What is biofuel
The energy hidden in plant matter is practically inexhaustible, because its source is our sun. Plants know how to use the energy of the sun, processing it for their growth. In turn, animals and birds receive energy by eating biomass, while producing waste products. By definition, biofuel is a fuel obtained from raw materials of plant or animal origin, as well as waste products and various industries associated with the processing of biomass.
Modern technologies make it possible to obtain biofuel in three forms: solid, liquid and gaseous. We encounter solid fuel in life most often in the form of pellets and various briquettes obtained by pressing. Liquid fuel - biodiesel - is still rare in the countries of the post-Soviet space, this is due to the presence of a large amount of fossil hydrocarbons at an affordable price. While obtaining liquid biofuel from vegetable oil is quite expensive and technologically difficult.
The production of combustible biogas is much simpler and cheaper, as a result of which it is gaining increasing popularity. Owners of livestock and poultry farms are increasingly thinking about purchasing a biogas plant, because they have at their disposal a huge amount of litter and manure, which is perfectly suitable for this purpose.
It makes no sense to list here all types of plant raw materials for processing into fuel, their sources and production technology. We are only interested in those types of biofuels that can be successfully produced at home without investing large amounts of money. Here they are:
- biogas extracted from waste products of domestic animals and poultry;
- briquettes from various plant wastes;
- charcoal.

Of course, if you try really hard, you can make pellets, eco-diesel, and even eco-gasoline yourself. People do such things as a hobby, spending years of their lives and often considerable money on it. Such complex technologies are inaccessible to a wide range of users, and therefore we will not consider them.
Production of fuel granules (pellets)
Pellets, fuel granules, as well as fuel briquettes, are made from sawdust, other wood waste, sunflower husks, and straw. The plant mass is placed in bio-installations, that is, containers where grinding occurs. It turns out to be practically flour from plant waste. This mass enters the dryer, where the liquid is evaporated. It is this process that prepares the mass for high-quality pressing.
In a granulator press, when vegetable flour is compressed, the temperature of the mass increases. Plant particles contain lignin, which is similar in composition to resin. It melts and glues dried plant particles together to produce granules of the size specified when setting up the equipment.
For granulation, special molds are used, the so-called ring stamps. They rotate using rotary rollers, and during rotation, the plant mass enters the round holes of the mold, that is, into the dies. The layout of the device resembles a regular meat grinder with a knife that cuts off cylinders of granules from the outside.
This is a simple description of the technology that ends with refrigeration and packaging. The volume of one package is at least 2 kg, but each plant, as a rule, sells granules in bulk, which is convenient for buyers - industrial enterprises.
Benefits of biofuels
Everyone knows that any invention is a well-forgotten old one. So, biofuel is far from a discovery of our time, since they knew how to produce it back in Ancient China. At that time, plant tops, grass, various wastes and manure were used as starting materials. There are many advantages of such raw materials, so it is worth familiarizing yourself with the main ones.
Low cost
In the modern market, biofuel is equal in cost to gasoline. But it is cleaner and produces minimal harmful emissions. When using such fuel, it is possible to significantly reduce the maintenance costs of those units where it is used.
Renewable sources
Fermentation of manure in the device
As you know, gasoline is obtained from oil, which is a non-renewable resource. And, despite the fact that oil reserves will last for more than one decade or even a century, it will eventually run out sooner or later. In turn, biofuels are made from raw materials such as:
- manure;
- waste of cultivated and wild plants;
- the plants themselves in the form of soybeans, rapeseed, corn or cane;
- wood and so on.
All of them tend to be constantly renewed.
Reducing emissions
During combustion, fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, peat) produce significant amounts of carbon dioxide, which scientists call greenhouse gas. The use of oil and coal increases the temperature of the atmosphere, which is one of the causes of so-called global warming. To significantly reduce the greenhouse effect, biofuels should be used.
Studies have shown that biofuel significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions by up to 65%.
As you know from a school botany course, when growing plants, carbon monoxide is partially absorbed from the atmosphere and oxygen is released into the atmosphere. This makes the use of biofuels even more attractive.
