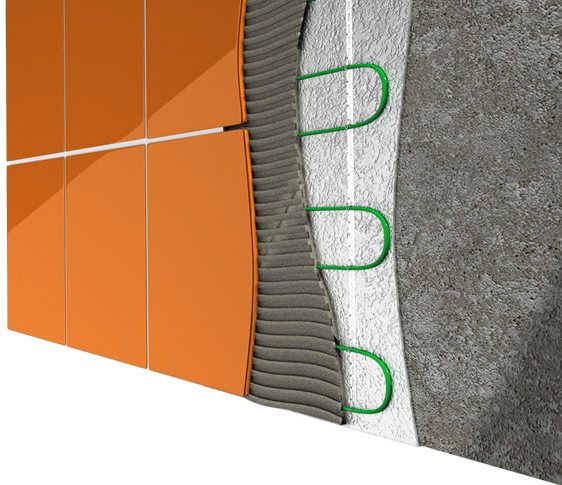
Set contents:
- Heating section
Heating section GB is a piece of heating cable of a fixed length, equipped with an installation wire 3 m long for connection to the electrical network. The connection of the heating cable with the installation wire and the end seal are made in sealed connection and end couplings. The cable insulation is made of durable, temperature-resistant, non-flammable fluoropolymer. The cable shield is made of aluminum foil reinforced with copper conductor and provides mechanical and electrical protection. The cable sheath is made of heat-resistant, rigid PVC. In the production of heating cables, high-quality materials from the world's leading polymer manufacturers are used. The two-core design of the heating cable allows power to be supplied from one end of the section. - Mounting tape for attaching the cable to the floor surface.
It is necessary to fix the heating section on the surface with a certain layout step, which is determined according to the calculation formula. - Installation and operating instructions
Contains comprehensive information on preparation for installation, installation and operation of a heated floor system based on two-wire heating sections. - Passport
It indicates the technical characteristics of the sections and a mark on passing technical control at the exit from production (QC).
Parameters of GREEN BOX sections
Set
| Heating section | Mounting tape length, m2 | Type of packaging | |
| Green Box GB150 | GB150 | 3 | small |
| Green Box GB200 | GB200 | 5 | small |
| Green Box GB500 | GB500 | 10 | small |
| Green Box GB1000 | GB1000 | 18 | big |
Table of areas and Green Box kits
| Heated area*, m2 | Connection diagram | Total power, W | Maximum current, A | Layout pitch, cm |
| 0,9–1,3 | GB150 | 140 | 0,6 | 9,3–12,7 |
| 1,4–1,9 | GB200 | 210 | 1,0 | 8,0–10,9 |
| 1,9–2,5 | GB150+GB150 | 280 | 1,3 | 9,3–12,7 |
| 2,3–3,2 | GB150+GB200 | 350 | 1,6 | 8,5–11,6 |
| 2,8–3,8 | GB200+GB200 | 420 | 1,9 | 8,0–10,9 |
| 3,3–4,5 | GB500 | 490 | 2,2 | 9,3–12,7 |
| 3,7–5,1 | GB150+GB200+GB200 | 560 | 2,5 | 8,3–11,3 |
| 4,7–6,4 | GB200+GB500 | 700 | 3,2 | 8,9–12,1 |
| 5,6–7,6 | GB150+GB200+GB500 | 840 | 3,8 | 9,0–12,2 |
| 6,5–8,9 | GB1000 | 980 | 4,45 | 8,0–10,9 |
| 7,5–10,2 | GB150+GB1000 | 1120 | 5,1 | 8,1–11,1 |
| 8,9–12,1 | GB150+GB200+GB1000 | 1330 | 6,0 | 8,1–11,0 |
| 9,8–13,4 | GB500+GB1000 | 1470 | 6,7 | 8,4–11,4 |
| 10,7–14,6 | GB150+GB500+GB1000 | 1610 | 7,3 | 8,5-11,5 |
| 11,2–15,3 | GB200+GB500+GB1000 | 1680 | 7,6 | 8,3–11,4 |
| 13,1–17,8 | GB1000+GB1000 | 1960 | 8,9 | 8,0-10,9 |
| 14,0–19,1 | GB150+GB1000+GB1000 | 2100 | 9,5 | 8,0–11,0 |
| 14,5–19,7 | GB200+GB1000+GB1000 | 2170 | 9,9 | 8,0-10,9 |
| 16,3–22,3 | GB500+GB1000+GB1000 | 2450 | 11,1 | 8,2–11,2 |
| 19,6–26,7 | GB1000+GB1000+GB1000 | 2940 | 13,4 | 8,0-10,9 |
Technical characteristics of Green Box sections
| Section brand | Shell color | Rated power, W | Cable length, m | Operating current, A | Recommended heating area, m2 | Resistance, Ohm |
| GB150 | Red | 140 | 10 | 0,6 | 0,9 – 1,3 | 333,01 – 385,76 |
| GB200 | Green | 210 | 17,5 | 1 | 1,4 – 1,9 | 218,26 – 253,03 |
| GB500 | Grey | 490 | 35 | 2,2 | 3,3 – 4,5 | 88,41 – 102,62 |
| GB1000 | Green | 980 | 82 | 4,5 | 6,5 – 8,9 | 42,78 – 51,37 |
What coatings are suitable?
