Coolant parameters for heating systems
To date, an ideal liquid for heating systems has not been invented, which means that each type of coolant should be used only under certain conditions (read: “Choosing a liquid for heating systems at home”).
One of the most important indicators is the temperature of the coolant in the heating system, since when it changes, the substance can change its inherent properties, as a result of which the house may be left without heating. The parameters of the heating system coolant must meet a number of requirements:
- promote the transfer of maximum heat in a short period of time around the perimeter of the heating object with minimal losses;
- have a low degree of viscosity, since the speed of the coolant in the heating system and, accordingly, the efficiency value depend on this;
- the liquid should not cause corrosion processes in the components of the equipment;
- ensure safety for the residents of the house - in terms of toxicity and ignition temperature;
- its cost should be affordable for many consumers. If the liquid is expensive, it is necessary that its properties allow the coolant to be used for a long time without replacement.
Types of coolants and their comparative characteristics
Before you buy a coolant for a heating system, you need to decide on the type. As a rule, water or antifreeze liquid is used. Only fully purified water – distillate – is suitable for heating systems. Running water contains many third-party components that have a negative impact on the functioning of the heating system, reducing its service life. Therefore, preparing water for the heating system is a very important process.
To determine the maximum temperature of the circulating fluid in the heating system, you need to know the properties of the coolant and what restrictions exist in the use of pipes and batteries. The elements of the heating system should not be damaged by high thermal effects.
Distilled water has the following characteristics:
- mass density: 1000 kg/cub.m at a temperature of +4 degrees. When heated, the specific gravity decreases;
- heat capacity is 4.2 kJ/kg*C;
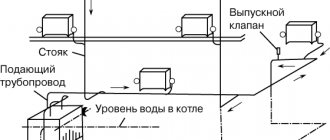
- boiling point - +100 degrees. But as the pressure increases, it increases. For example, at a pressure of 2.75 atmospheres, the boiling point will be +130 degrees. It should be noted that the optimal coolant temperature in the heating system is +75 degrees. But when weather conditions change, this indicator can be adjusted. For example, in steam systems the normal temperature is + 120 degrees.
Antifreeze is often used as a coolant.
This liquid has a low freezing point - about -30-65 degrees. Contains ethylene glycol, which is hazardous to health. But many modern brands of antifreeze are produced using harmless propylene glycol. The main advantage of antifreeze liquid over water is its high resistance to frost. You can read about the choice between water and antifreeze for coolant here.
To determine which coolant is better for the heating system, you need to compare the characteristics of the two liquids:
- Water is not harmful to human health. But antifreeze is toxic.
- When overheated, water does not change its properties. Antifreeze foams and releases a sediment that remains on the walls of the heating structure in the form of soot. Which has a bad effect on the operation of the heating system.
- Price difference: an antifreeze system will cost 10-40% more than a water one.
- Water can be combined with pipes made of any material. Antifreeze - no.
- Water is always suitable, and the service life of antifreeze is no more than 5 years.
For electrode heating boilers, a special antifreeze is used, which has a special composition and provides the necessary ionization, electrical conductivity and electrical resistance. You need to choose a coolant for electrode heating boilers by monitoring the market and reading user reviews. After all, you can buy antifreeze that is optimally combined with boiler equipment, or you can buy an unsuitable option or a fake.
Water as a coolant
Heating systems mainly use water, which is the safest, most inexpensive and environmentally friendly coolant. The reason for this is the highest heat capacity among liquids and no less high density. Thus, one kilogram of water heated to 90ºС, cooling to a temperature of 70ºС, is capable of releasing 20 kcal of heat.
If a leak occurs, the volume of coolant in the heating system can be easily replenished by pouring the missing amount into it. Water has no competitors in terms of price - consumers cannot find a cheaper liquid. At the same time, you should know that experts do not recommend using ordinary tap water in heating systems, since it contains a lot of salts and oxygen, which will certainly lead to the appearance of scale and corrosion processes.
The process of water softening helps to eliminate the problem with the functioning of the equipment.
You can use one of two methods:
- The first option is thermal, which is based on conventional boiling
. Water is placed in a metal container and heated. When boiling, salts are deposited at the bottom of the tank. Carbon dioxide is also removed, but persistent calcium and magnesium compounds are still present in the water. - The second option is chemical and involves the use of reagents
. The use of soda ash, sodium orthophosphate and slaked lime makes the salts present in the water insoluble, after which they precipitate. Residues of these substances are removed by filtration.
It is considered ideal to fill the heating system with a coolant, which is distilled water. The only disadvantage of filling the heating system with water is the need to purchase it, while ordinary water is taken from the tap, however, you also have to pay for it, but much less than for distilled water. You can use rainfall, which compares favorably with well, artesian or tap water.
For such a coolant, its temperature regime is of great importance. If the temperature in the house drops below 0 degrees, frozen liquid will pose a serious threat to the integrity of the heating structure.