19.04.2017

A soybean biodiesel bus operated by the Nebraska Soybean Program. Biodiesel is obtained from soybeans. US Department of Energy
Energy and transport are the foundations of the industrial world. The fuel for them now mainly (share >2/3) are products obtained from oil and gas. Although there is public agreement on the need to switch to less environmentally harmful and renewable sources, there are no fundamental changes in the structure of the fuel sector. In the end, everything is decided by the market. And as long as it is cheaper to “heat” with oil and gas, they will be used. Also in favor of the latter are proven and widespread, and therefore inexpensive, technologies for extraction, processing, transportation, combustion to produce heat and perform useful work.
However, oil and gas will inevitably be exhausted, and alternatives will have to be turned to. One of these is biofuels. Behind this term is a broad class of fuels, from firewood to fats and alcohols obtained from plant materials and animal products. And not just firewood and alcohol, but their convenient modern derivatives: fuel briquettes, pellets (fuel granules), liquid biofuels, gasoline-replacing mixtures based on bioethanol or real biogasoline from light hydrocarbons, biodiesel, etc.
What fuel raw material is destined to become the main one after oil? It will probably be of plant origin. Solar or nuclear energy requires capacious, safe means of accumulation and transportation, which have not yet been created. At the same time, fuel products of plant origin are already available in convenient and familiar formats, for which storage and delivery means have been developed. Firewood and fuel pellets, combustible oils, ethers and alcohols are common fuels, similar in physical parameters to products made from coal, oil and gas. Biofuels also include products of animal origin. However, the industry for the production of such biofuels most likely has no prospects. Enzymes of fungi and bacteria or enzymes obtained in biosynthesis processes cope better and more efficiently with the processing of plant raw materials into fuel than animals.
Ethanol as a component of fuel mixtures (E85, E30, E20 - ethanol content in %), information site American Coalition for Ethanol
In favor of biofuels and its conceptual similarity to fossil hydrocarbons. For nuclear energy, for example, previously non-existent technologies still need to be developed. It is unknown how they will affect the environment and the biosphere as a whole. And biofuel is the same product of photosynthesis as coal, oil and gas. Moreover, its cycle is short, determined by the time of plant growth. Therefore, such fuel is significantly less harmful (than fossil fuels) to the environment. The production and combustion of biofuels does not release additional amounts of carbon (more importantly, carbon dioxide), as is the case with fossil fuels. Plants first accumulate carbon, converting carbon dioxide into energy carbohydrates, and then release it during combustion. New carbon does not enter the biosphere.
The only reason why biofuel has not yet replaced gas and oil products is economic infeasibility. Moreover, as already noted, it is not simply due to the relatively low (so far) price of fossil fuel production. But also because the technology for extracting and refining oil and gas was simply lucky. Their development coincided with the industrial boom. If history had turned out a little differently, maybe biofuel or something else would have been used now instead of oil and gas.
The industry adapts quite quickly to changes in the composition of available raw materials. And what was unprofitable yesterday against the backdrop of cheap coal or oil becomes no alternative tomorrow. A striking example of economic adaptation to new realities is the establishment of a rather expensive process for the production of liquid fuel from coal by Germany during the Second World War. Or, which is closer to the topic of biofuel, the abandonment of blubber, a product of whaling that is shameful for humanity, in favor of gas and electricity.

Algenol fuel ethanol is synthesized by cyanobacteria
Technologies for the production and use of biofuels are not new. And even quite well worked out. But biofuels have two important competitors - oil, which in the recent past could be pumped cheaply, and agricultural production, focused on food for a growing population and consumption level. In the first decade of this century, especially in the second half, due to rising oil prices and awareness of the importance of environmental issues, biofuels received strong support from regulatory government and international institutions. Enterprises that undertook the development of technologies and the production of biofuels received targeted loans and tax breaks. Biofuel production grew markedly between 2000 and 2013. Biofuel already makes up a significant share in the overall balance - more than 1/10. And the increase in the production of the most popular fuel ethanol (both bioethanol and obtained from petroleum products) over the first decade of the 21st century is approximately fivefold!
