Preparing to perform a manual operation
It is believed that the history of the first screw connections began long before the birth of Christ. The pioneer is the ancient philosopher, mathematician and mechanic Archytas of Tarentum, who lived in the 3rd century BC. His follower was the world-famous Archimedes, who took advantage of this teaching and applied science in practice to move liquids and solids. However, theoretical teachings were not included in textbooks or were forgotten (exactly unknown), and the technological peak occurred in the 19th century AD. The English scientist or inventor Henry Maudsley first introduced to the scientific community an apparatus in the form of a screw-cutting lathe, with the help of which point cutting was carried out. As a result, the date of creation of the equipment is equated to the industrial revolution, since until that time nothing like this had been invented and it was from this moment that a breakthrough occurred in all sectors of the national economy throughout the world. Scientists involved in the problems of metallurgy, mechanical engineering, materials science, machine tool building and other applied sciences that are important for life had their hands in this process.
Now let's look at the preparatory work for cutting pipe threads by hand.

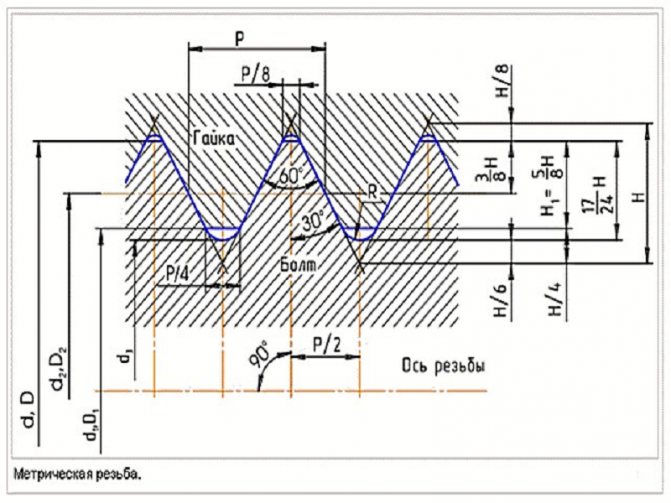
First, let's figure out what this means and what its parameters are. These are cut grooves with a uniform pitch between turns and with the same geometric profile on a material of conical or cylindrical shape. They are used to connect various parts and assemblies everywhere from house construction and water supply to machine and shipbuilding.
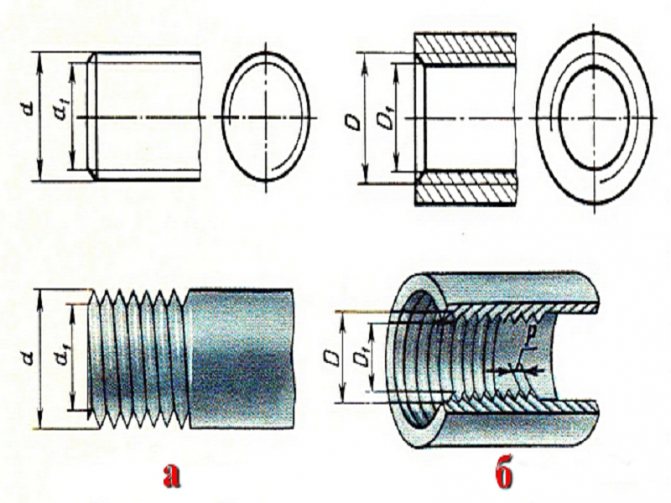
We provide you with a schematic diagram to refresh your memory.
a – denotes external thread. More often, citizens have to cut this type themselves to connect plumbing fixtures.
b – internal processing.
In the picture, in both versions, the diameter is indicated by the English letters d, d1 and, accordingly, D, D1.
You are mistaken in thinking that threading cannot be done at home without the use of special equipment. Everything can be made independently without excessive financial investments using available tools.

