21.05.2018
Heat pumps are becoming increasingly popular in the heating equipment market. The main reason for the growing demand is compelling: while gas, electricity, coal, diesel and firewood are steadily rising in price, the energy of land, water and air remains free. According to scientists, the continuation of this trend is inevitable: heat pumps are the future, which, by the way, has already become the present in Sweden, Norway, Switzerland, and Germany.
What is a heat pump: operating principle
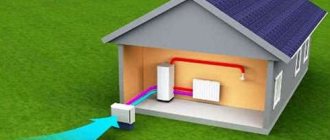
There is always a huge amount of low-grade heat in water, soil and air. It is technologically possible to extract, concentrate and use it for heating and hot water supply of a wide variety of objects. It is with the help of a heat pump that the low temperature of the energy carrier is transformed into a high one, after which hot water flows to the radiators and mixers. Moreover, some units not only heat rooms in cold weather, serve the hot water supply system, but also act as an air conditioner to cool rooms in hot weather.
According to the laws of thermodynamics, a refrigerator and a heat pump operate on a similar principle, only with opposite results. If the first one produces frost and releases excess heat outside, the second one works in the reverse order. For heating to function using a heat pump, 3 circuits arranged in series are used: external, internal and central, equipped in the unit itself.
- Moving along the external circuit, the coolant passes through a low-temperature source and heats up by several degrees. It reaches the evaporator, gives off some of the energy and returns back after cooling.
- The refrigerant in the central circuit evaporator, which has a low boiling point, turns into gas. It enters the compressor, is compressed and, as a result, gets very hot. Passing the condenser, it gives off heat and goes into a second cycle in a liquid state.
- The coolant of the inner ring is heated in the condenser and sent to the heating system. Having given off energy, it returns to the heat exchanger in a cooled state.
A heat pump for heating a house consists of a compressor, evaporator, condenser and throttle valve: the elements are insulated to avoid noise. The working ring is filled primarily with antifreeze. Compressors are usually used rotary and scroll (domestic), as well as screw (industrial).
Types of heat pumps
Depending on the energy source, units are divided into geothermal (ground, water), air and using secondary (industrial) heat. Their names include soil, water and air in different combinations.
"Ground-water". Energy is used that is extracted from the ground below the freezing mark. In some places, it is enough to dig trenches (pit) to a depth of 1.2 m and lay pipes with brine in a horizontal position. Such a device for the external circuit is not always rational, since significant areas are taken away from agricultural use: 1 kW of energy requires up to 50 m2 of land. An alternative option is to drill several wells to a depth of up to 150 m and then use deep probes.
"Water-water." There are no fundamental structural differences between heat pumps of this type and the previous one. Horizontal laying of pipes assembled in a ring-shaped system is carried out in lakes, rivers, ponds: immersion to a frost-free depth is carried out using a weight. An important point: the surface water source must be close to the heating object. Otherwise, high efficiency will not be achieved. Wells and boreholes are used to exploit groundwater.
"Air-water". A universal heat pump for heating that performs 3 functions as needed: heating, air conditioning and providing the hot water system with hot water. As a rule, it is installed on the roof, so it secondary (by a fan) extracts the heat leaving the house. Unlike the above models, it does not require expensive installation: no excavation work is required for its installation. The weak point is the unstable efficiency: as the air temperature drops to –25 °C, the power decreases proportionally. Most practical in places with mild climates.
"Air-to-air." In this case, unlike the previous version, both circuits are atmospheric. The schematic diagram of the pump is still the same, but the design has its own characteristics. The unit consists of 2 blocks: external and internal. The first can be mounted on the wall, the second - under the ceiling. Most models stop producing heat when the air temperature outside the window is below –25 °C. Therefore, in places with severe winters, the heat pump must be duplicated. It is controlled by a remote control and looks no different from an air conditioner.
"Water-air". Heating and air conditioning are carried out by air flows: in contrast to the internal circuit, the external circuit is water. Pumps are produced in different designs: they can be divided into standard (vertical and horizontal), console and split systems. In their manufacture, a fan unit and a freon circuit are used. The design contains a scroll or rotary compressor, a coaxial heat exchanger, and a reversing valve. Sound insulation of elements is provided.
With us you will always find the right heat pump for heating your home/cottage or commercial/industrial facility. The Geopumps product range includes the most popular models Mammoth, Chofu, Ecoforest.
Closed systems are the most reliable
You can assemble a heat pump in any configuration with your own hands. Closed-loop systems are practically eternal; during their operation there is no sediment on the heat exchanger, as well as the risk of freezing or rupture of any of the elements. In this case, you can also use wells, but pipes with coolant are already immersed in them.