Now, however, the situation is not so rosy. Declining oil prices over the past three years have led to the curtailment of programs and the closure of many biofuel production facilities. However, after the wave of interest in biofuels, another problem became obvious. Its production competes with the production of equally important food products. The passion for biofuels has also contributed to the current global political instability - indirectly through a reduction in the volume of growing grain crops in favor of technical ones. At the same time, in favor of biofuels, traditional agricultural structures were destroyed, and soils were depleted as a result of the use of unsustainable crop rotation cycles.
Assortment of fuels for vehicles on the AFDC information site about alternative energy, two positions - biofuels, biodiesel and ethanol (AFDC/Alternative Fuels Data Center)
Current conditions do not imply that traditional fuels will soon be replaced by biofuels. However, already in some countries the production of liquid biofuels to replace gasoline (or for use together with gasoline) is comparable to the production or import of gasoline from oil. A striking example is Brazil, where gasoline with ethanol from cheap sugar cane is more profitable than purchased petroleum gasoline. The problem of competition with food agricultural production is also being overcome. One of its promising solutions is to use as raw materials not field industrial crops, but wood or only food crop waste, secondary raw materials containing complex hydrocarbons (industrial and household waste).
According to current concepts, liquid biofuels are divided into generations, according to the processes and raw materials used to produce them. The first generation includes fuels made from conventional or modified fats (biodiesel), ethanol and methanol. The raw materials for them are industrial and food crops containing oils or easily accessible sugars. On the one hand, fuel from such raw materials is obtained as a result of fairly simple processing and is therefore profitable. On the other hand, it is the production of such fuel that is destructive for the traditional agricultural industry and indirectly affects the environment. Therefore, great hopes are placed on fuels made from second generation raw materials (agricultural and industrial waste, wood and wood processing waste) and third generation (algae).
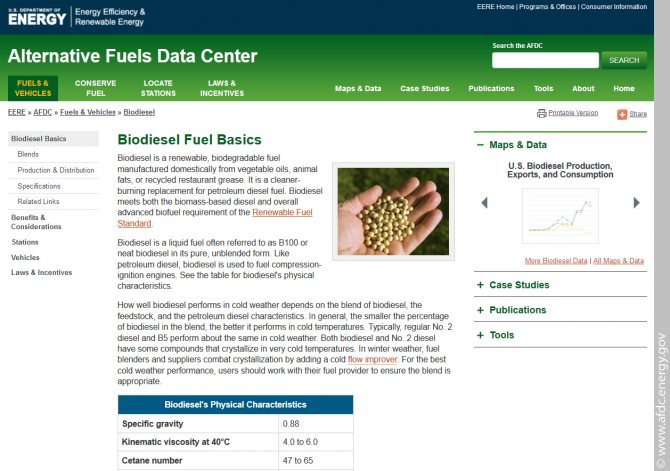
Biodiesel page on the AFDC alternative energy information site, two items - biofuels, biodiesel and ethanol (AFDC/Alternative Fuels Data Center)
With the technologies and solutions currently available, the most promising ones for implementation are processes for producing fuel from second-generation raw materials. These raw materials are available in large quantities. Its cultivation does not compete with traditional agriculture and even allows for the disposal of crop waste. There are effective technologies for its processing: pyrolysis, processes of organic chemistry and biotechnology, which are also used to produce fuel from first-generation raw materials.
It is clear that in terms of the degree of concentration, the raw materials of the second generation are inferior to the raw materials of the first (therefore, in the overall balance, the share of fuels from such raw materials is now small - percentage). But the negative impact on the agricultural sector may be an unacceptable price to pay for cheap fuel from first-generation feedstock. As for the third generation raw material, algae, it is likely that it has a promising future, but there are no technologies ready for mass introduction into production yet. Therefore, the expected near future is the replacement of liquid fuels with biofuels from wood, wood processing waste and crop production.
Biofuel is an accessible and inexhaustible resource
Biofuels are substances of biological or animal origin used to produce thermal energy.
Both renewable natural resources and waste generated by the wood processing, pulp and paper industries and human consumption are suitable for the production of biofuels.
Depending on the purpose and purpose, biofuels have different physical states: solid, liquid and gaseous.
Solid
Solid biofuel today holds the title as the most popular type of alternative fuel.
