Why is it important to do thermal engineering calculations?
The number of radiator sections directly affects the room temperature during the cold season. Low temperatures are often caused by incorrect thermal calculations. In such situations, the thermal power of the installed radiators is significantly lower than the heat losses of the room. The following are important criteria for the volume of heat loss:
- how many walls are in direct contact with the street: a private house or a corner apartment;
- window size;
- purpose of the room: bedroom, bathroom, kitchen;
- Are the walls additionally insulated from the outside?
- wall material: brick, marl, etc.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the material from which the battery is made, the declared thermal power, and the temperature of the coolant.
All these factors influence the final number of radiator sections.
Experimental data.
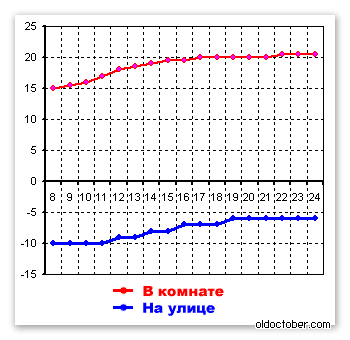
First day of the experiment.
All graphs show temperature changes from 8:00 am to 12:00 pm.
The coolant temperature is 42ºС.
The graph shows that the system worked more efficiently while the temperature difference between the air and the battery was large. When the difference decreased, the system stabilized.
The air temperature in the center of the room at a height of 65 cm from the floor rose from 15ºС to 20ºС in 9 hours.
Subsequently, the temperature rose another 0.5ºС.
The fan power consumption was 35.2 Watts.
When, during the experiment, I left my room into the corridor, I immediately felt the temperature difference, because by that time I had already taken off my warm clothes.
I went to the barn and brought out another fan. This fan was not equipped with a power switch, so I connected it through a homemade triac regulator, the design of which is described in detail here.
Well, life has become better, life has become more fun!
Second day of the experiment.
In the morning I again measured the coolant temperature, as well as the air temperature in the room. All values remained unchanged, including the outside temperature.
No changes in temperature were noticed during the day.
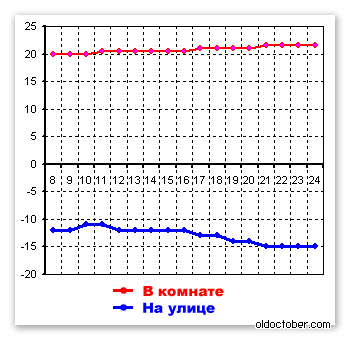
Third day of the experiment.
The coolant temperature increased by one degree and amounted to 43ºС.
The temperature outside dropped and reached -15ºС.
At the same time, the temperature in the room increased by another 0.5ºС and reached 21.5ºС.
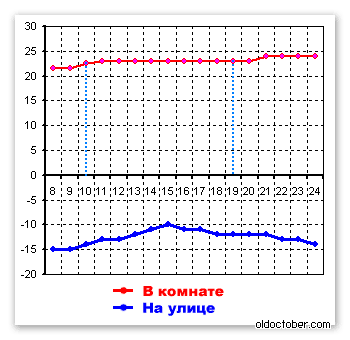
Fourth day of the experiment.
The coolant temperature is still 43ºС.
The temperature outside in the morning is -15ºС.
The temperature in the room in the morning was 21.5ºС.
Since no significant changes in temperature were noted over the past 24 hours, I decided to increase the air flow and installed a second fan at 10.00.
After 10-15 minutes, the air temperature immediately increased by one degree, and then by another half a degree and reached 23ºС.
Let's go for a walk, I thought, and at 19.00 I turned on both fans at full power. The temperature increased by another degree in two hours and reached 24ºС.
Lack of radiators
Too few sections in the installed radiator leads to insufficient heating of the room. In addition to the fact that you will simply freeze, there is a threat of dampness and mold, which entails not only colds, but also other diseases. You will have to additionally heat the apartment using electric or other heaters, which entails, at a minimum, extra financial costs.

What radiators to put in an apartment with central heating
It is still difficult to give an unambiguous answer to this question, because everything depends on the specific situation, for example, living conditions and the price range acceptable to the apartment owners. However, experts most often advise the following. For centralized heating today, it is still worth choosing bimetallic structures that combine strength, aesthetic appearance and good heat transfer. Cast iron heating elements are also a good option, but they require proper care and are more expensive.