This also includes the horizontal contour. When laying it, the pipes are dug in at least 1.5 m, and the distance between them to eliminate mutual influence is about 1 m. To obtain 10 kW of thermal energy, for the climatic conditions of the Moscow region, 5-6 acres of land are needed. All of them will be used for laying a circuit for the extraction of geothermal energy, with the exception of the area under the house. This is cheap if the cottage is just under construction and the site is vacant: not all owners of already inhabited houses will agree to such manipulations.

If there is no required area for laying the contours, you will have to drill wells - horizontal or inclined. Simple mathematics works - 600 linear meters of horizontally laid cable can be replaced by the same number of meters of well depth, that is, drill 6 of them per 100 m (or 12 of them per 50 m).
Current prices for heat pumps 2020
| Type of heat pump | Heating power | Heated area | Price |
| “water-water” (“ground-water”) | from 7.8 to 90 kW | from 50 to 500 | from 253,000 to 25,129,000 rub. |
| "air-water" | from 8.0 to 72 kW | from 50 to 350 m2 | from 212 to 1,763,000 rub. |
| "water-air" | from 2.4 to 23.5 kW | — | from 147,000 to 579,000 rub. |
| "air-to-air" | from 2.25 to 18 kW | — | from 21,000 to 253,000 rub. |
Heating with a heat pump: advantages and disadvantages
You can heat a private or apartment building, industrial or commercial facility either centrally or individually - using gas, fuel oil, electricity, coal, diesel. Against the background of these methods, each of which has its own strengths and weaknesses, heating using a heat pump looks preferable in many respects. The main advantage is minimal operating costs due to high efficiency: with the consumption of 1 kW of electricity, 3 to 6 kW of thermal equivalent is produced.
- Many stations are universal in use. They can heat and cool rooms, as well as heat water for the hot water system. Thanks to this, profitability, albeit indirectly, becomes even higher.
- Modern heat pumps do not require maintenance because they operate autonomously. For automatic operation, it is enough to connect the unit to the electrical network: single- or three-phase according to the operating instructions.
- Heat pump units are absolutely safe. They, unlike many boilers, do not burn, do not explode, do not smoke, and do not emit toxic substances. In addition, the performance of the structure is not affected by unexpected stops: cycle continuity in this case is not technologically necessary.
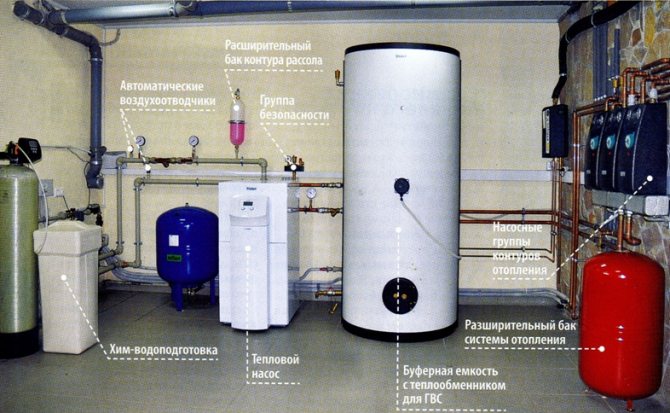

- The unit does not require a special room. Reasons: it does not pose a danger, thanks to total insulation it is almost silent, it does not use fuel, which requires storage space. It can be installed in a special room only for technological reasons.
- The heat pump is completely environmentally friendly. Moreover, it uses only renewable resources of the planet: in times of global warming, rising sea levels and other natural disasters, this factor is important.
- Heat pumps are reliable and durable. Various manufacturers claim that their product is designed for 20, 50 and even 100 years of continuous service. True, the compressor needs to be replaced every 2 decades.
- High comfort of use. Many systems perform 3 of the above functions at once. In addition, they are easy to control, and very rarely, since they are autonomous.
Return on investment
Liquefied gas and diesel fuel cannot compete with heat pumps either in terms of operating costs or operating comfort. The use of solid fuel for heating is difficult to automate and requires a lot of labor. Electricity is a comfortable but expensive form of energy. To connect an electric boiler you need a separate powerful line. Until now, in domestic conditions, natural gas has remained the most popular and convenient type of fuel. But it has a number of disadvantages:
- Registration of permits.
- Coordination of the project with regulatory authorities and neighbors.
- Some insertion and connection operations can only be performed by authorized organizations.
- Periodic verification of the meter.
- Limited network distribution and remote connection points.
- High costs for laying the supply line.
- Gas-using equipment is a source of potential threat and requires regulated control.
The only significant drawback of a heat pump is the high capital investment at the stage of purchasing equipment and installation. The price of a standard heating system based on a heat pump with a geothermal heat exchanger consists of the cost of the work of drillers and specific equipment with installation. The kit includes:
- Heat pump;
- probe set;
- propylene glycol;
- indirect heating boiler for hot water;
- set of pumping equipment and automation.

