The need for air circulation in a gas boiler room
Even with a small amount of carbon monoxide, the well-being of the residents of the house worsens. Headache, pain in the eyes, lethargy - this is the least that accompanies a person with gas poisoning.
Its leaks are the most dangerous, as this often leads to an explosion or fire. And also an incorrectly calculated hood directly affects the performance of the boiler.
This is because fuel requires fresh oxygen to burn properly. And if there is not enough gas due to poor ventilation, then the gas burns worse and, accordingly, the boiler gives off less heat.
ATTENTION! A bad exhaust hood with a floor-standing boiler serves as a source of gas and fume accumulation inside the exhaust pipe, as a result of which its passage is reduced, draft deteriorates and smoke occurs in the room.
Hood requirements
Gas boiler houses place increased demands on the ventilation system.
In this case, the following premises may be equipped:
- As a separate building.
- Attach to a house building.
- In the basement.
- In a dedicated room in the building.
If the equipment is designed for liquefied gas, then basements and attics cannot be used for these purposes, since the specific gravity of gas is greater than that of air.
As a result of this, it will fall down in case of leaks and will be explosive. Along with the allocation of separate rooms, modern wall-mounted boilers are allowed to be placed in the kitchen.
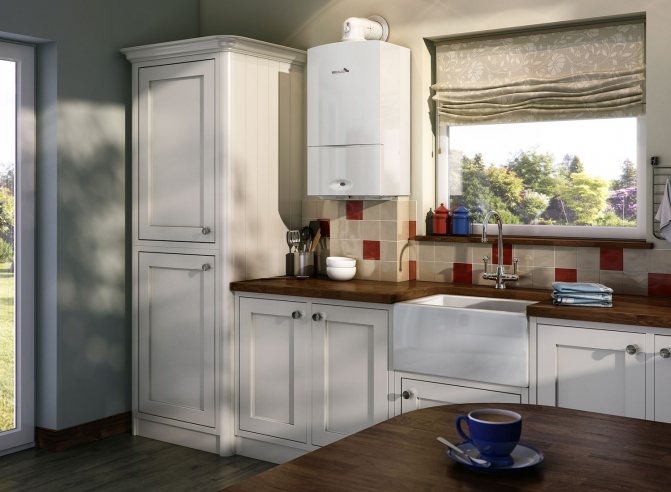

Despite the coaxial chimney, the rooms for them must meet the following requirements:
- Area about 12 m2.
- The height to the ceilings is more than 220 cm.
- The window size should be at least 0.05 m 2 per 1 m³ of room volume.
- The presence of a vent or opening window.
- The boiler is hung on a wall made of non-flammable material, and the distance from the adjacent partition must be at least 20 cm.
- Correspondingly sized openings for air flow from the adjacent room.

Gas boiler room ventilation standards according to SNiP
When installing a supply and exhaust system, you must strictly comply with all the requirements of building codes and regulations dated April 2. 05-91.
For boiler houses operating on gas, three air exchanges per hour must be taken into account, and if such ventilation is not created naturally, then forced exhaust must be provided.
The air circulation scheme should be adopted according to the appendix. 11 SNiP:
- The gas boiler room must be equipped with ventilation, and the air duct outlet must be located on the ceiling.
- Air flow is provided through the ventilation duct or through openings at the bottom of the doors.
- Consumption is calculated based on the boiler power: per 1 kW of power there must be at least 0.08 m 2 of vents.
- Coming from an adjacent room: per 1 kW of power - over 0.3 m 2 holes.
Other standards for ventilation system equipment can be found in legal documents.

When is the act drawn up?
Regardless of what type of building the building in use belongs to (owned by a legal entity or an individual), if it uses heating appliances running on gas, solid or liquid fuel, it is necessary to carry out inspections of chimneys and ventilation ducts at certain intervals. The result of the inspection is a report on the chimney.
And if chimney pipes, under the influence of negative factors of fuel combustion, quickly collapse and become unusable, then the ventilation ducts narrow in cross-section over time, which leads to a decrease in the efficiency of removing used air from the premises . And this affects sanitary standards, especially in those rooms where heating devices are located.

Therefore, these two systems must be monitored and, if necessary, repaired. But in any case, regardless of whether an inspection was simply carried out or repairs were carried out, a VDPO act is drawn up according to standard form number 20.
Today, various organizations (government and commercial) are involved in the inspection of chimneys and ventilation ducts, which will draw up a report on the chimney based on the monitoring actually carried out. No one will draw up documentation based on fictitious indicators, because people's lives depend on it.
Types of ventilation for gas boilers
The ventilation system is a list of elements for the intake and removal of air, and it differs in the following ways:
- Based on the principle of air exchange (natural and forced exhaust).
- By appointment. Exhaust, supply and combined ventilation.
- By design (channel and simple).
Let's take a closer look at the first two types of ventilation.

Natural ventilation in a gas boiler room
If the house has a boiler with a power of up to 30 kW, then it is enough to ensure the flow of air by installing an exhaust hood at the bottom of the wall or door. A hole with a diameter of 10-15 cm can serve as such a source.
To create a ventilation duct for air flow you need:
- Install a piece of pipe made of any material (plastic, asbestos cement) into the hole.
- Attach a mosquito net to the outside of its end.
- It is advisable to install the supply hole next to the firebox in the wall so that air can be drawn directly into the combustion chamber without creating dust in the room.
- The exhaust duct is installed through the roof. It looks like a pipe of the same diameter, and at the same time it is equipped at the top with a protective net against insects and an umbrella that protects from precipitation.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! The diameters of the exhaust and supply ventilation pipes must be the same size for optimal air exchange.
The door in the boiler room, if equipped with a grille at the bottom, can also serve as an element for the hood.

