Versatility is the main trend in the development of modern household appliances. Initially, food processors began to have versatility. Afterwards, the mobile phone turned from a means of communication into a full-fledged media center, and after a while into a portable PC. This trend has appealed to the modern consumer, since by purchasing one device, you become the owner of a whole set of equipment. [contents] The trend of versatility has also affected climate control technology, namely the modern air conditioner, which began to perform the exact opposite task of cooling, heating the home. Heating a house with air conditioning will be discussed in this publication.
Why some air conditioners can heat the air
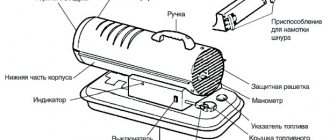
To understand how you can heat your home with a household split system, you first need to understand the principle of its cooling operation. The operating principle of the air conditioner is clearly shown in the figure.
- The refrigerant moves through the refrigeration circuit.
- In heat exchangers, its transition from one state of aggregation to another occurs.
- When condensing, the refrigerant gives off room heat to the heat exchanger, and when boiling, it gives off cold to the evaporator, and accordingly to the room air.
When the air conditioner operates for heating, it becomes a regular heat pump, although nothing in its operating principle changes. The “transformation” into a heat pump from an air conditioner occurs thanks to a four-way valve that serves to redirect the refrigerant. As a result, the heat exchangers seem to change places: freon evaporates in the condenser, and the refrigerant transforms into liquid form in the evaporator. Gaseous freon transfers the cold received from the room air to the atmospheric air, and in return transfers its heat into the room, turning from gas into liquid.
Additional functions of heat pump air conditioners
GREE U-CrownElectrolux VikingMitsubishi ZUBADANDaikin FTXM Air purification✔✔✔✔Self-cleaning✔✔✔✘Timer✔✔✔✔Turbo mode✔✔✔✔Self-diagnosis✔✔✔✔Auto restart✔✔✔ ✔High energy efficiency✔✔✔✔Night mode✔✔✔ ✔Centralized control✔✘✔✔Anti-corrosion protection✘✔✔✔Air ionization✘✔✔*✘*Depending on the indoor unit model.
So, we looked at the 4 most popular lines of heat pump air conditioners. You can purchase all of them in Elwes stores! Our specialists will help you decide on the optimal split system for you. In addition, you can take advantage of installation, delivery services and the current promotion - free installation on air conditioners with a heat pump!
We are waiting for you at Elwes!
Is it possible to heat your home with air conditioning?
From the above, it becomes clear that in order to heat the air in a room, it is necessary that outside the window there be a temperature sufficient for the refrigerant to boil in the heat exchanger. The lower the temperature, the more difficult it is to extract heat from it and the lower the performance of climate control equipment. As a rule, manufacturers of split systems capable of operating in heat pump mode limit the temperature of use of their products at 0°C and here’s why:
- Condensation will form on the cold heat exchanger of the outdoor unit, which will freeze in sub-zero temperatures. Icing of the external unit of the split system can lead to fan failure and depressurization of the freon circuit.
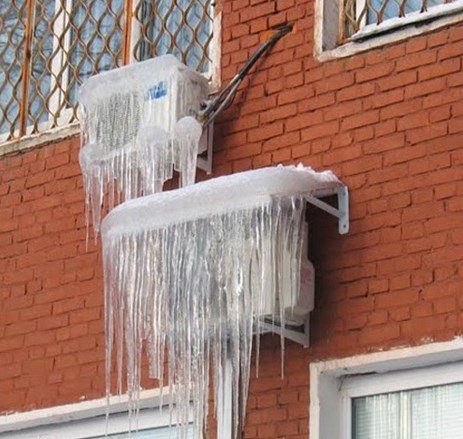

- Solidification of oil in the compressor crankcase. Viscous oil causes an increased load when starting the compressor, and an increase in the starting current, which entails overheating and subsequent burnout of the compressor starting winding.
- Decrease in productivity. As the amount of thermal energy in the air decreases, it becomes more and more difficult for the air conditioner to extract it from the air, the performance of the device decreases, and energy consumption increases.