The work is carried out by qualified personnel with professional tools. The slightly higher initial costs are balanced by serious advantages:
- The heat pump system is very economical, which allows you to recoup the additional costs in just a few seasons.
- There are ample opportunities to implement flexible automated control with a minimum of maintenance.
- Comfort of use.
- Well suited for installation in residential areas thanks to its aesthetic and modern design.
- Cooling of premises based on the same set of equipment.
- When working for cooling, in addition to the active operating mode, it is possible to use the lower temperature of natural water and soil to implement a passive mode without unnecessary energy consumption.
- The low power of the equipment does not require laying a large-section power cable.
- No need for permits.
- Possibility of using existing wiring of heating devices.
How to choose a heat pump for heating a cottage, home, or industrial facility
There are many ways to heat a dacha, private home, hotel, industrial facility. Before you settle on one of them, you need to take many factors into account, such as evaluating options with different types of fuel. The most attractive energy carrier is gas: compared to other consumables, it is the cheapest. If a gas pipeline is not laid near the house, then the optimal prospect becomes inaccessible. Electric heating is very expensive. Liquid and solid fuel boilers are somewhat popular, but they have their drawbacks: you need to set up a special room, constantly maintain the equipment, regularly purchase a new batch of coal, firewood, briquettes, diesel fuel, and diesel.
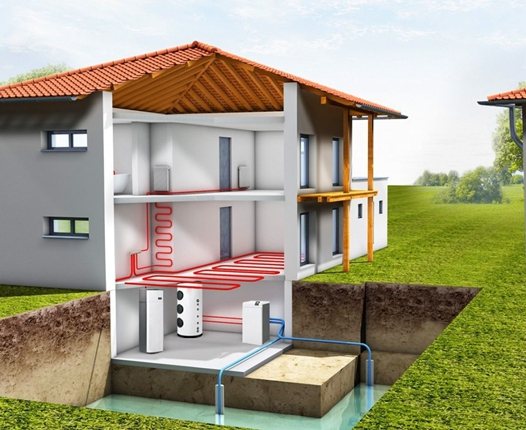

There is another option that is rapidly gaining popularity in highly developed countries - heating with a heat pump. At first the price is scary, but you need to understand that over time the investment will pay off and have an economic effect. You need to select a model based on the following considerations. If there is a sea, river, lake near a house or industrial building, it is advisable to use a water-to-water pump. When there is a spacious lawn near your home on which no crops are grown, a suitable solution is a “soil-water” unit with horizontal pipe laying.
If the garden area is small, wells are recommended: for deep drilling, official permission is required.
Heat pumps with air intake are more suitable for warm regions: in the north it is better to install a bivalent system. It is also possible to exploit the potential of wastewater and heat emissions from factories. The conclusion is obvious: heating your home using a heat pump means a profitable investment. Do you want to buy a heat pump for heating at affordable prices? Contact us - the Geopumps trading company. Return to list
Heat extraction from the ground
The most effective, but also the most expensive schemes involve the extraction of heat from the ground, the temperature of which does not change throughout the year already at a depth of several meters, which makes the installation almost independent of the weather. According to 2006 data, in Sweden there are half a million installations, in Finland 50,000, in Norway 70,000 were installed per year. When using soil energy as a source of heat, the pipeline in which antifreeze circulates is buried in the ground 30-50 cm below the freezing level of the soil in a given region.
In practice - by 0.7 - 1.2 meters. The minimum distance recommended by manufacturers between collector pipes is 1.5 meters, minimum -
1.2. No drilling is required, but more extensive excavation is required over a larger area and the pipeline is more susceptible to damage. The efficiency is the same as when extracting heat from a well. No special soil preparation is required. But it is advisable to use an area with wet soil; if it is dry, the contour must be made longer. The approximate value of thermal power per 1 m of pipeline: in clay - 50-60 W, in sand - 30-40 W for temperate latitudes, in the north the values are lower. Thus, to install a heat pump with a capacity of 10 kW, an earthen circuit 350-450 m long is required, for the installation of which a plot of land with an area of about 400 m2 (20x20 m) will be required. If calculated correctly, the contour has little effect on green spaces.