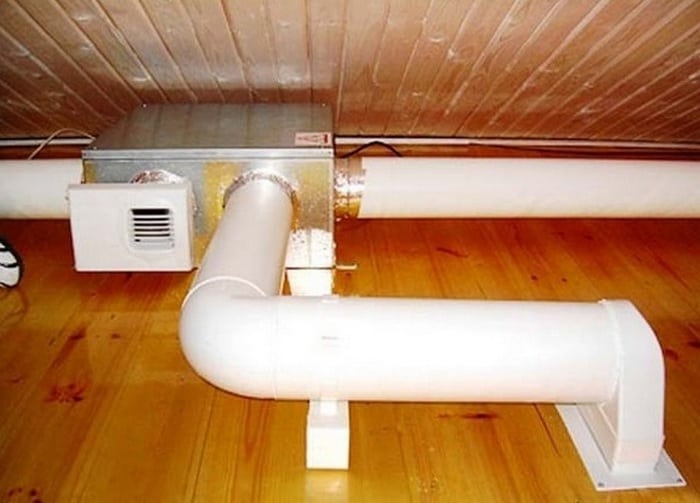
Placement of ventilation ducts in a private house
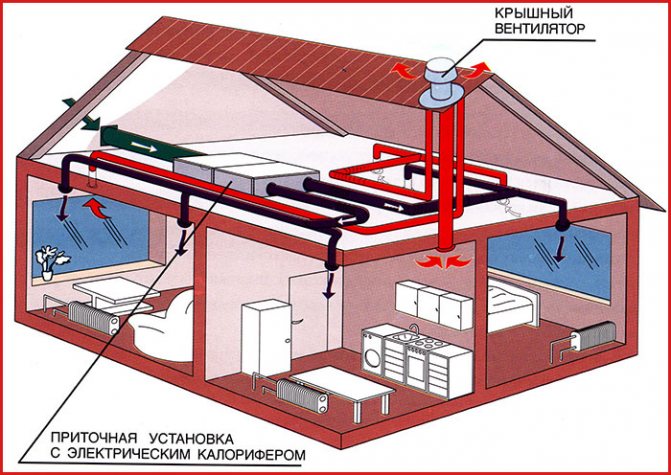
Ventilation ducts must be built into the structure of the house at the design stage. They should be present not only in the kitchen and bathroom, but in general in every room of a private house. When constructing a permanent building, ventilation ducts are usually made of brick.
In frame house construction, you can use plastic pipes or boxes made of thin galvanized metal. The main channel is being installed. As a rule, in the central wall, and branches diverge from it into different rooms.
The central pipe leads to the roof of the building. It should be remembered that you should not make many horizontal branches. They greatly reduce cravings. The vertical channel of the central pipe should be twice as long as the horizontal sections.
Installation Standards
- When constructing a central ventilation duct made of brick, the thickness of its walls should not be less than 500 millimeters. With a smaller thickness, in winter, the air in it will quickly cool and fall down, which will lead to malfunctions of this system. If the channel is made of galvanized boxes, then it must be covered with heat-insulating materials.
- The ventilation pipe should be higher than the ridge of the house, this is necessary in order to avoid air turbulence and improve draft.
Basic Rules
- The ventilation system in the kitchen and bathroom must have a combined scheme, natural and forced. A kitchen hood can be used as a forced one, and a ventilation duct must be installed for a natural one. It is most advisable to install the ventilation duct on the opposite wall from the kitchen hood. The width of the suspended hood must be at least the width of the gas stove.
- All rooms in the house must be equipped with ventilation ducts.
- In the bathroom, forced ventilation should turn on automatically when the lights are turned on.
- It is necessary to provide for the installation of replaceable filters in exhaust devices.
Forced ventilation
Artificial hood can be not only supply, but also combined, that is, supply and exhaust.
This process occurs when air is forced through the supply and exhaust pipes by fans - forcibly. In an hour, such a device pumps more than a dozen cubic meters of fresh air.
Modern ventilation units contain control and regulating equipment, which allows not only to maintain the microclimate in the boiler room at the proper level, but also ensures the correct operation of the boiler.
Such ventilation systems are divided into:
Monoblock installations. Devices of this type can be installed in any room.
Supply and exhaust systems. The intake and exhaust of air here is carried out in a forced manner. Such equipment is usually installed in basements, mainly where high-performance gas boilers are used.
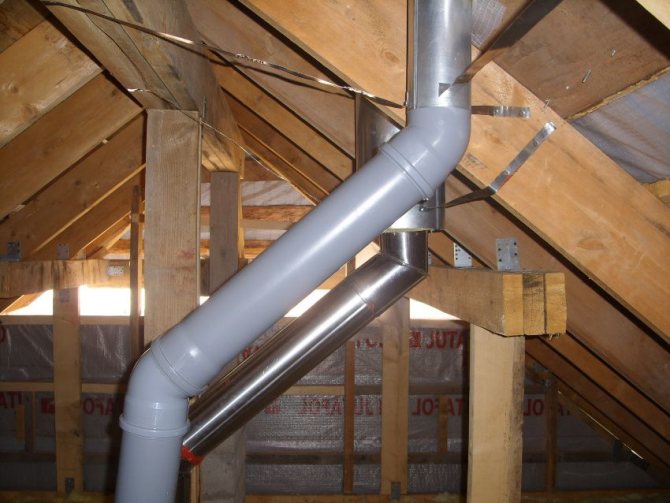
The best and safest type of forced ventilation is a boiler with a coaxial chimney. In this combined pipe, fresh air from the street is taken in through the outer gap, and exhaust carbon monoxide is released through the inner hole.
In addition, such ventilation increases the productivity of the boiler, since already heated air is supplied to the room, thanks to the counter-emission of exhaust gas through the internal pipe.

How to choose a ventilation system
The boiler room and ventilation scheme are designed at the stage of construction of a private house. Three types of air exchange systems are used:
- Natural, but in the house it can work intermittently in the summer and if PVC windows are installed.
- Flow-through, suitable for a house up to 300 square meters.
- Supply and exhaust, used for large houses.
Natural ventilation can be done with a minimum set of tools. To do this, a hole with a diameter of about 20 centimeters is made in the wall. The chimney pipe, valve and mesh are installed. The room must have a window and a vent. This system can be made additional.