The conclusion from this is simple: heating a home with air conditioning is possible, but only in the off-season and provided the air temperature is not lower than 0°C, and only in one room where the split system is located. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vv8Fl50M-zk Another thing is the inverter split system, which can independently control the fan speed of the external unit. As the speed decreases, the efficiency of the device that operates for heating increases. In addition, most inverter air conditioners are equipped with a low-temperature start system, in which the oil in the crankcase is heated by the compressor itself, only after which it starts. The presence of a low-temperature start-up system pushed back the lower temperature limit for the operation of climate control equipment to -10 °C.
Operation of the device at sub-zero temperatures is possible, but the thermal energy in the air is so small that heating with an inverter air conditioner even at an air temperature of -5°C becomes extremely difficult.
Choosing a data center cooling system: freon or water?
Integration Infrastructure
08/24/2016, Wed, 14:42, Moscow time, Text: Pavel Pritula
Its key characteristic – reliability – directly depends on the correct choice of the data center cooling system.
There are several ways to remove heat from a data center, but we will consider only the two most common of them - “freon air conditioners” (air-cooled) and “water air conditioners” (receiving cold from chillers). So, “freon” or “water”? Like any complex technical area, the topic of heat dissipation in data centers is surrounded by a large number of myths and prejudices.
The first group of myths says that “water is a danger to IT equipment.”
Myth 1: Water cooling is when there is water inside the server
This is not entirely true: there are server platforms with direct cooling using water, but this is still exotic. The most common way to remove heat from IT equipment is by forcing air through its radiators. The heat removal methods described above describe the process at the level of the data center as a whole, and not at the level of units of IT equipment.
Myth 2: Water in a server room is an unacceptable risk
There are many technical solutions to prevent water from leaking into IT equipment. To do this, it is necessary to work out possible accident scenarios and make appropriate design decisions.
The second group of myths: the water system is very expensive and difficult to operate, while the freon system is more common and more efficient.
Myth 3: a water system is too complicated and expensive
Specific cases need to be considered. A situation is possible when, on the contrary, the freon system will be too complex and expensive, especially if we consider not only the construction of a data center, but also its maintenance.
Myth 4: Water cooling is for large data centers
Yes, you can have a regular server room with 20 racks. But it is necessary to make an assessment, because it may turn out that this server room will require 20 separate freon air conditioners, so a water system will be more profitable in operation.
The third group of myths is generated by ignorance of the design of cooling systems.
Myth 5: The water system is powered by the water supply mains
No, water systems are fed from the chiller with specially prepared purified chilled water or a water-glycol mixture with the addition of corrosion inhibitors.
Myth 6: You can use a household freon air conditioner
The idea of “blowing cold on the equipment” from a household air conditioner is a consequence of an incorrect understanding of the task. It is necessary not only to supply cooled air to the equipment, but also to remove excess heat to ensure appropriate operating temperature conditions. In this case, the cooled air only acts as a coolant to move a certain amount of heat from the data center premises to the street. As you know from a school physics course, the amount of heat is equal to the specific heat capacity multiplied by the mass of the substance and the temperature difference before and after heating. If the mass of the substance (the volume of air supplied from the air conditioner) is significantly less than necessary, then even lowering the air temperature will not help. Household air conditioners have several times lower air supply capacity than precision air conditioners. To this we can add that part of their power is spent on dehumidifying the air (to create comfortable conditions for humans) and that they have a short resource (they are not intended for constant operation around the clock in all seasons).
We, the people of the third millennium, have no need to vegetate among myths and misconceptions. We can evaluate the situation in the light of knowledge. Let's limit ourselves to the basic properties of both options and consider them more carefully.
Advantages of freon systems
Relative simplicity of the system
In fact, a freon air conditioner, like a home split system, consists of two halves: the air conditioner itself, installed in a refrigerated room, and an external unit, which is located outside. Typically, the air conditioner itself contains fans, an air-cooling heat exchanger (evaporator), a compressor and control electronics. Additionally, the air conditioner may have a steam humidifier that raises the air humidity to the required level, air filters, etc. The external unit of a precision air conditioner is designed quite simply: only a heat exchanger that releases heat into the air around it, a fan, and an automatic system that controls this fan.