To do this, before starting work, you should pay attention to the following points:
- Contamination of the workpiece. If there are foreign inclusions, soil, rust, scale, oily deposits, traces of petroleum products, etc. on the surface, then it is absolutely clear that these problems must be eliminated by cleaning. Otherwise, foreign inclusions will likely deteriorate the quality of the turns made.
- From manufacturers we often receive a part with a chamfer at the end, that is, with a turn. This defect must be eliminated using a grinder, or best of all, a file. This way you will get a high quality sample.
- If you want to get the product to the required level, you will have to apply a lubricant.
We recommend that you listen to our advice, otherwise the working part may wear out greatly, and the event itself will drag on indefinitely and it is likely that failure to comply with the conditions can lead to deformation of the part and ultimately to its failure.
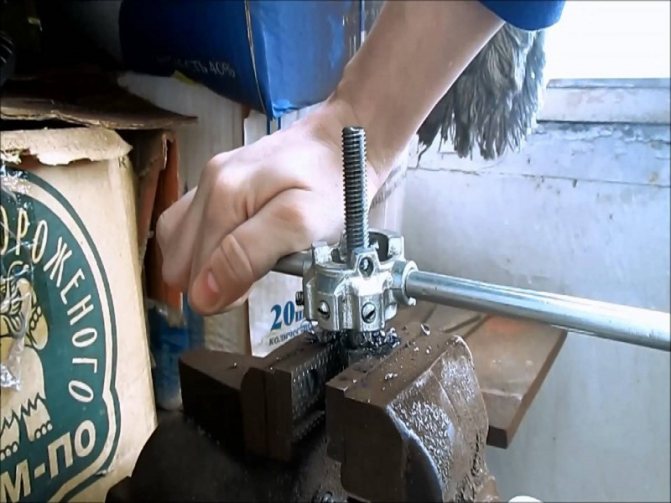
How to Manually Cut Threads with a Die on a Pipe - Step-by-Step Guide

At the end there are holes in the form of flower petals, necessary for removing waste chips. The inner part is represented by sharp cutting edges. There are two holes drilled on the body into which the handle is inserted to ensure uniform impact. It is the most common model due to its ease and ease of use:
- We fix the vertically located pipe using clamps (vices).
- We clean the surface from dirt.
- We create a chamfer for precise alignment.
- We apply oil to the plane for better movement of the die.
- We insert the element strictly perpendicular to the workpiece to avoid distortion, which even at a slight degree can lead to incorrect creation of turns.
- We turn the handle clockwise, make two turns and come back. In this way we release waste chips.
Cutting pipe threads with a clamp
Such a mechanical kit is sold in any specialized stores and is especially popular among users, since there is no need to carry out an alignment operation. This feature is included in the package.
The external structure of the clamp looks more complex, but the internal contents are so constructive that it allows you to get the job done quickly and efficiently.
The tool consists of:
- Round metal frame cast from durable alloy.
- Four removable cutters or blade combs. The second sample has a tremendous advantage. When moving, the first cutters make shallow grooves, and the next, higher ones, sliding along the “rough” path, cut out a full-fledged one, ready for use.
- A wide holder with a guide tube that minimizes the process of distortion.
Instructions for use:
- The clamp is installed in the ratchet, and a guide is installed on the edge of the workpiece.
- The cutters are lubricated for smooth operation/
- The work of the ratchet begins, which rotates around its axis.
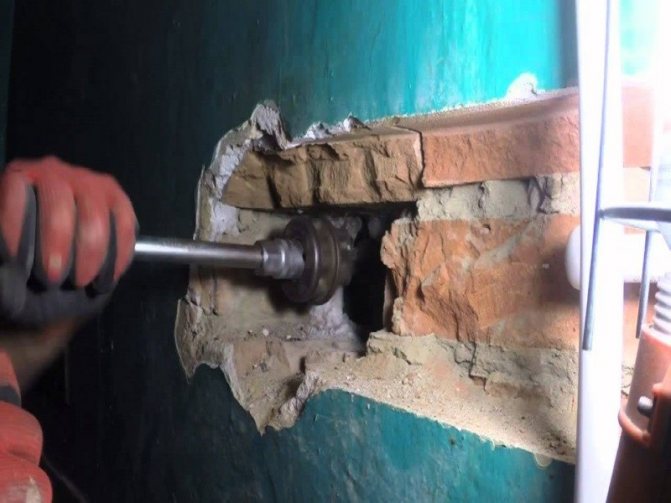
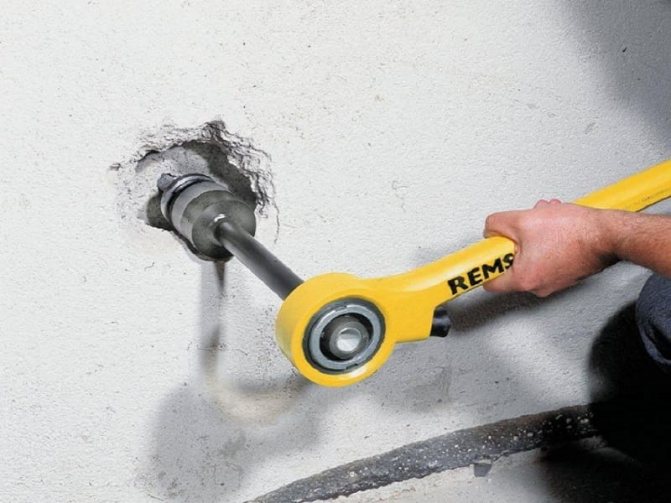
Cutting a thread on a pipe near the wall