The raw material for the production of solid biofuels is biomass formed from plant residues, stalks and seeds of corn, rapeseed, straw, sawdust, wood chips, pine needles, leaves, as well as twigs, branches, bark, cuttings of boards, defective parts of wood, manure, peat etc. Biomass is pressed into fuel granules (pellets) or briquetted.
Energy forests, which include fast-growing trees and shrubby plant groups, make it possible to maintain a balance of raw materials, providing the necessary amount of material for the production of biofuels.

Fast-growing trees are planted to later be used as raw materials for the production of biofuels
Liquid
Liquid biofuels contain alcohols, ethers, and oils. The raw material is the same biomass, consisting of plant residues, stalks and seeds of corn, rapeseed, sugar beets and cane, wheat, as well as cake, marc, molasses, etc.
The formation of fuel occurs as a result of alcoholic fermentation of biological mass with a high content of starch and/or sugar, as well as hydrolysis. The solution resulting from fermentation, after purification and distillation, is converted into bioethanol, biobutanol, biomethanol, and biodiesel.
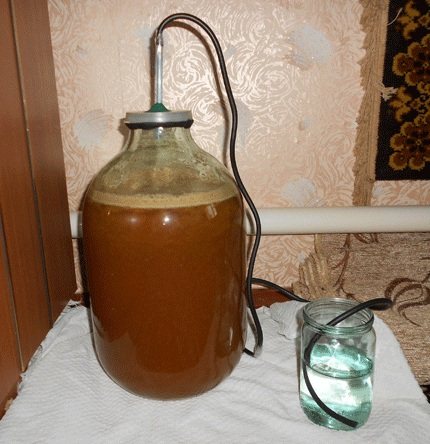

The simplest device for anaerobic fermentation
Gaseous
Gaseous biofuel or biogas is formed as a result of anaerobic fermentation (overheating) of organic substances. To produce biogas, methane-forming, hydrolysis or acid-forming bacteria are used.

Location of environmentally friendly production
Along with the generally accepted one, an alternative classification of biofuel by generation is used:
- The first generation includes biofuels produced from biological raw materials through fermentation;
- second generation biofuel is obtained from non-hazardous production and consumption waste;
- The third generation includes the production of biofuel from vegetable fats contained in algae.
Bioethanol production
Industrial technology for the production of bioethanol involves the processing of plant raw materials, which is very similar to the production of conventional alcohol. The first stage of the process is the preparation of raw materials, their grinding. The main condition for guaranteeing the successful production of bioethanol is a high content of starches in the raw materials. This is why cereal crops are best suited for bioethanol. After grinding, the raw material undergoes fermentation, that is, starches are broken down by interaction with yeast. The result is alcohol, fusel oils and stillage go to waste. The latter is used in the manufacture of feed.
The quality of production of bioethanol and similar biobutanol is gradually improving, as scientists are developing new types of bacteria that improve and reduce the cost of the production process. The advantage of such biofuel is ease of storage; no special equipment is required for transportation, since bioethanol does not mix with water.
DIY methods
There are many options for producing biofuel at home. We will consider these options.
Biofuel from manure
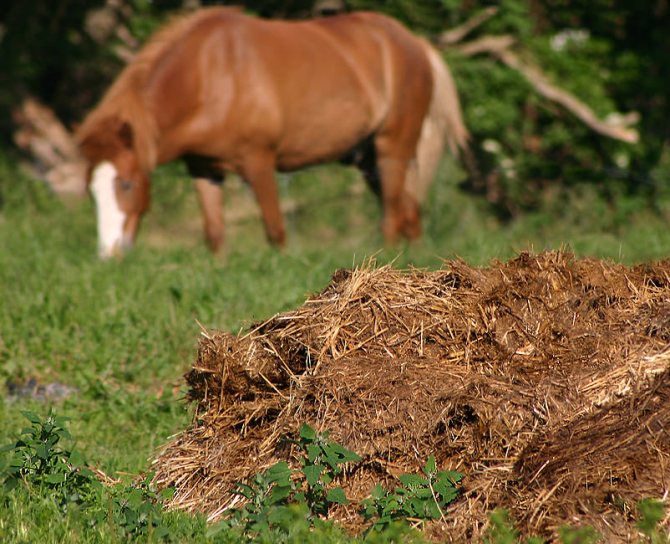

Biofuels from manure are produced by fermenting organic waste. The mixture is placed in a special sealed bunker for a long time. As a result of the evaporation of the liquid, gas is released, which can be used for heating residential premises or for cooking and liquid fertilizer, which is the basis of organic farming.
