What is home attic insulation?
What is the work involved in insulating an attic space? The technology is quite simple: insulating material can be laid on the floor, in the space between the floor beams and, additionally, between the roof rafters. If we talk about insulating a room located at the bottom of the attic, then it is enough to insulate the floor. If you want to store something in the attic or use it as an attic from time to time, the roof is also insulated.
What materials can be laid in the attic for insulation? In this article we will look at the different options and their pros and cons. Let us immediately note that there are several types of insulation:
- Slab.
- Rolled.
- Sprayable.
- Bulk.

Each of the insulation options is good in its own way. We will select the optimal insulation materials that are suitable for this purpose. You must understand that the choice is yours. Our site will offer you only a list of proven materials for attic insulation, which have won many positive reviews. So, we will consider the following options:
- classic – mineral wool;
- indispensable polystyrene foam;
- expensive, but very high quality polyurethane foam;
- simple and cheap bulk materials such as expanded clay, sawdust or slag.
What are they? What is the technology for laying each insulation and its advantages? Let's find out further.
Insulation with mineral wool
Perhaps only the grandmother in the village has not heard of mineral wool, and that is not a fact. This is the most common insulation for home insulation, which is used both for independent insulation and by professional teams. I would especially like to note basalt wool, which does not burn at all and has excellent characteristics. Why do people love mineral wool so much? Let's look at its positive aspects.
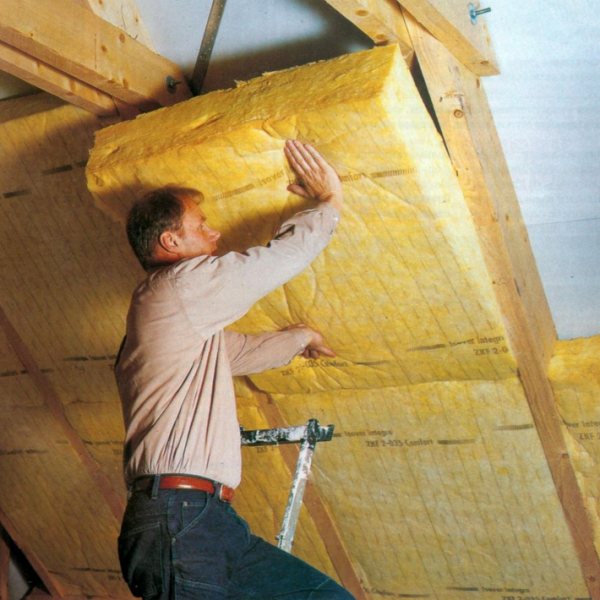


Why is this attic insulation so good? Mineral wool is sold both in slabs and in rolls. It holds its shape well, and you can easily insulate the attic floor, as well as the roof. It is enough to lay mineral wool in the space between the beams and cover everything with hydro- and vapor barrier. This is very important, since the main disadvantage of the material is that it is afraid of moisture. It will destroy the insulation, which over time will lose its original properties.
You can see the technology for laying mineral wool in the video.
Classification of materials
The owner, who is thinking for the first time about how to insulate the attic ceiling, is faced with another difficult question. How to insulate the ceiling in a private house? It is not enough to lay the material; it is also important to choose it correctly. After all, there are a huge number of materials on the market today, and it is not always clear whether they are suitable for the area in which the house is located; In some areas the temperature is lower, in some – higher. Depending on the type and design of the roof, three types of materials can be used for insulation: “light”, bulk, or roll, or “heavy” slabs. The first type is suitable if the roof is covered with wooden beams, then the material from which the house is built will “breathe” and allow air to pass through to the ceilings; the last one - if the floor is made of concrete, then it won’t matter what you put in. There are different types of rolled materials, but most of them are quite environmentally friendly and can be used in a home made from natural materials (pro
Review of the best insulation for ceilings
The choice of installation method also determines the list of possible heat insulator options. When insulating from the attic side, the range of materials is much larger - from natural compounds to technologically advanced modern solutions. Installation from inside the room imposes a number of restrictions.
Regardless of the placement method, the insulation for the ceiling system must have low thermal conductivity. The coefficient determines the ability of the insulator to transfer energy from heated elements to cold ones. The lower the thermal conductivity, the better the material retains heat.