The air conditioner and its external unit are connected by a pair of copper pipes of small diameter (usually 15-20 millimeters, rarely more), which can be laid even in cramped conditions.
The duration of installation of one air conditioner usually does not exceed two to three days. Regardless of the power of the air conditioner, the principle of its operation does not change: both a small 7 kW ceiling unit and a huge 200 kW machine are designed, in principle, the same way.
Complete independence of air conditioners from each other
If several air conditioners are needed, they are installed as units independent of each other. Each air conditioner has its own external unit with separate pipelines. The following additional advantages arise from this property. The first is the high reliability of the redundant system: several air conditioners operating in the same room do not have common units or units, they are completely independent, and, therefore, there is no single point of failure. The failure of one air conditioner does not affect the operation of the others. The second advantage is the ease of expanding the system: in many cases, to increase the performance of the system as a whole, you can simply install another air conditioner in the same room.
Less initial capital investment
As a fair result of the above (and many other) objective properties, the freon system turns out to be significantly (sometimes two to three times) cheaper in purchase, installation, and commissioning than a water system with similar performance. The simplicity of laying copper pipes and installing an external unit, the complete independence of air conditioners from each other and a simple commissioning procedure allow you to deploy cooling systems quite quickly and relatively inexpensively.
Disadvantages of freon systems
Relatively low permissible energy density of the data center
Unfortunately, the “power density of one air conditioner” is not very large. Especially if we consider the most efficient and currently popular design: compact in-row air conditioners installed in rows with server cabinets. A power of 15-20 kW for a 600 mm wide case (the size of a regular server cabinet) and no more than 10-12 kW for a compact 300 mm case is practically the limit for freon machines. There are some examples whose power is slightly higher than the “market average”, but this is achieved by compacting the internal layout, and as a result, reducing the maintainability of the device.
As a result, high system power can only be achieved by installing a large number of air conditioners: each with its own external unit, with its own pipelines... As a result, the use of freon air conditioners in a medium-density data center, with a specific load per rack from 7 to 10 kW, seems difficult, and with a specific load of 15 kW or more - almost impossible.
Each indoor unit must have a separate outdoor unit
A classic case when dignity turns into a disadvantage, moving from quantity to a new, but already negative, quality. Try to imagine what the facade of your building will look like if you hang ten to fifteen external blocks on it (each size, for example, one and a half by two meters). What about a mine with three dozen pipes? Comments on this picture are perhaps unnecessary. Attempts at “optimization” can only aggravate the problem: there are quite strict restrictions on the distance from the air conditioner to its external unit. The typical length limit for tubes is 30-40 meters, rarely more, and it is not the actual length that is considered, but the “equivalent” one: taking into account all the bends and turns. Therefore, it will not be possible to evenly distribute external units over a large area: they will still create a “crowd” near the computer room of the data center.
Low system flexibility
In the cooling option with air supply through a raised floor, the power of one air conditioner can reach 200 kW or more; this is already a fairly large unit, several meters in size and weighing a couple of tons. The power is fine, but how to regulate it? A freon refrigeration machine has such a parameter as a minimum load: if a 100-kilowatt air conditioner is forced to remove only 5 kW of heat from the data center, then it simply will not cope with this task. Too small a heat load will not be able to evaporate the amount of freon that is sufficient for the normal operation of the refrigeration machine cycle. Manufacturers go to various lengths to overcome this problem, for example, they equip air conditioners with built-in heaters, which “load” the air conditioner with additional heat. This creates an absurd situation: in order to cool the air, you must first heat the air, spending electricity not only on cooling, but also on heating. Which brings us to the next disadvantage of freon systems.
Low energy efficiency
Roughly speaking, the efficiency of any air conditioner is 200 percent or more: in order to “blow away”, for example, 100 kW of heat from the equipment, the air conditioner consumes no more than 50 kW of electricity from the network, and often even less. However, in practice, everything is not so good: taking into account the problems of power regulation and some “overhead costs” for cooling equipment with freon air conditioners, you will spend almost as much electricity as the cooled equipment itself consumes. But, as they say in “shop on the couch,” that’s not all. If we try to plot a graph of current consumption over time, we will see that electricity is consumed inconsistently and unevenly. There will be periods of time on the graph when consumption is low (at these times only the fans are running and the freon compressor is idle). Also on the graph we will see periods with “normal” energy consumption (both fans and compressor are running).