Products grown using such fertilizers are environmentally friendly and their sales value increases compared to products grown using pesticides and other chemical fertilizers.
Biogas production
The second product that we obtain as a result of manure fermentation is gas.
To obtain gas from this raw material, the following is used:
- manure;
- bird droppings;
- toilet drains;
- food waste;
- plant matter;
All raw materials must be crushed, otherwise the pipes intended for the removal of waste raw materials may become clogged.
You can also obtain gas at home. To do this, you need to purchase a gas-tight container. This container must be sealed, since air should not come into contact with the resulting gas.
Then you need to place the raw material (manure) inside this container, heat it a little and wait 5 days. Then, collect the resulting gas in a container and use it at your discretion. You can assemble a device for producing biogas yourself, or you can purchase it from a company that specializes in selling this equipment.
Schemes of homemade biogas plants
The simplest scheme of a biogas plant is a sealed container - a bioreactor, into which the prepared slurry is poured. Accordingly, there is a hatch for loading manure and a hatch for unloading processed raw materials.
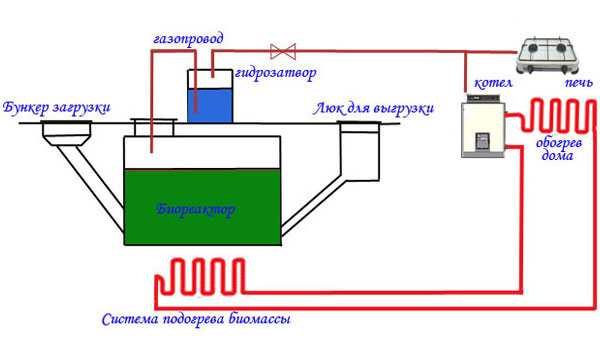
The simplest scheme of a biogas plant without any bells and whistles
The container is not completely filled with the substrate: 10-15% of the volume should remain free to collect gas. A gas outlet pipe is built into the tank lid. Since the resulting gas contains a fairly large amount of water vapor, it will not burn in this form. Therefore, it is necessary to pass it through a water seal to dry it. In this simple device, most of the water vapor will condense, and the gas will burn well. Then it is advisable to clean the gas from non-flammable hydrogen sulfide and only then can it be supplied to a gas holder - a container for collecting gas. And from there it can be distributed to consumers: fed to a boiler or gas oven.
Large industrial installations are placed on the surface. And this, in principle, is understandable - the volume of land work is too large. But on small farms the bunker bowl is buried in the ground. This, firstly, allows you to reduce the cost of maintaining the required temperature, and secondly, in a private backyard there are already enough all kinds of devices.
The container can be taken ready-made, or made from brick, concrete, etc. in a dug pit. But in this case, you will have to take care of the tightness and impermeability of air: the process is anaerobic - without air access, therefore it is necessary to create a layer impenetrable to oxygen. The structure turns out to be multi-layered and the production of such a bunker is a long and expensive process. Therefore, it is cheaper and easier to bury a ready-made container. Previously, these were necessarily metal barrels, often made of stainless steel. Today, with the advent of PVC containers on the market, you can use them. They are chemically neutral, have low thermal conductivity, a long service life, and are several times cheaper than stainless steel.

The bioreactor does not have to be buried. This is a very good option, and it is convenient to maintain. But in winter you will have to take additional insulation measures. And the gas is diverted into special gas tank bags
But the biogas plant described above will have low productivity. To activate the processing process, active mixing of the mass located in the hopper is necessary. Otherwise, a crust forms on the surface or in the thickness of the substrate, which slows down the decomposition process, and less gas is produced at the outlet. Mixing is carried out in any available way. For example, as demonstrated in the video. In this case, any drive can be made.