YouTube responded with an error: The request cannot be completed because you have exceeded your quota.
- Related Posts
- Is it possible to install aluminum radiators on central heating?
- Which radiators are best suited for autonomous heating?
- Which central heating batteries to choose?
- What is the pressure in central heating radiators?
- How to install central heating on a balcony?
- What types of regulators are there for central heating radiators?
Excessive number of sections
The opposite situations also occur, when the thermal power of radiators significantly exceeds the heat losses of the room. It seems that there is nothing wrong with this. However, high indoor temperatures in winter lead to a decrease in the healthy amount of humidity, negatively affect the mucous membranes, force windows and vents to open, which threatens drafts and, as a result, colds.

Heating radiator sizes
The standard height of the most popular models of heating devices with the center distance along the connections is 500 millimeters. These are the batteries that in most cases could be seen about two decades ago in city apartments.
Cast iron radiators
. A typical representative of these devices is model MS-140-500-0.9.
The specifications for it include the following overall dimensions of cast iron heating radiators:
- length of one section – 93 millimeters;
- depth – 140 millimeters;
- height – 588 millimeters.
Calculating the dimensions of a radiator from several sections is not difficult. When the battery consists of 7-10 sections, add 1 centimeter, taking into account the thickness of the paronite gaskets. If the heating battery is to be installed in a niche, it is necessary to take into account the length of the flushing tap, since cast iron radiators with side connections always require flushing. One section provides a heat flow of 160 watts at a temperature difference between the hot coolant and the air in the room of 70 degrees. The maximum working pressure is 9 atmospheres.
Aluminum radiators
. For aluminum heating devices on the market today, with the same center-to-center spacing of the connections, there is a significant variation in parameters (for more details: “Dimensions of aluminum heating radiators, section volume, preliminary calculations”).
Typical sizes of aluminum heating radiators are:
- the length of one section is 80 millimeters;
- depth 80-100 millimeters;
- height – 575-585 millimeters.
The heat transfer of one section directly depends on the area of its fins and depth. Typically it ranges from 180 to 200 watts. The operating pressure for most models of aluminum batteries is 16 atmospheres. Heating devices are tested with one and a half times higher pressure - this is 24 kgf/cm².
Aluminum radiators have the following feature: the volume of coolant in them is 3 and sometimes 5 times less than in cast iron products. As a result, the high speed of movement of hot water prevents silting and the formation of deposits.

Bimetallic heating radiators have the following section dimensions:
- length 80-82 millimeters;
- depth - from 75 to 100 millimeters;
- height – minimum 550 and maximum 580 millimeters.
In terms of heat transfer, one bimetallic section is inferior to an aluminum section by about 10-20 watts. The average heat flux is 160-200 watts. Due to the presence of steel, the operating pressure reaches 25-35 atmospheres, and during testing - 30-50 atmospheres.
When arranging a heating structure, you should use pipes that are not inferior in strength to radiators. Otherwise, using durable devices loses all meaning. For bimetallic radiators, only steel liner is used.
Optimal solution
There are building codes and formulas by which the required number of sections of a heating battery is calculated.
For standard apartment buildings, the standards provide for a power rating of 100 W per square meter of space. Thus, knowing the power of the radiator section declared by the manufacturer and the square footage of the room, you can calculate the standard number of sections, rounding the result up. If there are low window sills, you should add 2-3%, if the room is corner - 20%.
Non-standard rooms, for example, with high ceilings, are calculated using a similar formula, but the cubic meter is taken as the basis. The average power rate is 41 W per cubic meter.

When installing sectional heating radiators, be attentive to construction and technical standards. The correct number of battery sections affects not only the comfortable temperature in the house even in severe frosts, but also your health and well-being.
How can I do it?
Below is a schematic diagram of the heating system of a two-story house without radiators.