An important selection parameter is moisture resistance. The ability of the material to maintain physical characteristics in a humid environment is especially important when insulating the attic side, when the roofing covering is sufficiently worn out
Additional requirements include:
- durability;
- environmental friendliness and safety for humans;
- low flammability - it is better to use non-flammable insulators, compositions with minimal smoke generation;
- resistance to rodents - important for materials placed in the attic.
It is important to take into account the vapor permeability of the insulation. But there are nuances here. When thermally insulating a concrete slab from the attic side, it is necessary to use a material that allows steam to pass through. For installation from inside the room, on the contrary, use vapor-tight insulation.
Type #1 – mineral wool insulation
The popular heat insulator maintains its leadership position due to its affordability, ease of installation and good thermal efficiency.

Mineral wool has good vapor permeability, so the insulation is perfect for attic work on brick and concrete floors
For installation under a cold roof, mineral wool with a synthetic binder, basalt insulation and glass wool are used. The latter option provides maximum thermal efficiency. The thermal conductivity of glass wool is 0.044 W/(m°C).
However, it should be used with caution - the particles cause irritation to the skin and mucous membranes. Glass wool is not acceptable for indoor use. Basalt insulation does not have these disadvantages. Additional advantages of the material: fire safety and plasticity.
Variety of materials for insulation
Those owners of private houses who have decided to insulate the attic of their home are faced with the question of how and with what means this can be done. At the moment, construction stores offer a huge range of different insulation materials that are suitable for such work. But not everyone can figure it out and make a choice, because each material is suitable for a certain temperature range.
In appearance they can be bulk, rolled or slab. If the ceiling in the attic is made of wooden beams, then bulk beams are perfect, through which the roof can “breathe.” But their use is not very convenient due to the installation option. Roll insulation materials are suitable for environmentally friendly buildings, since most of them are environmentally friendly. Slab, heavy options are laid if the floors are made of concrete, which itself is very dense in structure.

Property No. 3. Compressive strength
Modern materials are produced both elastic and loose, and in the form of rigid and semi-rigid mats for those systems where the insulation experiences special deformation loads.
Now let's explain in more detail. Because Insulation boards need to be inserted against each other so that they stand on their own (and only very little of them can be supported by crossed threads), then their compressive strength should be from 5 to 80 kPa. This is at 10% deformation. After all, how does the process of installing any insulation on the roof take place? We lightly squeeze the slab with our hands, insert it - and the insulation holds on itself. And it is important that at the same time it is really compressed a little springily, and not just deformed. This is why builders are irritated by those materials on which you accidentally drop a hammer and the dent will never be straightened out.
Typically, the denser the insulation and the more binder it contains, the greater its compressive strength. And there is a certain limit for each material, beyond which the bonds between the fibers are destroyed, and the product itself is no longer able to return to its original shape.
Thus, Isover mineral mats today are distinguished by the greatest elasticity, thanks to which they fit tightly to all three planes: the wall, the rafters and to each other. The installation of such slabs completely eliminates the presence of so-called “cold bridges”, in other words, the presence of air pockets through which heat can penetrate:

But ordinary fiberglass is bad because it is not able to hold its shape, rolls up and even settles under its own weight. For insulating pitched roofs, this is one of the cheapest, but at the same time, the worst options.
And finally, in terms of elasticity, basalt mats are the most pleasing. Here is the most typical situation with insulating the roof of a house: after repairs everything is fine, in the summer everything is fine, in the fall too, but after the first heating of the house the roof suddenly began to blow out. How can this be? It’s very easy if the rafters in the roofs are wooden. Wood is a living material, and therefore in normal times the rafters have the same structure and volume, but after the first kindling they dry out a little and gaps appear between them and the laid insulation. And these are real bridges of cold. Basalt slabs are valuable because when the rafters dry out, they easily expand in width and cover any cracks:

Comparison of the main characteristics of insulation materials
Insulation Density kg/cub.m Thermal conductivity W/(m*K) Flammability
| Minvata | 35 — 40 | 0,035 — 0,039 | NG |
| Glass wool | 15 — 20 | 0,035 — 0,042 | NG |
| Polyurethane foam | 60 — 80 | 0,023 — 0,032 | NG |
| Expanded clay | 300 — 500 | 0,09 — 0,1 | NG |
| Ecowool | 38 — 41 | 0,038 — 0,041 | G2 |
| Styrofoam | 10 — 37 | 0,033 — 0,041 | G1 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 26 — 32 | 0,028 — 0,031 | G4 |
| Sawdust | 0,10 — 0,25 | 0,07 — 0,09 | G3 |
Calculation of the amount of insulation for floors
Before you go to the building materials store, you need to calculate how much insulation is needed on the ceiling to create an effective layer of thermal insulation.
To do this, use the general formula:
V= Lхg, where:
V – volume of insulation in cubic meters;
L – perimeter of the working surface in meters;
g – material thickness in meters.
According to the EnUV standard, adopted in 2009, the heat transfer coefficient of the thermal insulation coating must be no less than 0.24 W/sq.m.xK. This value can be provided by a layer of insulation 13–40 centimeters thick, depending on the material and its thermal conductivity.
Scope of application of insulation in rolls ↑
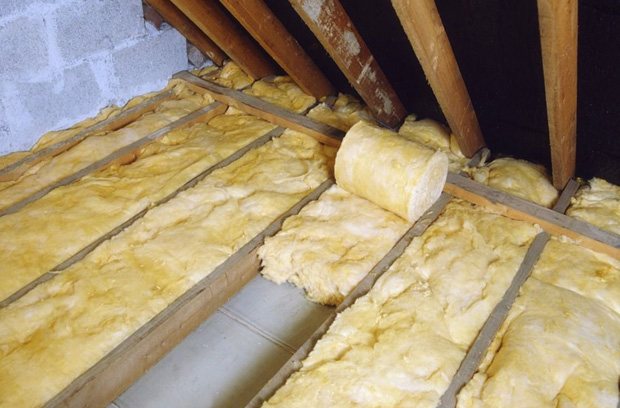