In addition, the graph will show short-term, but very unpleasant moments with sharp and significant surges in current consumption. These are the moments when the compressor turns on after being idle, and these surges are called “starting current”. The magnitude of the starting current is usually very noticeable, and exceeds the rated value by 10-15 times. This means that all components in the air conditioner's power supply system must withstand short-term but significant overload. For example, if the air conditioner is powered by an uninterruptible power supply, this UPS must withstand an overload of 1000% for 5-15 seconds. Unfortunately, such UPSs do not exist, and to ensure the functionality of the entire system, you have to use a obviously more powerful (oversized) UPS, which costs “oversized” money. That is, the freon system places special demands on the adjacent system, significantly increasing its cost.
No free cooling
In addition to the fact that a freon air conditioner consumes a lot of electricity, it should be noted that it consumes it constantly. All year round. And if it’s winter outside and there’s a lot of “free” cold air all around, a freon air conditioner can consume even more electricity, because it is forced to heat up its external unit “so as not to freeze.” Alas, there are no opportunities to save at the expense of nature.
Difficulties of repair
And about repairs. If water drips from a pipe, then the pipe is usually wet, and there is a puddle under the pipe. This greatly simplifies the search for a leak: where there is a puddle, there is a leak. Freon flows only at a pressure of tens of atmospheres, so at the slightest damage to the pipe it simply evaporates invisibly. Finding a leak is not a trivial task and takes a lot of time. To restore the system, in many cases it is necessary to stop the air conditioner, remove the refrigerant and completely recharge after repair.
Advantages of water systems
Having considered freon air conditioners, let’s turn our attention to a more complex and expensive option: a water system. Here it is already difficult to talk about individual air conditioners (it is possible, but difficult, to imagine a single water conditioner); we will consider a system of several devices working together. Let's start again with the advantages.
Free cooling and energy efficiency
The main reason for the existence of water air conditioners in the data center is, of course, high economic efficiency, due to both the high efficiency of the system as a whole and the possibility of “free” use of “street cold” for several months a year. In the conditions of central Russia, even a standard system with water air conditioners, operating in a “normal” temperature regime and not “tailored” specifically for high energy efficiency, allows “free” cooling of IT equipment for 4-5 months (when the air temperature outside is negative ). With the use of some technological tricks, the operating period of free cooling can be increased to 7-8 months. The electricity consumption of the air conditioning system in free cooling mode is extremely low. For example, a 100-kilowatt system will consume about 1 kW for pumps pumping coolant, approximately 3 kW for fans blowing the heat exchanger outside, and about 12 kW for fans in air conditioners. In total, the “conditional efficiency” is approximately 600%, and not 200, as with freon systems.
High permissible energy density of the data center
Unlike a freon air conditioner, a water air conditioner is very simple: it has neither a compressor inside, nor a complex system for regulating the pressure of the working substance, nor many tubes and valves... Essentially, a water air conditioner is simply a heat exchanger with fans pumping air through it. The space freed from the complex filling is not wasted: it is occupied by a heat exchanger, which is noticeably larger than in a freon apparatus. And the larger the heat exchanger, the more powerful the air conditioner, all other things being equal. That is, in the same size. A modern in-row water conditioner with a power of 60 kW can be assembled in a housing the size of half a server cabinet: 300 mm wide. Thanks to such compactness and high “power density”, water conditioners make it possible to build “energy-dense” data centers with a specific load per server cabinet of 15-20 kW or more, without the air conditioners taking up more space than IT equipment.
Possibility of choice
Let us remember what is the source of cold for a water conditioner: very generally speaking, it is a “pipe with cold water” (by the way, although we say “water,” in our climate this word usually means a non-freezing mixture, antifreeze). If the system is built correctly, the operation of all other air conditioners does not depend in any way on the water consumption of one device. The consequence of this is the fundamental possibility of organizing the system in such a way that powerful air conditioners for the computer room of the data center, less efficient air conditioners for the UPS area, and very small devices for auxiliary rooms - such as an electrical panel room, switching room, etc. . P.