The supply air is brought to the roof of the house, above the place where the equipment is installed. Two pipes are installed: the first for the supply of fresh air, the second for the removal of combustion products and gases. The first one can be additionally equipped with a smoke exhauster.
The air exchange system for a gas boiler in the house can be installed independently.
To install exhaust ventilation, you will need a grille to prevent dirt from entering, a fan with a check valve to prevent gas from entering the house, and an air duct. It must match the diameter of the fan. The chimney exits through the roof and connects to the boiler.
Ventilation for a gas boiler with a closed combustion chamber differs from the air ventilation system of a boiler with an open chamber.
Heating units with an open combustion chamber should only be installed in a well-ventilated and ventilated area . Boiler rooms are mainly used to install such heating equipment. Mandatory conditions are windows, vents and a door with openings.
Boilers with a closed chamber use a chimney with air intake from the street and from neighboring rooms. Such devices can be installed in any room. Installation in basements and basements is now allowed; the requirements for installing such equipment have been simplified.
Calculation of the ventilation system
The performance of gas equipment and the safety of people depend on the correct installation of exhaust devices in a boiler room; therefore, there is no need to strive to do everything yourself for the sake of saving money.
ON A NOTE! When drawing up a project, it is necessary to bring the outlet of the supply pipe as close as possible to the fuel chamber for better air flow and, accordingly, for optimal fuel combustion.
When calculating the ventilation system, it is important to know the following parameters:
- Air speed.
- The volume of the room taking into account the ceiling height.
- Air exchange in a room per unit of time.
The volume of air space is calculated using the following formula V=L×S×H×n, where: V – volume of air for exchange in 1 hour; L – length of the room; S – width; H – height; n – air exchange rate.
For floor-standing gas boilers, the fan is selected with a power reserve that exceeds the normal load by 25-35%.
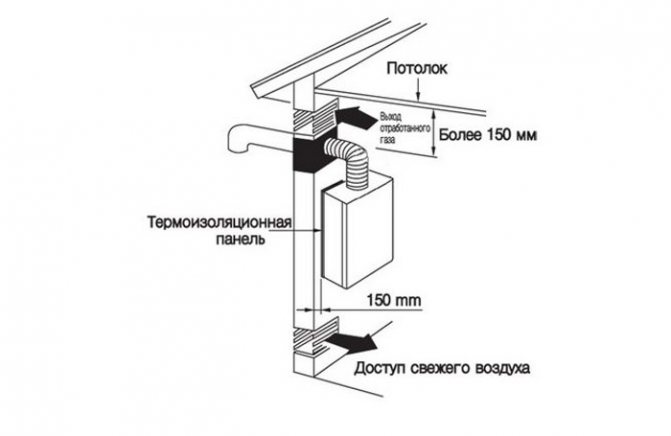
The role of ventilation in the boiler room
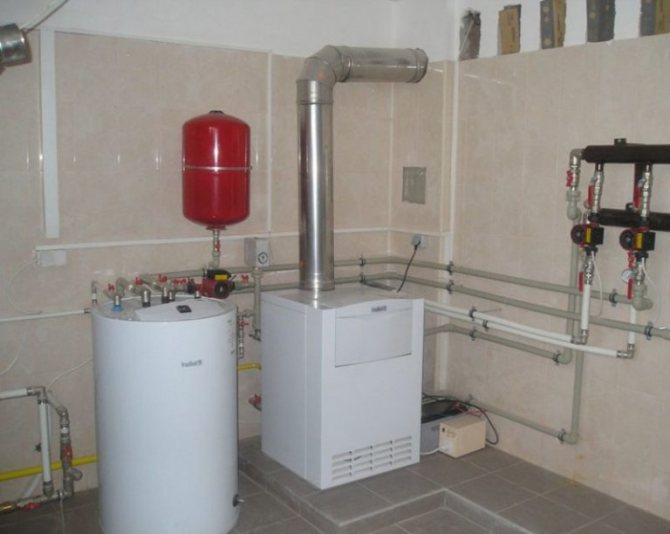
The basis of any heating system is design documentation. Therefore, even during the drafting of a residential building, a special section is devoted to thermal calculations and precise determination of the characteristics of the ventilation system. For buildings with a powerful boiler, it is necessary to have a separate building, extension or room dedicated to a ventilated boiler room.
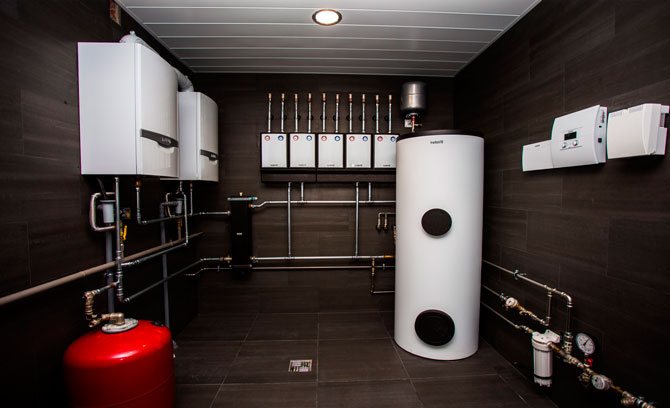

Boiler room in the cottage
The main purpose of arranging ventilation is to remove carbon monoxide generated during combustion from the boiler room. The penetration of even a small volume of combustion products into housing leads to the most severe consequences for people. Fuel gas leaks are no less dangerous. In locked rooms it accumulates quickly and, when a critical volume is reached, an explosion occurs.
This mainly applies to powerful floor-mounted heating units. The combustion chamber quickly becomes clogged with soot and soot. As a result, the cross-section of the air outlet is reduced, and part of the resulting combustion products passes into the boiler room rather than being removed outside.
The absence of a hood or a malfunction in its operation negatively affects the efficiency and economy of a gas heater. Normal combustion is ensured only with a constant supply of air in the required volume. If the efficiency of the ventilation system is insufficient, the regime in the combustion chamber is disrupted, which leads to a decrease in heat transfer and excessive gas consumption.