It is successfully used for roofs and basements, floors and ceilings, pipes and more. Installing thermal insulation from this material is a fairly simple process. Moreover, the work can be done independently, without the involvement of additional labor. Therefore, this type of thermal insulation has gained great popularity in private construction, in particular, bathhouses, outbuildings, etc.
Attention!
Insulation in rolls is not recommended for thermal insulation of vertical surfaces subject to high loads.
General installation principles
The insulation of the rafter system and the floor beams are similar. We assume that the rafter system is assembled and covered with roofing material, and the attic floor beams are lined with a subfloor underneath.
Step-by-step installation:
- Vapor barrier. First, a vapor barrier is attached to the base. Keep in mind that the canvas is placed so that steam escapes from the room towards the street, and moisture is blocked on the reverse side.
- Insulation. Next, insulation is laid or filled between the rafters or beams.
- 2nd layer of vapor barrier. Another layer of vapor barrier is mounted on top of the insulation; it is positioned in the same way as the previous one.
- Overlap on beams. Next, if a ceiling is installed along the beams, then the floor is laid, and when insulating the attic roof, the interior finishing is attached.
Insulation of pitched roofs
You can insulate a roof with a frame made of rafter systems in one of four ways: by laying insulation between the rafters, on the rafters, under the rafters, or in a combined way. In most cases, thermal insulation is carried out in the simplest way - by laying thermal insulation material between the rafters.
Roof insulation between rafters
The insulation with this method of insulation must be continuous, gaps are not allowed. This also applies to areas adjacent to walls, pipes and windows that are built into the roof plane. This approach is explained by the fact that any place where thermal insulation is interrupted leads to the formation of a cold bridge. Also, in insufficiently insulated places, condensation may occur due to temperature differences, which will gradually destroy the entire structure. It must be remembered that the attic always brings greater heat loss than other floors, since its entire surface is in contact with the street. Since heat escapes not only through the slopes, but also through the gables, it is necessary to insulate the entire roof contour.
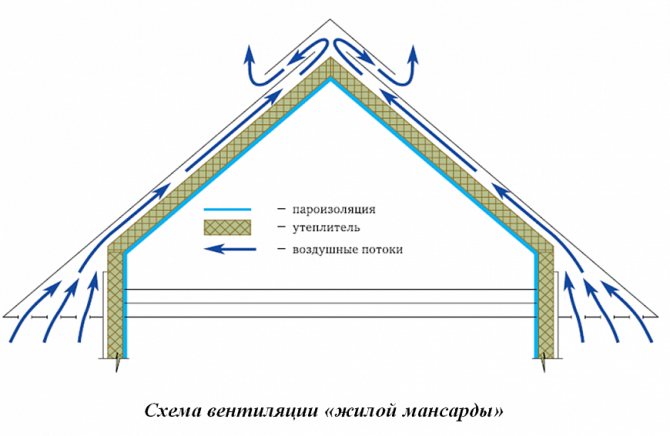
For example, an uninsulated gable wall connecting to the roof structure can cause a problem. When insulating walls, Mauerlats are usually not insulated. When thermal insulation of a roof slope is carried out, it is also quite often brought only to the level of the Mauerlat. Thanks to this, a powerful cold bridge appears, along which heat leaves the room. To avoid such a negative phenomenon, you need to wrap the insulation of the attic slopes onto the Mauerlat to the place where the insulation of the outer wall reaches.
Choose by cost
The cost of insulation changes very quickly. Therefore, as an example, we present a small plate with the cost of some popular insulation materials.
| Mineral wool | Amount in a package | Thickness, mm | Cost in rubles | Cost in dollars |
| TechnoNIKOL Greenguard | 4 | 100 | 380 rubles | 6,5 |
| Paroc Extra | 8 | 100 | 1000 rubles | 17,2 |
| Isover Classic cooker | 10 | 100 | 525 rubles | 9 |
| Izovol St-50 | 4 | 100 | 400 rubles | 6,9 |
| Styrofoam | Amount in a package | Thickness, mm | Cost in rubles | Cost in dollars |
| Knauf Therm | 10 | 100 | 2200 rubles | 38 |
| TechnoNIKOL Carbon Eco | 4 | 100 | 2600 rubles | 45 |
| Penoplex Comfort | 18 | 20 | 1200 rubles | 20,6 |
Blowing polyurethane foam will cost 200-300 rubles per square meter (labor and material). Ecowool will cost 3000-4000 rubles per cubic meter. The cheapest insulation is probably sawdust, 300-500 rubles per cubic meter. Using the above figures, you can calculate the approximate cost per square meter of insulation.
Installation process
Having decided on the material for thermal insulation, the question arises: how to properly insulate the attic floor? If we talk about mineral wool, what density should it have and what layer of insulation will be best?
Selecting the layer and density of mineral wool
It is better to do insulation with mineral wool in two layers
In short, the larger the layer of mineral wool, the better. However, you need to remember that mineral wool has its own coefficient of thermal conductivity. The lower this coefficient, the higher the thermal insulation properties, and, therefore, it is possible to lay a smaller layer of wool or have greater insulation efficiency. Mineral wool with a thickness of 15-20 centimeters is often used, however, to ensure increased thermal insulation, a 30-centimeter layer of insulation can be used. It is also worth noting that with equal insulation thickness, two layers of mineral wool are always better than one.
You also need to pay attention to the density of mineral wool, because it varies: from 30 kg/m3 to 220 kg/m3. Thermal insulation properties practically do not depend on density. Denser insulation is used for facades and floors under screed. Mineral wool with a density of 35 kg/m3 is also suitable for attic flooring, since the insulation will be located on a horizontal, non-loaded surface.
Vapor barrier
Since mineral wool tends to absorb moisture, you need to start insulation by laying a vapor barrier material.
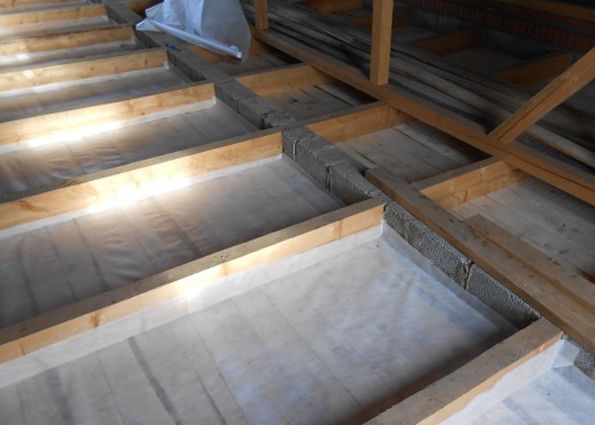