More about closed systems
What does a closed hot water supply system mean? What is this solution and where is it used? Let's figure it out.
In a closed system, water is in continuous circulation and is heated from the heating network. This keeps her temperature at 70 degrees. The liquid is suitable for direct tapping and filling the heating circuit.
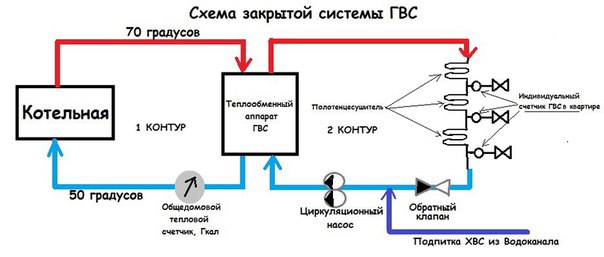
Unlike open solutions, closed ones are more difficult to implement. At the same time, they ensure high quality of the final product and minimal heat losses.
Closed systems are used in most new buildings and are installed in houses after major renovations.
Heating system operating on antifreeze
With the arrival of winter cold, non-freezing coolant for heating systems becomes relevant (read: “Non-freezing liquid for heating systems - making the right choice”). Pipelines filled with such coolant will not be damaged at low temperatures. This is relevant for owners of buildings in which they do not live all the time and use heating systems periodically. This coolant includes antifreeze for the heating system, the properties of which allow it to be used at temperatures of minus 30°C and even at extremely low temperatures.

When this type of liquid returns to its original state, its parameters are maintained and there is no threat to the integrity of the heating circuit. To remove scale or possible pockets of corrosion, special inhibitors (additives) are added to the liquid at the production stage. As a result of their use, the service life of the heating structure increases, and significantly. But we should not forget that antifreeze for heating is not a universal coolant, so additives can be used provided that the structural elements are made of certain materials. The fact is that some inhibitors destroy polymer pipes, while others promote electrochemical type corrosion.
On average, antifreeze can last for 5 years. After this, the coolant in the heating system is replaced (for more details: “How to replace the coolant in the heating system of different heating systems”). Antifreeze manufacturers themselves recommend doing this every three years.
Antifreeze has a number of disadvantages compared to water:
- quality such as increased viscosity requires the installation of a powerful circulation pump;
- the heat capacity of this liquid is 15% lower, which means less heat supplied to the room;
- detachable connections require better sealing;
- it is necessary to use radiators with a volume 50% larger than when using water;
- it is necessary to install a closed expansion tank, since increased expansion of the liquid is observed when heated;
- toxicity of the composition, for example, ethylene glycol.
Thus, when using antifreeze, the pipes must be large in diameter and the radiators more voluminous. When sealing detachable connections, it is advisable to use Teflon or paronite gaskets. To dilute antifreeze, you can only use distilled water. Before changing it, drain the coolant from the heating system and thoroughly flush it, including the boiler.
Selection of coolant
When choosing, take into account the technical requirements that must be met by the temperature of the liquid and the pressure of the coolant in the heating system.
If the area experiences relatively warm weather all year round (at least +5°C), it is preferable to use purified water. Low winter temperatures require the use of antifreeze. The type of heating system should be selected when designing it. If antifreeze is preferred as a coolant, you should first study:
- its characteristics;
- composition of additives and their purpose;
- the ability to interact with system elements made of plastic, rubber, various metals and alloys;
- period of application;
- permissible temperature;
- safety for humans and the natural environment.
Characteristics of water as a heat conductor
Many heating systems are filled with water as a working medium - the most accessible and versatile coolant. It is freely available, and its reserves in nature are regularly renewed. Up to 70% of heating systems are filled with natural liquid.
The popularity of water is due not only to its availability, but also to environmental safety. Also among its positive features are high density and specific heat capacity. An important performance characteristic is low chemical activity, good heat transfer coefficient, minimal viscosity. Water meets all these requirements. If necessary, its heating temperature can be adjusted.
Among the characteristics of natural liquid, there are also disadvantages. These include:
- low upper heating limit (temperature maximum in the heating system up to 150 °C);
- freezes at 0 °C, turning into a crystalline form with a significant increase in volume, which leads to the destruction of equipment and pipelines of heating systems;
- the possibility of corrosion processes with the formation of metal oxides (rust) and destruction of equipment surfaces;
- scale formation on pipeline surfaces when heated to 80 °C.
If water freezes in the pipes in winter, the entire heating system may become unusable. Often rust and deposits appear on metal pipes and fittings. To minimize the risk of their occurrence, distilled water is used or special additives and alkalis are added to process water.
Heating devices where water serves as a coolant require regular maintenance - flushing heat exchangers and pipelines, periodic boiler repairs, and adjustment of resistivity during the heating season.