The operating parameters of the boiler room exhaust system depend on:
- gas boiler performance, its functionality;
- room area;
- heater loading;
- the size of doorways, the number and area of windows;
- climatic features of the region of residence.
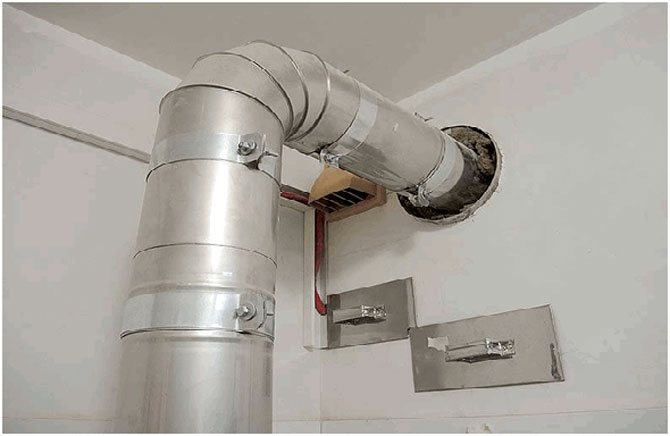

Boiler exhaust
Why do you need ventilation in the boiler room?
The operation of any boiler equipment is associated with the combustion of fuel and, as a result, intensive oxygen consumption occurs during the combustion process. The key task of ventilation of a private boiler room is to prevent reverse draft, in order to avoid the spread of carbon monoxide throughout residential premises. If you do not provide an adequate supply of fresh air, carbon monoxide begins to fill all available space, causing a fire hazard and reducing the intensity of combustion.
In addition, decomposition products can significantly affect the well-being of the residents of the house: weakness, poor health, dizziness and pain in the eyes - this is the most harmless thing that people who involuntarily inhale combustion products can feel. To ensure safe and productive operation of the equipment, prevent the leakage of flammable or explosive fuel and provide comfort to users, it is necessary to install a properly calculated and designed boiler room ventilation system, the standards for which are regulated in the relevant SNiP.
What is examined during the audit
When conducting an examination, you should establish:
- materials from which the channels were made, the cross-section of the latter;
- length of channels, places of connections, narrowings and outlets, marks of congestions and cracks found in the system;
- density of channels, their isolation;
- the presence of traction, horizontal sections, wind support zone (or its absence);
- condition of hatches intended for cleaning, fire-prevention cuttings, heads;
- tightness of pipes;
- general state of the system.
Also, during the inspection of ventilation ducts, the condition of ducts, exhaust shafts, and air intake grilles is checked.
If the channel size is insufficient, when it is impossible to use liners, they usually resort to lining with compounds intended for this purpose or lining with polymer liners.
Chimneys are often difficult to access for inspection
During operation, the smoke duct is constantly exposed to various loads. Soot deposits, condensation, acid deposits, temperature changes, and simply poor-quality masonry or chimney installation can cause fires and carbon monoxide poisoning. To avoid such problems, the chimney must not only be cleaned regularly, but also be inspected periodically. In accordance with regulatory documents, a chimney inspection must be carried out three times a year: the first time - no later than a week before the start of the heating season, the second time - in the middle of the heating season, the third time - a week after the end of the heating season. The chimney is cleaned based on the inspection results, but at least once a year.
Requirements for boiler room ventilation
Due to the fact that, as a rule, small rooms or extensions are allocated for boiler rooms, high-quality ventilation of a boiler room in a private house is an important condition, the fulfillment of which requires compliance with established standards and requirements.
The following provisions are defined in SNiP (II-35-76, 2.04-05) and apply to both gas and solid fuel boilers:
- The boiler room ventilation system must have a separate air exhaust route;
- It is necessary to install an air duct in the ceiling;
- The presence of two chimney channels in the wall: one for the chimney and one for its maintenance (located under the first and has a diameter of at least 25 centimeters);
- Clean air can be supplied from the street or through a special grille in the boiler room door;
- Openings for air flow from the street are calculated based on 8 cm 2 per 1 kW of heating unit power or 30 cm 2 per 1 kW if the air flow is from the inside;
- For any gas equipment, it is required to provide three air exchanges during one hour of boiler operation, without taking into account the air sucked into the furnaces of the boilers for combustion;
- Finishing flooring and walls from non-combustible and fire-resistant materials. The wall adjacent to the adjacent room is also finished with fireproof floor slabs, with a fire resistance limit of at least 0.75 hours.
In accordance with current laws and regulations, the height of the boiler room must be at least 6 meters. If compliance with this parameter is impossible due to the peculiarities of the building, for such cases the rule applies: the lower the height of the boiler room, the greater the air exchange should be. If the room height is less than 6 m, the air exchange rate should be increased at the rate of 25% for each meter of height reduction.
If it is impossible to ensure the necessary air exchange due to natural ventilation, mechanical ventilation should be designed.
If a low-power gas boiler (up to 30 kW) is enough to heat a private house, a separate room will not be required. The requirements for such equipment are as simple as possible: the area of the room must be from 15 m2, the ceiling height is from 2.20 m, the flow of fresh air is carried out through a window (based on the glazing area of at least 0.3 m2 per 1 m3 of the room) or a window. The equipment is installed at a distance of at least 10 cm from a wall made of non-combustible materials.
What are the requirements for ventilation of gas boilers?
The heater must provide constant air outflow and inflow. When calculating the exhaust power, the area and volume of the room, the characteristics of the heating equipment, the type of chamber and other factors are taken into account.
Despite the fact that for some systems building codes allow installation in residential premises, the boiler exhaust cannot be ducted into a common kitchen duct. It is necessary to equip a separate ventilation duct for it.
A complete list of requirements for ventilation of gas boilers is set out in DBN V.2.5-20-2001, SP 8913330, 41-104-2000 and 42-101-2003, GOST 30494-2011, SNiPah II-35-76, 31-01-2003 , 2.04-05, etc. Compliance with building standards is also regulated by Federal Law No. 384, Government Decrees No. 87 and No. 410.