At the moment, the following types of coatings for heated floors are the most popular:
- Carpet. Very soft and pleasant to the touch material that gives an incredible feeling of comfort. However, it is not a good conductor of heat, so the temperature will have to be higher than on other coatings. Ideal for bedrooms and rooms that require comfort and coziness. Can be installed on any type of floor.
- Parquet. Warm floors require special types of parquet boards that will not emit acetone vapor when heated and will not require constant moistening.
- Ceramic tile. It has the highest thermal conductivity and is ideal for a bathroom or any other wet room. But it is worth remembering that infrared heated floors are not suitable for tiles.
- Linoleum. The most popular flooring material since the times of the USSR. It is very economical and practical, but it can conduct heat worse than laminate; many models are not suitable for heated floors, and linoleum itself must be without a backing, which will lead to its excessive fragility.
- Laminate. A very comfortable cover that is easy to put on and take off. It is easy to saw, so getting around difficult places in the apartment (protrusions, corners, etc.) will not pose any special problems. Before purchasing a laminate flooring for underfloor heating, you need to clarify whether it can be used for these purposes. Typically, laminate manufacturers provide similar information. The disadvantage may be the fact that the laminate is often laid on a heat-insulating substrate, and the thermal conductivity of the laminate is also not high. Therefore, rooms with such a coating will have to be heated properly. Can be installed on any type of floor.
Which heated floor is better?

If you need to heat a small room or you plan to install floors in an apartment, then it is better to use electric heated floors.
It all depends on the rooms you are going to heat. If a large, multi-storey private house needs heat, then it is better to use water heated floors, since they can replace the heating system, and in the basement (or on the lower floor) there is room for a boiler and collector. In addition, the rooms in cottages are often quite high and an increase in floor height will not be noticeable.
Adviсe:
- To use a heated floor as the main source of heating, it must occupy at least 70% of the room area.
- For the middle zone in Russia, floors with a power of 110-120 W should be installed if the floor is used as an auxiliary heat source and 150 W if used as the main one.
What power and for what area should I choose?
If you plan to use a heated floor as an additional source of heating, then you are not limited in your choice. You can lay one square meter of floor of any thickness near the door to the kitchen, or cover the entire house with a network of heated floors. If you need a warm floor as the main source of heat, then you will need to place the heating elements closer to each other and not use thin heating mats.
The power varies depending on how cold the room is, whether it is glazed or not. Also, keep in mind that your wiring may not be able to handle the excess power of your floors, so pay extra attention to it. If its power is not enough, then it is better to power the floors from a separate line with its own machine
.
Installation procedure for water heated floors
Installation of a hydraulic (water) floor is carried out in the following sequence:
- First of all, the collector block and mixing unit are installed. Installation is carried out at an equidistant distance from all circuits.
- The collector itself is installed directly into the housing. Case dimensions may vary. They depend on how complex and extensive the heating system is (number of sensors, drain holes). The housing and the collector itself are mounted strictly above the level of the heated floor. Otherwise, the system will constantly be filled with air, and the air exhaust mechanism will not function properly.
- The old screed, if any, must be dismantled. If there are differences of more than 10 millimeters, the floor surface is leveled.
- The leveled surface is covered with a waterproofing layer. A tape is glued to the walls along the entire perimeter, the purpose of which is to compensate for the thermal expansion of the screed (concrete layer).
- The floor is insulated. Depending on whether it is a private house or an apartment in a high-rise building, various types of insulation are used: polystyrene foam of different thicknesses, expanded clay layer, etc. Moreover, many slabs of insulating material have grooves on the outside for laying pipes in them.
- A reinforcing mesh is placed on top of the insulation.
- The tightness of the entire system is checked, after which the concrete screed is poured. You must wait a month after installing the heated floor before starting to operate the heating system.
Reviews
- Nikolay, Ufa : We installed heated floors in every room and abandoned carpets. Now the hallway and bathroom are always dry, there is no dampness, and after a shower you can safely stand with your bare feet on the warm tiles.
- Elena, Nizhny Novgorod: My child had health problems, he often caught colds and therefore appeared at school much less often than others. Hence the failure, grades... I decided to insulate the house and ordered heated floors. They installed it quickly and now the house is always warm (as soon as the temperature drops, the floors turn on automatically). Now the child is healthy, and the house has become truly comfortable. I recommend!
- Angelina, Moscow: We have long wanted to insulate our Stalin building, but something always got in the way: the water in the radiators is lukewarm, the ceiling is low, etc. We decided to install a thin heating mat and now in winter we no longer freeze! Tweak the regulator a little – and it’s already summer at home! I recommend to all!