If the workpiece is located in a place where there is no space to approach and carry out the operation, then we offer several methods that minimize the financial costs that will certainly arise in an unusual situation:
- If it is possible to dismantle a small section of the wall, for example, removing ceramic tiles, then take advantage of this. This will free up a significant amount of space for you to complete the task at hand.
- The pipeline consists of several parts. You will have to disassemble the line and cut on the removed section.
- As we wrote above, cutters need constant lubrication. However, oil drains from a horizontal surface. Therefore, it is recommended to perform the manipulation in several passes - this way an ideal surface quality is created.
- Strictly control the position of the tool parallel to the axis and apply sufficient load.
What and how to properly cut threads on a water pipe

Currently, plastic or metal pipes are mainly used for laying water supply systems.
Plastic products are connected to each other, as a rule, by welding (a special welding machine is used for these purposes).
Metal pipes are joined with threaded fittings, in this case the connection is as strong as possible.
articles:
Not many people have thought about how to connect the water supply to a private house.
It consists of:
- pipes,
- valves,
- valves
- taps and other components.
All this is assembled into a single system using threaded connections.
To ensure that the process of replacing an old part with a new one does not take much time, there is a thread.
Sometimes you have to deal with cases when you yourself have to change a worn-out element (for example, a pipe), but there are no grooves on it.
What to do in this case?
The way out of this situation is very simple - cut the thread with your own hands. The ideal option is when you have the opportunity to use a lathe.
But not every home craftsman has such equipment.
It is expensive, and in order to use it you need to have certain experience and skills.
Do you know the cost of installing radiators in an apartment? The approximate cost of aluminum, bimetallic and cast iron radiators for heating living space is indicated in a useful article.
Find out what can be glued with silicone sealant on this page.
If you need to equip a pipe with threads , for example, to connect a membrane tank for water supply (written here), you can use one of two types of devices designed for cutting grooves:
- thread cutting table,
- pipe wrench.
This tool is used to cut threads in water and sewer pipes (read why a water seal is needed here), which are used in the utility networks of multi-storey buildings and private buildings.
How to properly cut internal pipe threads