Why is ventilation needed?
This function in gas installations performs several tasks:
- provides air flow, which is necessary for combustion of the heat source;
- prevents an emergency situation with natural and liquid fuels if there is a gas leak in the system;
- removes excess heat from pipelines and the heating installation itself;
- prevents poisoning of residents by combustion products (primarily carbon monoxide).

Convection is provided not only by special air ducts, but also through vents, special grilles and openings under the door.
Requirements for ventilation equipment in the boiler room
Depending on the type of equipment, SNiPs require the organization of double or single air exchange. The following requirements apply to boiler room ventilation:
- the hood parameters are selected so that the entire volume of air changes three times within an hour in a room with a gas installation;
- depending on the type of boiler, a full chimney or a coaxial air duct is connected to it;
- with a heater power of 30 kW or more, the pipeline is routed outside and not into the interior of a private house;
- the width of the ventilation passage is calculated depending on the characteristics of the heating system and the volume of the room;
- air channels must be sealed and equipped with sleeves for maintenance;
- if the air duct is located less than 1.5 m from the middle of the house, when creating ventilation, the pipe is brought out 0.5 m above the level of the ridge, at a distance of 1.5-3 m - flush with it, at more than 3 m - lower, but so that the tangents to the ridge and pipe form an angle of 10°;
- on the laying path, no more than 3 bends are allowed (angle up to 30°) and no more than 3 horizontal sections up to 1-2 m long;
- between the end of the ventilation duct and the external wall of the building there must be at least 0.3 m;
- air ducts are made of stainless and galvanized steel, asbestos, brick or ceramic materials;
- If materials capable of ignition are used at the outlet of the pipeline, they must be insulated.
Note: the recommended air exchange rate depends on regional building codes. For domestic installations in private homes, SP 281 allows a single change per hour.
Types of ventilation in a private boiler room
In order to ensure proper operation of the equipment in the boiler room, a constant supply of clean air is required. If sealed windows and doors are installed in the room, then the flow of incoming air will not be enough, and, therefore, additional efforts will be required to organize high-quality air exchange, i.e. installation of a ventilation system.
Boiler room ventilation can be divided into two types:
With natural ventilation, the movement of air masses occurs due to the difference in pressure outside and inside the room. At first glance, such a system seems quite attractive, because it does not require special equipment, it is economical and energy independent.
For the natural ventilation system to work effectively, it is necessary to create additional draft - for this purpose, the pipe is placed in a vertical position, and its height must be at least 3 meters. If it is possible to lay only a horizontal air duct, it must be equipped with a fan.
The disadvantage of this system is that you may not be able to provide sufficient air exchange rates. Such ventilation will completely depend on the stability of weather conditions, and for the normal organization of air exchange it will be necessary to provide a large cross-sectional area of the supply and exhaust ducts.
For gas boilers with a power of up to 30 kW, natural ventilation is organized by punching a hole in the wall or door to the street with a diameter of 100-150 mm at a height of 250-300 mm from the floor. A pipe is installed in it and closed on the street side with a fine mesh - this prevents the entry of small debris and insects. A check valve is mounted on the other end, which protects against backdraft. For the exhaust opening, the procedure is similar, with the exception of installing a check valve. The exhaust duct is covered from the outside with a canopy to protect it from precipitation.
IMPORTANT! The outlet of the supply pipe should be designed as close as possible to the fuel compartment - this way fresh air will flow directly into the chamber and promote the combustion process. It is strictly forbidden to direct air directly onto the boiler - this is unsafe!
Artificial (forced) ventilation can be organized as a supplement to natural ventilation. With its help, you can control and regulate the volume of incoming air masses. In addition, absolutely any diameter and length are allowed for air ducts, and the system will work in any weather and time of day.
Types of ventilation
To ensure safe and economical operation of a gas boiler, the following types of ventilation are usually installed:
- forced;
- natural.
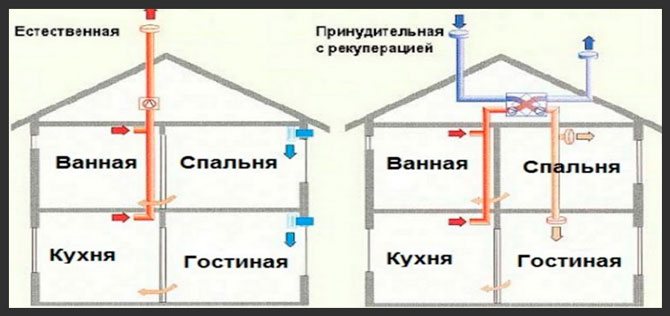
Ventilation schemes
Natural ventilation
For houses with an area of 80-100 m², a natural exhaust system is sufficient.
The top of the pipe is covered with a plastic or metal “umbrella”; a deflector is installed to enhance traction and improve the circulation of air masses. In order to prevent accidental release of air outside, a check valve is installed on the inside of the wall. The chimney is mounted directly above the heater, the air duct is installed behind the combustion chamber. A vertical pipe leads to the roof. Its top is located above the ridge at a height of 500 mm.
For boilers up to 30 kW, a vent measuring 150x150 mm is installed. A plastic pipe is installed in the ventilation duct, and a metal grille or mesh is placed outside.

A plastic grill protects the air vent from debris and rodents
In accordance with the standards, the effectiveness of a ventilation system is assessed by the ability to completely renew the air more than three times within an hour. It is impossible to calculate the exact characteristics of the supply exhaust from the boiler room. The intensity of air mass changes depends on many factors:
- wind direction and speed;
- atmospheric pressure;
- air temperature, etc.
The efficiency of ventilation also depends on the air duct; its diameter is determined by the power of the boiler. For a 24 kW device, a 120 mm pipe is enough; with increasing power, the cross-section increases. For a 100 kW boiler, a pipe with a cross-section of 230 mm will be required. The required cross-section is indicated in the technical data sheet of the device.