A small number of "external blocks"
Where does cold water actually come from in this pipe? The water is cooled by a refrigeration machine, “chiller”. According to the principle of operation, the chiller is very similar to a freon air conditioner, only it cools not air, but a coolant liquid. How many chillers should there be in the chiller system? As many as you like, starting from one. Yes, yes, if the power of the refrigeration machine is sufficient to operate all air conditioners, then there can be only one machine for any number of air conditioners. True, there are usually several chillers. This is done to increase flexibility, reliability and ensure gradual development of the system. But two, three, five chillers are not a dozen, two, or more external units. The data center does not look like a Christmas tree hung with toys - and that’s good.
There are no restrictions on removing chillers from air conditioners
One of the problems with a freon air conditioner is the short distance from the air conditioner to its external unit. How far away can the chiller be installed? Everything is determined only by the performance of the pump pumping the coolant and “cold losses” (heating of water “on the way” from the chiller to the air conditioners) due to imperfect thermal insulation. But these are surmountable difficulties, so it is quite possible to install refrigeration machines on the roof of a multi-story building, in the far corner of the territory, or in any other convenient place. There are buildings in which freon air conditioners cannot be installed in principle, but water systems are quite functional in such conditions.
Easy detection of leaks and prompt repair of lines
How can you detect that water is leaving a pipe? By pressure drop in the system. How to find the location of the leak? Visually! In most cases, leak detectors are not needed; there is no need to turn off the system and conduct a lengthy search for the leak location. Moreover, if emergency make-up equipment is available, the water conditioning system with minor leaks can function long enough for the repair to turn from an emergency into a planned one. The repair method, by the way, depends on the selected pipeline material, and in some cases it is possible without shutting down the system. And if you provide backup pipelines, then no leakage will be disastrous and will not lead to a shutdown of the data center. Yes, there is freon in the chiller, and it can also escape. But the chiller is a complete device that comes from the factory filled with freon and oil, so the likelihood of a leak is not very high.
Disadvantages of water systems
Of course, you can't get anything for free. Even if we do not mention such a disadvantage of the water system as significant capital costs at the initial stage (alas, the cost of equipment and installation work can exceed similar indicators for freon systems by two or more times), there are other problems. Which, of course, cannot be ignored.
Availability of water in the data center computer room
In fact, water is present in one quantity or another in any data center. This includes drainage of condensate from air conditioners, heating in adjacent rooms, there is also a risk of roof or water supply leakage, etc. But in the air conditioning system, the water is under pressure, which, although small (usually 2-3 atmospheres), is still still increases the risk of leakage and accelerates the flow of water through the damaged pipeline. In a water-conditioned data center, it is imperative to provide for water drainage from under the raised floor and take enhanced measures to waterproof floors and even walls.
Problems with low load operation
The chiller is a freon refrigeration machine, and, unfortunately, it is not free from such a disadvantage as the inability to work with too low a load. And since chillers are usually quite powerful, the minimum permissible heat load can be quite significant. Therefore, the new data center will have to be immediately loaded at least 30% of the capacity of a single chiller... or put into operation in the fall: in free-cooling mode there are no problems with the minimum power.
Place for installation of chillers
The downside to the small number of chillers and their high output is size and weight. The freon compressor and all its piping are located not in the air conditioner, but in the chiller, the heat exchanger for free cooling is also often integrated into the overall structure, as a result, even a 50-kilowatt unit weighs almost one and a half tons. You cannot hang such a unit on the wall - you need a platform on the ground or on the roof. For a conventional 100-kilowatt data center, three such chillers are needed (the third is a backup), in the end the site will be the size of a parking lot for three cars and it will also be loaded “for three cars” - almost five tons.
Expansion of the range of equipment in use
And, of course, hydraulics. Pumps, heat exchangers, shut-off valves - all this will lead to the fact that in addition to an electrician, a diesel operator, and a refrigeration technician, the data center staff will also have to hire a hydraulic plumber. By the way, all the pipes will have to be made at once, and at full capacity, no matter what the first launch complex is.