This is a tool with which you can make a screw hole in a regular home workshop that meets the requirements of GOST. It consists of intake, calibrating and tail parts. Allows, depending on the technological solution of the manufacturers, to create a thread in a prepared through or blind hole in one/two/three passes using a reciprocating movement.
The workflow consists of several stages:
The pipe is placed strictly perpendicular to the horizontal surface.
How to cut threads on a pipe yourself. Photo and video

How to correctly cut external and internal threads on a pipe using clamps and dies. Threaded connections of metal pipes are durable and airtight, and can withstand significant pressure. However, independent thread cutting requires knowledge of certain rules.
To work you will need tools and materials:
- Vernier calipers - for accurately measuring the diameter of the pipe.
- Vise - when using solid dies or a tap.
- Machine oil or any lubricant.
- A rag or sponge.
- Protective equipment - glasses, gloves.
And also, a device for cutting threads, depending on the specific task (solid or sliding dies, electric dies, ratchet dies or taps).
Preparing for work
First, you need to select and, if necessary, cut a suitable piece of pipe with a grinder or a hacksaw. When cutting, you need to make sure that the cut is strictly perpendicular to the planes of its walls.
Immediately before cutting the thread, you should clean the surface of the pipe from rust or old paint, and other foreign deposits using sandpaper and a file. In addition, you need to chamfer the end of the pipe with a file in order to make the thread easier. Now let's move on to preparing for thread cutting.
Basic mistakes when cutting threads
- the pipe diameter does not match the thread diameter;
- using incorrectly aligned, rusty or dull tools;
- working without lubrication of the tool and pipe leads to cracks or breakage of threads;
- excessive physical effort as a consequence of a complete lack of work skills leads to thread failure.
Cutting external threads with a solid die
Solid dies are often used for cutting external threads on pipes. They are a hardened nut with internal cutting edges. This tool is suitable for cutting threads with a diameter of up to 52 millimeters.
It is inexpensive, characterized by good rigidity and precision, but does not last long because it wears out quickly. Working with dies requires some experience, so in order not to damage the tool and pipe, it is advisable to practice on a section of pipe.
Grooving machine

However, the essence of all machines is the same - they are used to cut threads on an industrial scale. The advantages include:
There is a function for programming diameter and pitch parameters with automatic reverse.
Thread standards

Let's consider several options. It is worth considering that some have ceased to be used in production altogether. Therefore, we focus your attention on specific types that are in demand all over the world.
G - Straight (inch) pipe thread
In the Russian standardization system it is designated GOST 6357-81, in the world arena – BSPP. These products are in most cases used when working with gas or water pipes and are sold at any retail outlet. As a rule, bronze, steel, or brass plumbing fixtures are equipped with this standard. As for cutting it yourself, you will have to use the English abbreviation.
The advantages are as follows:
G is an international thread mark that is understandable to everyone.
| Pitch in mm, P | Number of turns |
| 0,907 | 28 |
| 1,337 | 19 |
| 1,814 | 14 |
| 2,309 | 11 |
The decoding is very simple and you can use it to understand which parameter means what. So:

For a complete understanding, you need to familiarize yourself with the table and use it in the future, since it is the values presented that are most often found in home engineering structures.
| Thread size G | Step in millimeters | Diameters (mm) |
| Row 1 Row 2 | d=D d2=D2 d1=D1 | |
| 1/8 | 0,907 | 9,728 9,147 8,566 |
| 1/4 | 1,337 | 13,154 12,301 11,445 |
| 3/8 | 16,662 15,806 14,95 | |
| 1/2 | 1,814 | 20,955 19,793 18,631 |
| 5/8 | 22,911 21,749 20,587 | |
| 3/4 | 26,441 25,279 24,117 | |
| 7/8 | 30,201 29,039 27,877 | |
| 1 | 2,309 | 33,249 31,77 30,291 |
| 1/8 | 37,897 36,418 34,939 | |
| 1-1/4 | 41,91 40,431 38,952 | |
| 3/8 | 44,323 42,844 41,365 | |
| 1-1/2 | 47,803 46,324 44,845 | |
| 3/4 | 53,746 52,267 50,788 | |
| 2 | 59,614 58,135 56,656 |
R - taper pipe thread standard
BSPT is an abbreviation of international significance and is subject to the domestic standard according to GOST number 6211-81.
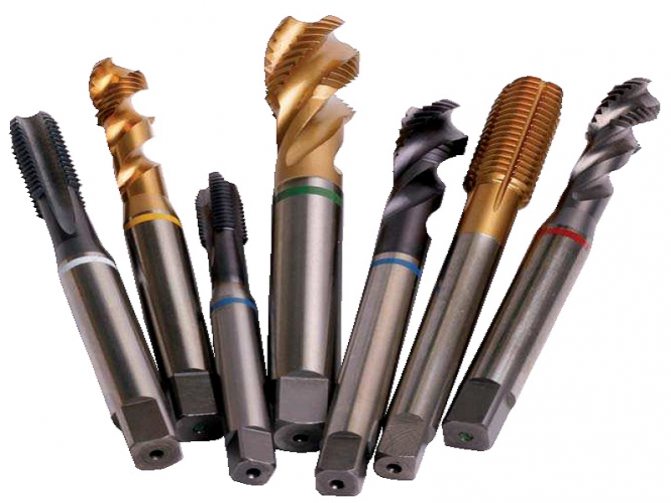

In its structure, the process resembles the action with a cylindrical workpiece, but only with a slight slope on a scale of 1:16.
According to the state standard, this process must meet the following requirements:
- The profile angle is 55 degrees.
- The step creation corresponds to a specific pipe size.
- The maximum possible diameter of the product used is 6 inches. Wider samples cannot be screwed together; in such cases, welding or flanges are used.
Connecting fittings of this standard are used in places with high pressure and temperature for maximum sealing of the system. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly comply with the standard for the ratio of parameters established by the country.
Other standards

There are several other types, but we will write very little about them, since a citizen most likely will not use them in everyday life:
- Metric cutting, which is not suitable for pipe installation. From the name it is clear that in diagrams and drawings the unit of measurement is the derivative of the meter, that is, the millimeter.
- The letters Kr on the product indicate that this is a plumbing product with a unique profile and smooth round thread.
- NPSM, NPT, NPTF are the designations of the American standardization system. The product has the shape of an isosceles triangle and differs from its analogues in the profile angle, which corresponds to 60 rather than 55 degrees.
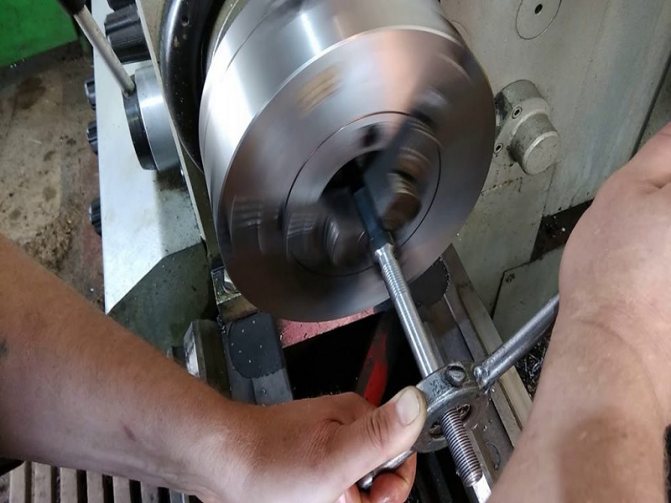