Calculation of boiler room ventilation
To calculate the ventilation system in a boiler room, the following parameters are important:
- room volume;
- air mass flow speed (min. 1 m/s);
- air exchange rate (depending on the height of the room).
Based on these indicators, using special reference tables, you can calculate the required diameter of the air duct.
The volume of air for ventilation of the boiler room is calculated using the following formula:
V = L * S* H * n, where
V is the volume of air that needs to be replaced in 1 hour,
L is the length of the room,
S - width,
H - height,
n is the air exchange rate.
For floor-standing gas boilers, the fan is selected taking into account a power reserve of 20-30% at maximum load.
The performance of the equipment and your safety depend on the proper ventilation of the boiler room, so you should not try to do the ventilation of the boiler room “with your own hands” for the sake of saving money. Trust the professionals and you will receive high-quality design, calculation and installation that will comply with the current regulatory and technological framework.
You can receive a free draft design and cost of ventilation for your boiler room
In private homes, air exchange needs to be organized not only in living rooms. Normal ventilation is also needed in non-residential premises, including the boiler room.
Ventilation of the room with the boiler must comply with established rules. If you do not organize sufficient air exchange here, the accumulated gas can cause an explosion or fire. Of course, such consequences rarely occur, but there is a possibility.
Let’s make a reservation right away: ventilation at such critical facilities as boiler rooms should be equipped by specialists . If you are not confident in your abilities, you should not start working on your own (or at least you should order a project with calculations, and work with your own hands only on it).
Is ventilation of a boiler room necessary in a private house, and why?
Yes, in boiler rooms of private houses it is necessary to organize ventilation that complies with SNiP standards.
In this room the ventilation system will perform the following functions:
- Provide oxygen flow for normal combustion. If there is not enough oxygen, any fuel will not burn completely. As a result, less heat is released, more fuel is spent to maintain the desired temperature in living quarters, boiler wear accelerates, and fumes accumulate inside the chimney.
- Remove carbon monoxide. Not all combustion products can be removed through the chimney; they can enter the room in small quantities. If ventilation does not provide sufficient air exchange, the concentration of carbon monoxide can rise to critical levels and penetrate into other rooms.
- Remove gas if there is a possible leak. Over time, the gas line to the boiler may become leaky and gas may accumulate in the room. If this is not noticed, an explosion or poisoning is possible.
That is, properly equipped furnace ventilation gives the following effect:
- the likelihood of a fire or explosion is reduced;
- the likelihood of natural or carbon monoxide poisoning is reduced;
- the boiler operates at full efficiency, without exceeding the load (which means it can last longer without repair);
- the temperature in the house is maintained without excessive load on the boiler and without exceeding fuel consumption.
Main rules and requirements for boiler room ventilation according to SNiP (+ video)
We found out whether a ventilation system is needed. Now about the main rules and requirements for its arrangement.
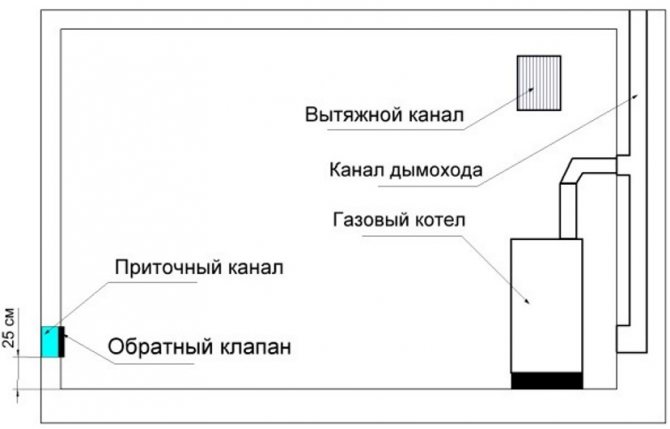
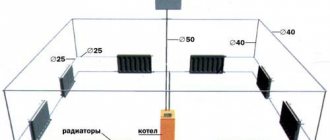
Simplified boiler room ventilation diagram
The boiler room can be installed in the following premises:
- A free-standing building or a block module.
- Extension.
- Room inside the house.
- Kitchen (permissible if the boiler power does not exceed 30 kW).
- Attic.
When building private houses, furnace rooms are usually installed in a separate room on the ground floor, next to a garage or other room.
Requirements and standards for the arrangement of boiler rooms in private houses are regulated in SNiP 42-02-2002.
Of the basic requirements:
- Requirements for the room, if the boiler is installed in a separate room: volume - from 7.5 m³, area - from 6 m², ceiling height - from 2.5 m.
- Boilers with a power of 30+ kW should be installed only in a separate room. Boilers with lower power can be installed in the kitchen.
- When installing the boiler in the kitchen, its area must be more than 15 m²
- The boiler room must have a separate door to the street.
- Cross-sectional area of the openings for inflow: from the street - from 8 cm² for every 1 kW of boiler power, from an adjacent room (for example, from the kitchen, through a wall) - from 30 cm² for every 1 kW of power.
Chimney outlet of a heating device in a private house
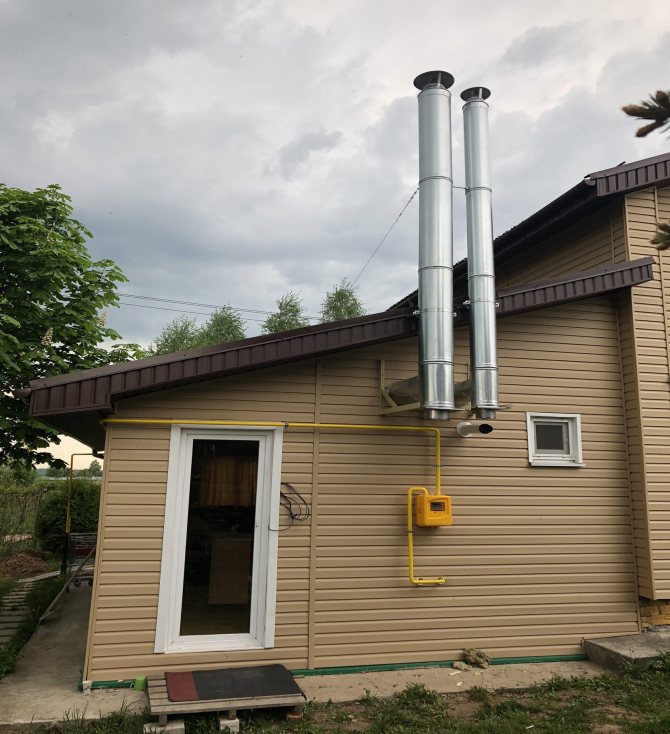

Chimneys and their installation require a specialized approach and compliance with certain requirements. The walls of the chimney are usually made resistant to temperature changes, corrosion and chemical compounds.