There is another way to mix the layers, but not mechanically - barbitation: the generated gas is fed under pressure into the lower part of the container with manure. Rising upward, gas bubbles will break the crust. Since the same biogas is supplied, there will be no changes in processing conditions. Also, this gas cannot be considered a consumption - it will again end up in the gas tank.
As mentioned above, good performance requires elevated temperatures. In order not to spend too much money on maintaining this temperature, you need to take care of insulation. What type of heat insulator to choose, of course, is up to you, but today the most optimal one is polystyrene foam. It is not afraid of water, is not affected by fungi and rodents, has a long service life and excellent thermal insulation performance.

Any heating technology is suitable to increase the temperature of the substrate. It is important to achieve the required temperature. The efficiency of the installation depends on this
The shape of the bioreactor can be different, but the most common is cylindrical. It is not ideal from the point of view of the complexity of mixing the substrate, but it is used more often because people have accumulated a lot of experience in building such containers. And if such a cylinder is divided by a partition, then they can be used as two separate tanks in which the process is shifted in time. In this case, a heating element can be built into the partition, thus solving the problem of maintaining temperature in two chambers at once.
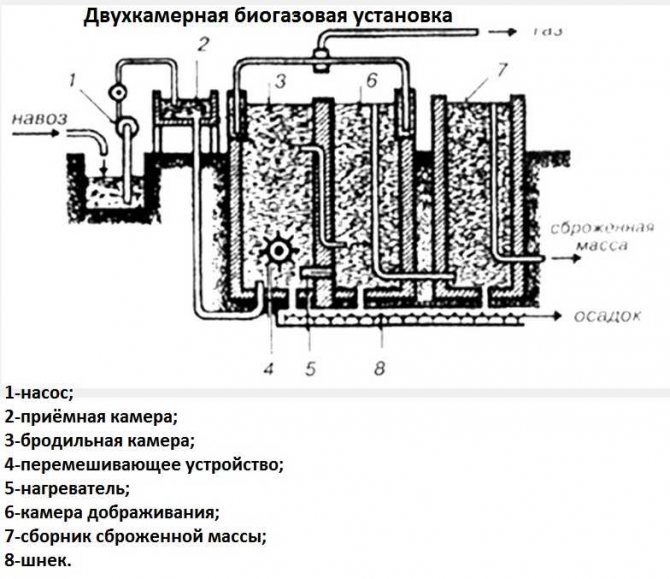
If an ordinary cylinder is divided by a vertical partition, you can get two chambers for processing
In the simplest version, homemade biogas plants are a rectangular pit, the walls of which are made of concrete, and for tightness they are treated with a layer of fiberglass and polyester resin. This container is equipped with a lid. It is extremely inconvenient to use: heating, mixing and removal of the fermented mass is difficult to implement, and it is impossible to achieve complete processing and high efficiency.
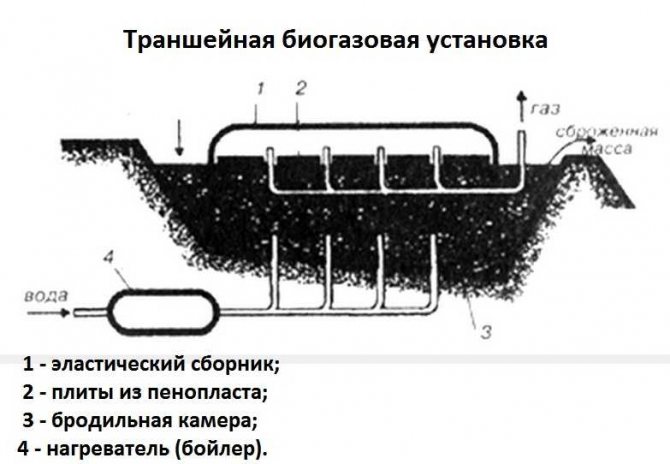
Do-it-yourself biogas plant: drawings of a trench-type installation
The situation is a little better with trench biogas manure processing plants. They have beveled edges, making it easier to load fresh manure. If you make the bottom at a slope, then the fermented mass will shift to one side by gravity and it will be easier to select it. In such installations, it is necessary to provide thermal insulation not only for the walls, but also for the lid. It is not difficult to implement such a biogas plant with your own hands. But complete processing and the maximum amount of gas cannot be achieved in it. Even with heating.