Of course, these types of standards are unlikely to be suitable for your work, but it is worth recalling the BSPP parameters so that you can distinguish them from others if necessary.
| Designation of conditional passage | Number of turns per 1 inch | d=D | d2=D2 | d1=D1 |
| 1|8 | 27 | 10,272 | 9,510 | 8,766 |
| 1|4 | 18 | 13,572 | 12,443 | 11,314 |
| 3|8 | 17,055 | 15,926 | 14,797 | |
| 1|2 | 14 | 21,223 | 19,772 | 18,321 |
| 3|4 | 26,568 | 25,117 | 23,666 | |
| 1 | 11 1|2 | 33,228 | 31,461 | 29,694 |
| 1 1|4 | 41,985 | 40,218 | 38,451 | |
| 1 1|2 | 48,054 | 46,287 | 44,52 | |
| 2 | 60,092 | 58,325 | 56,558 |
How to cut internal threads in a pipe?

Carrying out repairs or replacing communications cannot be carried out without cutting into the pipeline. Previously, welding was used for this task, but this is quite labor-intensive work, and in order to use welding equipment on a pipeline, you must have fairly high qualifications.
Welding could be used for rolling metal pipes, but what to do when you need to connect two pipes made of different materials? This is where the joining method comes to the rescue by cutting threads on the pipes and then connecting them. What it is and how it is performed, what tool can be used will be discussed in detail in the material presented below.
Types of threaded connections
First of all, it should be noted that you do not need to have any special skills to perform these actions. But you need to be able to distinguish the type of thread on a pipe. For example, it is important to distinguish between inch and metric knurling, left and right. In general, there are a large number of types, but these are the ones most often used - inch and metric.
The distinctive characteristics of the inch and metric types are as follows.
Inch type of thread on pipes:
- All items are measured in inches.
- The presence of a profile in the shape of an isosceles triangle with an angle of 55 degrees at the upper corner.
- Present big step. Consequently, this profile is larger and this type of cutting has higher strength.
Metric type:
- All elements are measured in millimeters.
- The profile is distinguished by the shape of an equilateral triangle.
- Smaller step.
IMPORTANT! Cutting on pipes for water supply is carried out in inch units, and for fasteners, measurements in mm are used.
Below we will consider what types of carvings there are.
- Right. This is if the nut is screwed onto the bolt in a clockwise direction.
- Left. In this case, the nut is tightened in the opposite direction.
High-quality cutting on a pipe can only be achieved if the volume of the drill or rod for making the hole is accurately selected.
On stainless steel
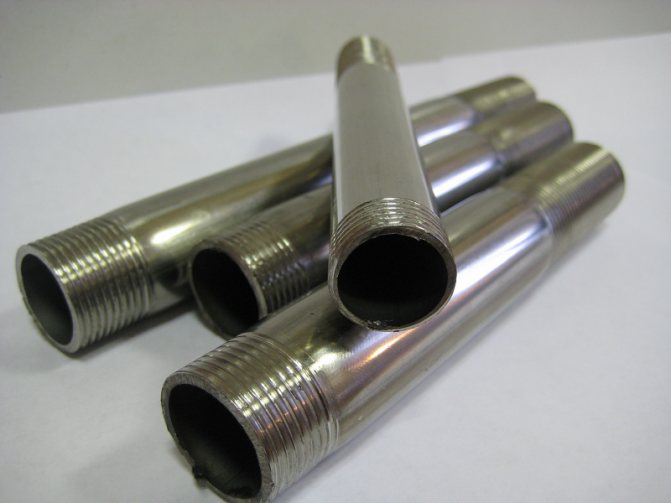

To make the task easier, a special type of lubricant and compliance with the requirements for sharpening the tool are required. We provide you with a video on manual tapping of water pipes. After studying the material, you will be able to do the work yourself without invited specialists:
Cold method of threading polypropylene pipes
Without heating, threads can also be cut using fittings. Only now you will need a vice for fixation. You need to secure the fitting and, using force, screw the pipe onto it. This process has the advantage that, without high heat, the carving lines are clear. There is only a danger of applying extra force, which could cause the pipe to simply burst.

Cold cutting can also be used to cut threads on polypropylene tees and couplings.