How to choose
What to choose in the end, “water” or “freon”? Since this is an engineering problem, it should be solved taking into account all the parameters of the facility under construction. Here is an expert opinion: for each of the real cases there is an optimal solution, and there is no single recipe for all, therefore, special attention must be paid to the choice of cooling system architecture, carrying out variant studies with the obligatory involvement of specialists. A preliminary assessment of the pros and cons can be made using the table given in the table.
Checklist for determining the technology selection vector
| Conditions | Answer |
| Design energy density lower than 10 kW per IT cabinet. | Not really |
| The number of IT cabinets in a server room or data center does not exceed 10 pieces. | Not really |
| At a distance of no more than 25 m (along the highway) and at the data center (server) level, there is a place to place external units (condensers) of air conditioners. | Not really |
| There is no strict power saving mode. | Not really |
| There is no possibility of installing a raised floor in the machine room. | Not really |
| The thermal load in the first months of operation of the data center will be less than 10% of full capacity. | Not really |
| There are problems with the proper operation of heating and water supply systems. | Not really |
| Is it easier to buy a powerful UPS than to complicate the cooling system? | Not really |
| A partial shutdown of the air conditioning system will not affect the operation of the main data center systems. | Not really |
| There is no clear understanding of the pace at which the data center will develop and how long it will be in operation before the first expansion? | Not really |
| Is the goal of reducing capital investments precisely at the first stage? | Not really |
If there are significantly more “yes” answers than “no”, then a freon system is quite suitable for your data center. If there are more “no” answers than “yes”, we recommend taking a closer look at the water system. However, a specialist will still tell you the exact recipe when he sees your data center “live”; his help should never be neglected.
Oleg Sorokin, data center expert at ICL-KPO VS
- Short link
Installation of winter kit
Equipping your climate control equipment with a winter set will significantly reduce the lower limit of the operating temperature range to -15, and in some cases, to -25 °C. This option includes:
- Installation of electronics that allows you to reduce the rotation speed of the external unit fan depending on the external temperature
- Installation of a heating element that heats the oil in the crankcase before starting the compressor.
- Equipping the drainage pipeline with an electric heater, consisting of a heating cable and a control board. The control element sensor independently regulates the heating temperature of the cable depending on the ambient temperature.
To heat the house in an alternative way during periods of slight frost, the most acceptable option would be heating with a ducted air conditioner, “shod” in a winter kit. A network of ducts can supply warm air to each room, creating an acceptable indoor temperature. But again we return to the air. At air temperatures below -5 °C -7 °C, heating efficiency decreases to almost zero.
The operation of climate control equipment for heating at sub-zero temperatures forces it to function at the limit of its capabilities. Long-term use of climate control equipment in this mode reduces their durability by three to four times.
How to turn on the heating
Many people will find it strange to ask how to turn on the air conditioner for heating. The thing is that this mode is not available in all climate control equipment. Even if the device is equipped with this feature, most users use this mode only in the off-season and quite rarely, since it is impossible to create full-fledged heating with its help. The instruction manual tends to get lost in a pile of documents. Some people forget, while others initially, from the moment of purchase, do not know how to turn on the air conditioner for heating. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzJIDbyCTm4
For everyone who wants to know how to set the air conditioner to heat, but the instructions have been lost somewhere, the following instructions have been prepared:
- The HEAT key on the remote control is responsible for switching the split system to heating mode. After turning on the device, press this key and after 7-15 minutes. Warm air will begin to flow into the room.
- If there is no such key, find the MODE button on the remote control. Press it until the word HEAT or the “sun” icon appears on the remote control screen.
- If there is no such key, try to find a button on the remote control with the icon “sun”, “snowflakes”, droplets, etc. Press it until the inscription HEAT or the “sun” icon appears.
If, when switching modes, the above icon or inscription is not displayed, but other modes work, then your air conditioner is not designed for heating rooms.
- After turning on the heating mode, set the desired temperature using the “up” - “down” or “+” and “-” keys.
If you decide to use alternative methods to heating radiators for heating your home, then do not stop at air conditioning - it is ineffective. Reverse mode can be used exclusively as an addition to an existing heating system.