Vapor barrier - the first layer of insulation
Important! It is best to lay a layer of vapor barrier under the wooden beams, because otherwise they will be very susceptible to rotting. However, if it is impossible to install a vapor barrier film under the beams, they need to be impregnated with solutions that protect against rot and mold.
The best option is to lay a continuous layer of vapor barrier, but due to the size of the attic this is not always possible, so all joints must be taped with special tape to ensure tightness. The edges of the vapor barrier must be raised above the level of the future insulation and taped with the same tape.
Thermal insulation
When working with heat-insulating materials, you need to wear special clothing
Next comes the installation of insulation. It must be laid so as to completely fill the entire space between the wooden beams. If we are talking about mineral wool, then it does not need to be pressed or squeezed. It should completely cover the space between the beams, leaving no cracks or gaps. It would also be a good idea to cover the floor beams themselves with heat-insulating material, because they can serve as a kind of cold bridges.
When laying mineral wool, it is very important to protect yourself, and especially your respiratory tract, from insulation fibers. Therefore, you need to use a respirator, as well as gloves, goggles and long sleeves.
Waterproofing
We complete the insulation of the attic floor with waterproofing and subfloor installation
Due to the property of mineral wool to absorb moisture, waterproofing must be laid over the layer of mineral wool. This is also necessary if a concrete screed will be poured over the insulation.
If the attic is constantly used, a subfloor can be made on top of such a heat-insulating “pie”. Its role can be a concrete screed or OSB slabs. If the attic is practically not used, then you can simply lay boards on top of the existing beams. Then, if necessary, go up to the attic, moving around it will not create difficulties.
As you can see, insulating the attic floor is an accessible task, even for those who have never done it. You need to decide on the material for thermal insulation, although most often it is mineral wool. When installing a heat-insulating “pie”, it is important to remember the need for vapor barrier and waterproofing. This will allow you to achieve high results in insulating the attic floor.
Do-it-yourself insulation of a flat roof
External insulation of a flat roof includes the installation of a vapor barrier layer, laying thermal insulation, waterproofing, and then a roll covering. The final layer is the laying of bulk material.
Before starting work, you need to clean the roof surface from debris, dust, and level it. Then install a vapor barrier as described above. After this, glue the insulation boards using cold mastic or special glue. The slabs are laid with a semi-overlapping seam, which ensures uniformity of the coating. It is permissible to lay several layers of slabs staggered and glue them with tape. This method of installation will prevent the occurrence of cold bridges.
Next, waterproofing is laid. The fire method of gluing a waterproofing carpet is often used: a cement-sand screed is laid on the slabs in a layer of at least 3 cm. After laying it, you need to wait until the concrete gains the necessary strength, then clean the surface from sagging and dirt. The waterproofing layer is glued using short-term exposure to fire. The gluing method is described in great detail on the packaging of the material. As a result of exposure to fire, the insulation does not lose its properties. After this, a rolled roof covering is laid and expanded clay or other similar material is poured.