The basic technical issues have been dealt with, and you now know several ways to build a plant for producing biogas from manure. There are still technological nuances.
Coal for creating biogas
To create biofuel, charcoal can also be useful, the same coal that we cannot do without in nature when frying vegetables and barbecue. You can buy it at the store, or you can make it yourself.
Coal can be made at home in 2 ways:
- in a barrel;
- in a hole;
Let's consider each method separately. And after that you will be able to make coal yourself.
To make charcoal in a barrel, you will need, strictly speaking, a 200 liter barrel. At the bottom of the barrel we make a fitting for pumping oxygen. Then we build a fire in a barrel, gradually adding logs.
When the barrel is half filled with firewood, we begin to pump in oxygen. To do this, you can use a vacuum cleaner. After this, the amount of smoke will decrease and the fire will burn better. When the logs burn out a little, you need to close the barrel with a lid and cover the existing cracks with wet clay or earth. We wait until the barrel has cooled completely and the charcoal is ready.
To make coal in a pit, we need to dig a hole, the diameter of which will be 0.8 m with sloping walls, and light a fire in it. But before you light a fire, take a sufficient amount of logs, dried wood, and tree branches from which you will get coal.
Place the wood in the fire tightly and gradually in layers, one after another. Wait until the firewood is completely burned out (this will take about 3 hours), then cover the logs with moss or dry leaves, sprinkle with earth and tamp everything down well. After 2 days the coal will be ready.
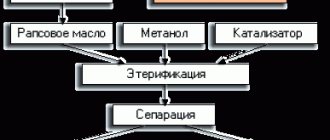
Rapeseed biofuel
Oil and meal are obtained from rapeseed seeds received at the oil mill. Next, this oil enters a special installation, where, as a result of various chemical reactions, methyl ether - biodiesel - is obtained from rapeseed oil.
Before use, it must be filtered. This type of diesel fuel has better flammability compared to conventional diesel fuel.
Burning charcoal
When we say charcoal, we immediately imagine outdoor recreation, barbecue, barbecue. Pleasant smoke, flickering lights in the barbecue! However, the use of charcoal is not limited to just cooking meat; it is needed in blacksmithing, foundry work, medicine, for filtering drinking water and even for making gunpowder and for household needs.
Those who have had to deal with charcoal know that buying it costs a lot of money, and they often think about how they can get it themselves at home or in the field, with their own hands - with their very skillful hands. Indeed, it is possible! Moreover, there are two most common methods - the production of this biofuel in a pit or in a metal barrel.
Method of making coal in a pit
Usually, coal burning is carried out in the forest, which is more convenient than at home, but due to widespread fires in forests, you need to think carefully about the place and time of the work.
A place is selected next to a large supply of dry wood or a fallen tree, and such as not to damage the surrounding vegetation. In order to get two bags of coal, it is enough to dig a hole 50 cm deep and 75-80 cm in diameter with slightly sloping walls. This is also easy to do yourself.
At the compacted bottom of the pit, a small fire is made by hand from dry birch bark and small branches, and when the fire burns well, small-sized prepared firewood, up to about 30 cm in length, is placed on it. If you choose branches with a diameter of about 7 cm, then you can completely cope with the cutting on your own, without an assistant. The firewood is stacked tightly and gradually as each layer is burned. Well-burnt firewood can be straightened with a long stick.
For complete burning in such conditions, 3 hours is enough. Then the coals are covered with moss, dry leaves or grass and covered with earth, which is compacted tightly. It will take another two days for the coal to cool sufficiently, after which the solid biofuel will be ready. After this time, a layer of earth is removed from the pit, the coal is raked out, sifted and packed into bags.
If a new pile of firewood is not made, then the hole is filled up in such a way that the fertile layer of soil is on the surface, and everything is also covered with leaves. Of course, such coal production requires some material and physical costs, but it is much cheaper than the cost of purchasing it, and there is also a moral aspect - everything was achieved through one’s own efforts and made with one’s own hands.