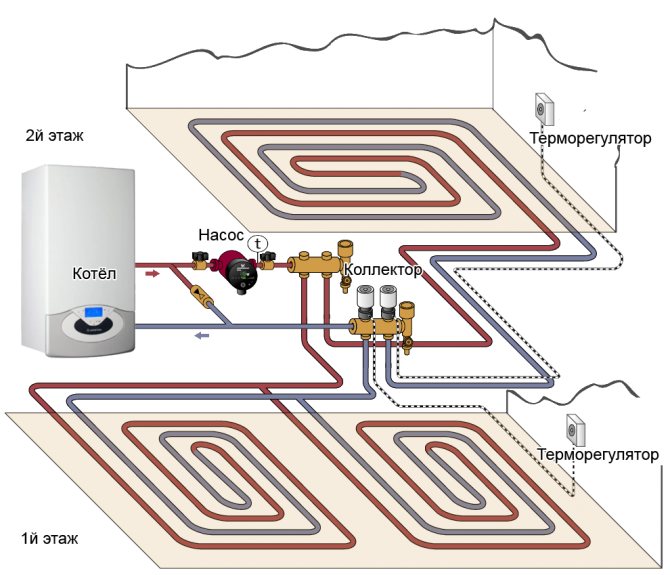
There are no fundamental differences in the design of the heated floor itself from the combined system with batteries. All the same components are used, and the floor “pie” is laid in the same way. The number of circuits will correspond to the number of rooms. But if the room area is large and the maximum loop length is exceeded, then the loop is split into two.
When heating a house without batteries, the main issue will be calculating the heat loss of the building, insulation of the walls and foundation. Therefore, the choice of a heated floor as the only source of heat must be approached at the stage of designing a house, when the material and thickness of the walls are determined. Even then you can understand whether the warm floor is enough to heat the house.
We hope that the article was useful to you. Leave your questions and comments in the comments below.
Any homeowner, one way or another, whether during the construction of a house or the overhaul of an old one, faces the question of organizing heating. Another thing is how to approach solving this problem - what to prefer: warm floors as the main heating or radiators. Moreover, heating a private house with heated floors is fundamentally different from the second option when choosing a heat source.
Low batteries
Radiators with a small center distance have the following advantages:
- they can be placed under a low window sill;
- they have maximum heat transfer per unit area.
Cast iron radiators
.
The dimensions of the MS-140M-300-0.9 heating radiator sections are:
- length 93 millimeters;
- depth – 140 millimeters;
- height – 388 millimeters.
Due to their smaller dimensions, the heat transfer of cast iron heating radiators is reduced - it is equal to 106 watts from one section at an operating pressure of 9 kgf/cm². Among foreign analogues, there are cast iron products with an interaxal distance along the connections equal to 200 and 350 millimeters; the power of a section of a cast iron radiator of this type is much higher.

Aluminum radiators
. For low batteries made of aluminum, both domestic and imported, the spread of the center distances is quite large. You can find radiator sizes of 150, 300 and even 450 millimeters. Since the possible section length starts from 40 millimeters, the device looks compact and unusual. Low aluminum heating radiators have height dimensions starting from 200 millimeters. The depth of many models compensates for the lack of the other two parameters and is 180 millimeters.
As for thermal power, it varies from a minimum of 50 watts per section to a maximum of 160 watts. The determining factor is the fin area of one section. At the same time, the change in dimensions does not significantly affect the operating pressure - low aluminum devices are designed for 16 atmospheres, and when testing - 24 atmospheres.
Bimetallic radiators
. All the sizes of heating radiators that they have are also typical for aluminum heating devices. Thermal power is within the same limits. On sale you can find aluminum low radiators with heat output of 80 and 140 watts per section. The working pressure is 25-35 atmospheres.
Bimetallic low radiators, such as in the photo, have two nuances:
- among heating devices there are batteries not with solid steel cores, but with steel tubes placed between aluminum collectors. Their operating pressure, indicated by manufacturers, is usually 12 or 16 atmospheres;
- they often do not have vertically located channels and, in the case of a lateral connection, can be heated by the collectors due to the thermal conductivity of aluminum. The circulation of the coolant is ensured by the last section, since it is flow-through.
Advantages and disadvantages
Steam heating is not the most popular, but it has both positive and negative aspects. Moreover, the advantages are quite significant:
- High heating efficiency. The fact is that the steam in the system does not just heat radiators and pipes to a certain temperature. Due to the large temperature difference, it condenses. And during condensation, 1 liter of steam releases 2300 kJ of heat. Whereas when the same amount of water cools by 50°C, only 100 kJ is released. Therefore, a very small number of radiators are required to heat the room. In some cases, a certain number of pipes is sufficient.