The hood for boilers in a private house must meet building regulations:
- SNiP 41-01-2003 “Ventilation and heating of residential premises.”
- SNiP 42-01-2002, 42-101-2003 “Recommendations and requirements for gas distribution complexes”
Thus, while maintaining these legislations, it is necessary to ensure that smoke removal corresponds to the required air exchange and air safety. And to do this you need to calculate the height and cross-section of the chimney and air duct. During installation, the following conditions must be observed:
- the pipe must be positioned strictly vertically;
- rise above the roof ridge no more than 0.5 m;
- the total height of the vein channel is no more than 5 m;
- The joints in the channel are insulated with heat-resistant sealant.
If the above requirements are met, you can install the ventilation pipe for the heating device yourself.
Creating natural ventilation for a boiler room (+ video)
The natural ventilation system (you can read more about its structure by following the link) operates without fans. The hood is organized through a pipe, which is installed as high as possible above the roof of the house.
This option is suitable if:
- the house is not located in a lowland;
- there are no taller buildings around the house or densely growing trees higher than the house (and there should be no barriers to the wind from any direction);
- the boiler is not very powerful and the boiler room is not very large (that is, not a large amount of air is needed).
If at least 1 point does not correspond to your situation, it is better not to use a natural ventilation system.
The design of such a ventilation system can be done as follows:
- We make air flow opposite the hood. It can be organized through a wall from the street (by installing a wall valve), through a window (micro-ventilation or a constantly open window), through a door (a gap under the door or a transfer grille in the door leaf). We choose the option depending on what your boiler is located opposite.
- Air is removed through an exhaust pipe. In the boiler room, its outlet should be located on the ceiling, and it should be discharged above the ridge of the roof (so that the wind can blow it from all sides, creating draft). In practice, exhaust ventilation ducts in the furnace of country houses and dachas are also made in the walls. In this case, you need to make the outlet of the exhaust pipe as high as possible, closer to the ceiling.
4.3.10. Before lighting and after stopping the boiler
the firebox and flue ducts, including recirculation ducts, must be ventilated with smoke exhausters, blower fans and recirculation smoke exhausters with the gas-air duct dampers open for at least 10 minutes with an air flow rate of at least 25% of the nominal one. Ventilation of forced-air boilers and hot water boilers in the absence of smoke exhausters should be carried out using blower fans and recirculation smoke exhausters. Before lighting boilers from an uncooled state with remaining excess pressure in the steam-water path, ventilation should begin no earlier than 15 minutes before igniting the burners. A mixture of coal or peat dust, as well as gaseous fuel and fuel oil with air is explosive under certain conditions. To remove such a mixture from the firebox and flues, the boiler is ventilated. There can be many reasons for the formation of such a mixture inside the boiler. Thus, gaseous fuel can penetrate into the combustion chamber through leaky fittings, as well as during an emergency shutdown of the boiler, when the gas fittings may close with some delay after the firebox goes out. Gas can also enter the furnace due to incorrect operations when lighting the boiler. A great danger is posed by deposits of unburned fuel oil on the walls and bottom of the combustion chamber, which form during kindling or when the boiler is stopped due to a malfunction of the fuel oil nozzles or low pressure and temperature of the fuel oil. The cause of an explosive mixture can also be deposits of unburned fuel on the heating surfaces and in the flue ducts of the boiler, which may occur when it is stopped. To prevent explosions due to the ignition of an explosive mixture, which can lead to damage to equipment and injury to personnel, the PTE provides for mandatory ventilation of the firebox and flues immediately after the torch goes out and before firing the boiler. In this case, the gates along the gas-air path must be installed in an open position, eliminating the formation of stagnant zones in the air ducts, burners, furnace and gas ducts. For boilers operating under vacuum, the degree of opening of the guide vanes in front of the smoke exhausters should not cause overload of the electric motors of the smoke exhausters. If the boiler is stopped by a protection that stops the blower fans, then after the protection is released they must be turned on to perform the required PTE ventilation. The danger of an explosion is especially high in boilers that burn gas as a backup or starting fuel, since in such installations, due to leaks in fittings or personnel errors, an explosive mixture can easily arise in the firebox or flue, and in dust and gas boilers it can also penetrate through dust ducts into the dust preparation path. To exclude the possibility of supplying gas to the burners without the necessary ventilation of the firebox, in accordance with [4] and [5], a lock must be turned on, prohibiting the ignition of the burners without ventilation of the firebox for at least 10 minutes. This blocking is introduced automatically when gas is supplied to the boiler or by existing input/output means in the circuits. Starting the boiler if such a lock is faulty is not allowed. The minimum duration of ventilation and air flow per boiler are determined from the condition of organizing multiple (more than 10) air exchanges in the volume of the furnace and flue ducts. The duration of ventilation before lighting a boiler that is in a hot or uncooled state (downtime less than 48 hours) is limited by the possibility of rapid cooling of heating surfaces, steam condensation in them and moisture getting on the hot surfaces of thick-walled boiler elements (steam pipeline collectors). Such overcooling of heating surfaces can cause not only additional losses of time and fuel for kindling, but also a reduction in the operating life of thick-walled boiler elements due to possible thermal “shocks”. Therefore, the duration of ventilation before lighting a hot boiler should not exceed 15 minutes.