A method for producing coal in a barrel on your own territory
In order to obtain solid biofuel at home, namely charcoal, a thick-walled metal barrel with a capacity of 200 liters is used. At the bottom you need to make a fitting for forced air injection with a household vacuum cleaner.
Just like in a pit, a small fire is built at the bottom of the barrel, and then small logs are gradually added. To stack the firewood more tightly, the barrel can be shaken periodically. After supplying air, the firewood will smoke less and be well engulfed in flames. The air supply from below should begin only after the barrel is filled with firewood approximately halfway. You also need to periodically adjust the coals with a pole and do not forget about safety precautions when working in “hot” conditions.
To continue the process of burning coal without air access, you should cover the barrel with a lid and cover all the cracks with a solution of earth and water. If there is no “original” lid, then it should be made from some piece of iron.
It should be taken into account that with this method of working in home, often unsuitable conditions, a certain amount of waste and ash is formed, but within reasonable limits. After the barrel has completely cooled, it is turned over, and the finished coal is sifted and packaged. This is a production that you can master with your own hands.
You may not get high-quality coal the first time, but patience and work will grind everything! The main thing is not to quarrel with your neighbors because of heavy smoke.
What can affect the production of biofuels?
What matters to us - those who plan to make biofuel at home - is, first and foremost, the environment. That is, the higher the temperature, the more intense all chemical reactions will occur, and the more actively gas will be released. It is for this reason that the first equipment producing biofuel at home was created and used in areas with a warm climate. But this does not mean that if the weather is cold, then such fuel cannot be made - after all, the structure can be insulated, heated with hot water, which, in fact, is what many are doing today.
Also, the production can be affected by raw materials, which must decompose quickly, contain a lot of liquid, and there should not be any cleaning agents or other preparations that can affect fermentation.
How biofuel is produced
Many people are interested in how to create biofuel with their own hands and what materials can be used. Let's figure it out together, as there may be several options.
Biofuel from manure
Manure is rightfully considered the most popular type of fuel, which is produced using artisanal methods. So if you have any living creatures, then it would be advisable to purchase the appropriate equipment for the production of biogas. Such a purchase can pay for itself within two to three years.
The maximum amount of heat is extracted from horse manure. At the same time, such manure is sometimes difficult to obtain, so some other type of manure may be suitable - cow, goat, pork, and so on.
In most cases, mixtures made from manure are used to heat a house:
- Manure and leaves in a ratio of 7 to 3.
- Manure and straw.
- Manure and sawdust – 7 to 3.
- Manure and fire from flax - 7 to 3.
- Cows and horses – 1 to 1.
- Manure and household waste – 4 to 6.
As already mentioned, the technology of such production is based on fermentation; it itself is carried out in special sealed containers at a relatively high temperature. At this time, unnecessary water is removed and biogas is released, which, in turn, can be used not only for heating, but also for cooking.
Important! If you use biofuel in a boiler, you will need to adjust the burner. For what? So that the combustion efficiency remains the same, despite the fact that there is not as much methane in biofuel as in the gas we are used to.
Application of charcoal
You can also produce biofuel at home from charcoal, which is needed not only outdoors when grilling barbecue, as it turns out. Those who have bought this kind of coal at least once know very well that it is expensive. But this is not a death sentence, since you can reduce waste by making coal yourself. All you need is some knowledge and “straight” hands. In general, there are two ways to do this.
Making charcoal in a barrel
To prepare charcoal, you will need a two-hundred-liter metal barrel. In its lower part you make a fitting in order to subsequently force the injection of oxygen, for example, using a vacuum cleaner.
Build a small fire in the barrel, gradually adding logs. To make the coal more dense, shake it from time to time. As soon as the barrel is half filled with firewood, you begin to pump in oxygen. After this, there will be less smoke, and the fire will burn better. Soon the barrel is closed with a lid, all cracks are covered with wet earth or clay mortar.
Video instructions. Subscribe to our youtube channel Ekonet.ru https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCXd71u0w04qcwk32c8kY2BA/videos
This method of producing coal is characterized by the fact that during its use a certain amount of ash may appear. So when the barrel has completely cooled down, pour everything out, sift out the ash, and put the finished coal in bags.