- Since steam heating is a small system, it has low inertia. The room begins to heat up literally a few minutes after the boiler is started.
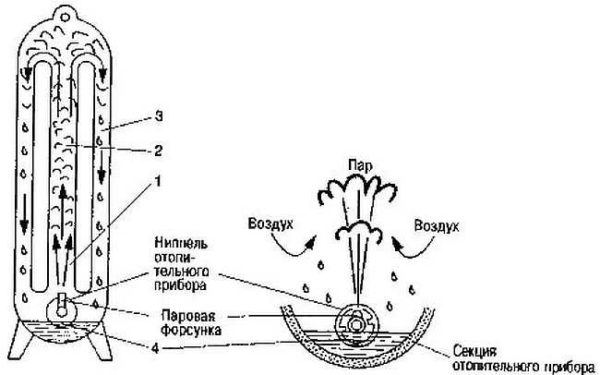
The steam in the radiators condenses, flows down, then is discharged through a special pipeline
The disadvantages of steam heating systems are even more impressive:
- The high temperature of the steam leads to heating of all elements of the system to 100°C and above. This leads to the following consequences:
- very active air circulation in the room, which is uncomfortable and sometimes even harmful (if you are allergic to dust);
- the air in the room dries out;
- hot elements of the system are dangerous and must be closed, and the pipes too;
- not all building materials can easily withstand prolonged heating to such temperatures, therefore the choice of finishing materials is very limited (in fact, it is only cement plaster followed by painting with heat-resistant paints).
- Simple steam heating has very limited capabilities for adjusting heat transfer. There is only one way to change the temperature - make several parallel branches and turn them on as needed. The second method is to turn off the boiler when it overheats and turn it on after the room has cooled down. This process is controlled automatically, but this method is far from the most comfortable, since there are constant temperature fluctuations.
- The system is noisy. When moving, the steam makes quite a lot of noise. In production workshops this is not a big problem, but in a private home it can be a problem.
As you can see, steam heating is not the best choice, although it is quite inexpensive to install.
Your home is warmer and your wallet is safer - use batteries wisely
A few simple nuances can reduce heating costs by almost 40% - without radical changes or big expenses.
Install reflective screens
If you install a heat-reflecting screen made of foil or phenol foam on the wall behind the radiator, you can reduce energy losses and increase the temperature in the room by 2-3 degrees. The energy will not go into the wall and through it to the street - instead, the screen will reflect heat into the room.
To increase the heat transfer of batteries by another 5%-10%, you can paint them dark. But the paint layer should not be dense so as not to become a heat insulator.
Don't clutter batteries
Make sure that warm air from the battery can freely pass into the room. Radiators should not be cluttered with furniture or covered with long curtains. This greatly reduces heat transfer, sometimes by up to 20%.
If the radiators are removable, they need to be washed regularly - scale forms in the radiators, as in any appliance with hot water, which serves as an insulator and greatly reduces heat transfer, so you have to spend a lot more energy on heating.
Central heating radiators should be bleed a couple of times a year, because air pockets do not allow water to circulate freely throughout the radiator and reduce the quality of heating. To remove air from the battery, use special “Mayevsky taps” at the top of the battery, which are slightly unscrewed and the air is released until water flows from the tap.
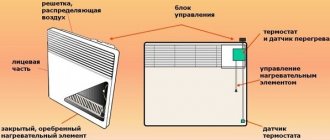
Control the heat in your home with a thermostat
The thermostat allows you to control radiators and eliminate unnecessary expenses. It makes it possible to change the heating power as needed. And advanced thermostats allow you to program the heating (for example, so that the temperature decreases at night and during the day when no one is home, and increases again in the morning and evening) and control the batteries remotely - including from a smartphone, for example, turning them on before returning from vacation.
A simpler option is a ball valve on a battery, which can be opened and closed, albeit manually (the thermostat, as a rule, works automatically). In addition, the ball valve usually has two positions: open and closed. If you use it to partially shut off the water supply, the ball valve will quickly fail.