Creation of forced ventilation of the boiler room
Forced ventilation is organized using fans. In private homes, you can get by with 1 fan that works as an exhaust hood. Supply ventilation can also be natural (air is supplied through existing openings, without a fan).
A forced scheme must be used if:
- You can’t/don’t want to install a common house exhaust air duct into the room;
- natural ventilation works poorly or does not work at all (the house is located in a lowland, there are taller houses or tall dense trees around);
- if the boiler is powerful and the room is large (in this case, natural ventilation is unlikely to cope).
The influx can be natural (as described in the previous paragraph), or supplied inside through a wall inlet or window fan.
The exhaust must be forced. Location options:
- Exit the pipe with the fan through the roof to the street, or through the wall to the street.
- Exiting the air duct from the boiler room into an existing ventilation shaft with a fan.
It is better to install an exhaust fan for continuous operation during the heating season.
Rules for arranging air supply and requirements for windows in boiler rooms (video with a conversation with a Gorgaz engineer)
Which system is better: natural or forced?
Even if natural ventilation works well, it is always better to use forced exhaust. Drilling a hole into the street and inserting a fan there will cost 5-10 thousand rubles.
A forced system is much safer than a fanless system for the following reasons:
- the operation of natural ventilation depends on the weather: the stronger the wind, the better the hood works, and vice versa (if there is no wind, air exchange may stop altogether);
- the frequency of air exchange is unknown, is not regulated and is not maintained at the required level;
- natural ventilation will not provide much air exchange (relevant if the boiler room is large, and if a powerful boiler is used - for a large country house).
The fan will do a better job of removing air if an emergency occurs (gas leakage). If the ventilation is natural, then if a gas leaks, it may not be completely removed and may accumulate in the room, which can lead to poisoning or an explosion.
Timing for inspection of chimneys and ventilation ducts
Since the life and health of people depends on the effective operation of the smoke removal and ventilation system, fire safety rules determine the timing of monitoring of these two important systems. It is recommended to carry out the examination three times a year:
- the first 7–10 days before turning on the boiler equipment;
- the second - in the middle of the heating season;
- the third – 7–10 days after the boilers are turned off.
Essentially, it is necessary to check how dirty the chimney pipes and ventilation ducts are. If the soot deposits are significant, then you will have to call a specialized service that will clean the two systems and issue an inspection report for the chimneys and ventilation ducts.
Monitoring specialists pay attention to different positions. They are mainly interested in traction and the quality of the device. If the customer is interested in other items, for example, the percentage of carbon monoxide in the air, then this is not a problem for specialized companies. This indicator must be reflected in the chimney certificate.
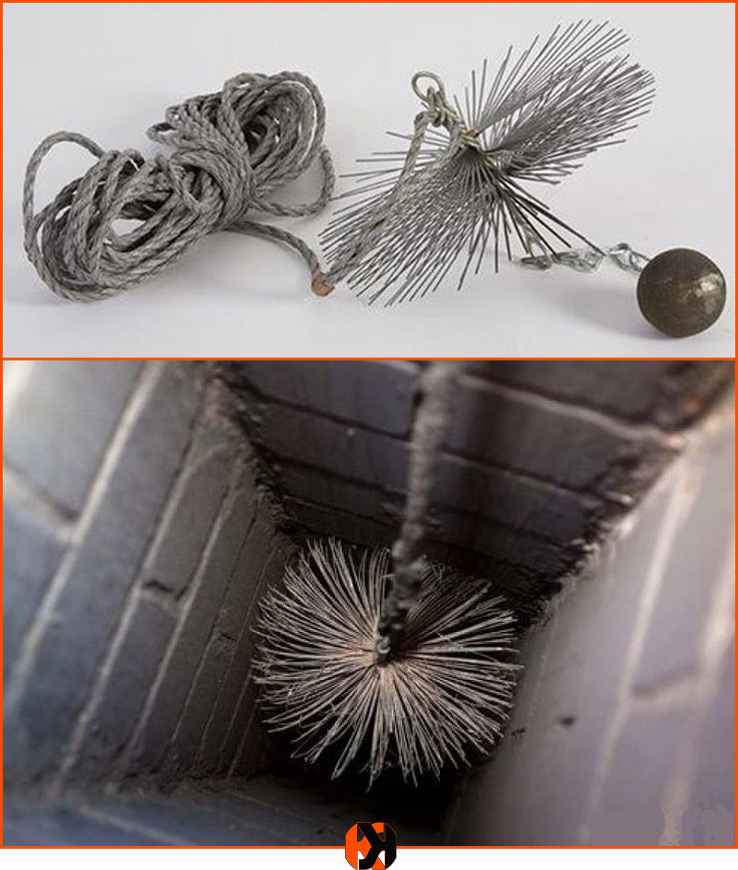
The classic way to inspect a chimney is with a weight suspended on a rope. With its help, rubble is found. Cracks, chips and other defects are detected using a flashlight and a mirror. It is imperative to do a check. Based on the results of its implementation, experts make a conclusion on the quality of the channels. And if in doubt, recommendations are given on how and by what means repairs can be carried out.

Video
Automation of boiler room ventilation
To increase the safety of residents, the ventilation of the boiler room can be automated.
- Choose a fan with a control panel or wall-mounted speed controller, a performance reserve (the larger the reserve, the better) and several speeds. The remote control must be secured at the entrance to the boiler room. If the concentration of carbon or natural monoxide suddenly increases in the room, you can turn on the maximum exhaust speed remotely. Fans with remote control are on average 10-20% more expensive than “regular” ones.
- Install a gas analyzer in the boiler room - a device that measures the gas concentration and gives a signal when it is exceeded. The average cost of a simple household model is 3000-6000 rubles.
- Choose boilers with safety features: a flame control sensor and a draft control sensor. They will automatically turn off the boiler if the burners go out or if the draft in the chimney is too low. In the middle and high price categories, these sensors are installed on almost all models.
To ensure safety, it is better to follow all the rules.