Read in this publication: Automation for solid fuel boilers: the principle of combustion control The advantages provided by an automation kit for a solid fuel boiler Automation diagram for solid fuel boilers: expanding the possibilities How to make the simplest automation with your own hands: tips and recommendations
Strange as it may sound, in our age of scientific and technological progress, solid fuel boilers still remain in demand and are even considered practically the most common heating devices. And if there is demand, then there will be offers - not only for the boilers themselves, but also for various devices designed to optimize their operation. One of such devices is automation for solid fuel boilers, which allows you to very effectively control the operation of the boiler, simplify its maintenance and operation. We will talk about how it works and on what principle it works in this article - in addition, together with the website stroisovety.org we will talk about how to independently automate the operation of a boiler that burns solid fuel.
Automation kit for solid fuel boilers photo
Automation for solid fuel boilers: combustion control principle
At first glance, it may seem that controlling the element of fire (even placed in a confined space) is very difficult, but in fact this is not the case. Remember what affects the combustion intensity of solid fuel - that’s it, oxygen, which is supplied to the boiler through the ash pan. Consequently, you can control the operation of the boiler by opening and closing the vent - yes, this is not very convenient and not very practical, but who says that you can’t come up with an alternative? It’s very possible - all you need to do is install an electric fan in the vent door. And people can control its rotation speed very effectively.
Thus, modern automation for a solid fuel boiler fan has the following form.
- Blower fan. As a rule, it is installed either in the blower door, or a separate hole is designed for it.
- A special controller is used to control the fan speed.
- Adequate operation of this controller is guaranteed by a thermostat, the sensor of which is mounted in the heating supply pipe.

Automation for solid fuel boiler fan photo
The required coolant temperature is set on the controller - when the water in the system heats up to the set point, the sensor is triggered and the automation turns off the fan. Oxygen stops flowing into the boiler firebox, causing the fire to die out. And, conversely, as soon as the coolant temperature drops below a certain value, the same sensor sends a signal to the controller, which starts the fan - an abundant amount of air in the firebox ignites the flame with renewed vigor. Everything is simple, and the most important thing is that the person will not forget to cover the vent, thereby bringing the boiler to a boil.
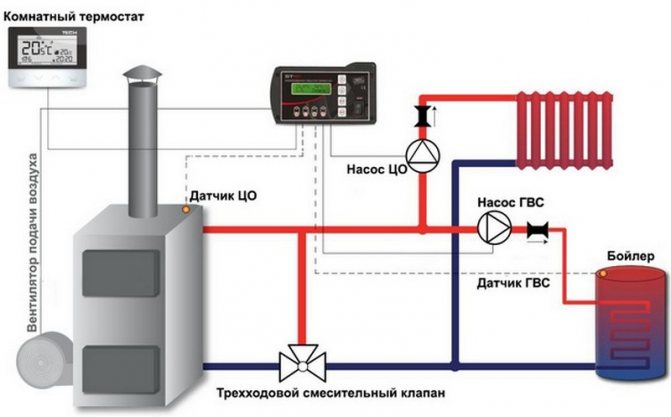
Operating principle of the control unit (controller) for boilers
Controllers are electronic devices that are designed to optimize the control of a gas heating device under changing environmental conditions. The capabilities and functions of different devices differ, but they are united by the presence of pressure and temperature sensors.
Example of controller connection diagram
The electronic gas boiler control unit (ECU) is responsible for the operation of the gas burner, heating of the coolant and the safety of the system as a whole. Its operating principle is based on the use of an electromagnetic valve.
The controllers of the latest heating devices are equipped with an automatic mode function, which allows you to regulate the operation of the device during the week without human intervention.
We recommend: Double-circuit floor-standing gas boiler: specifics of device and choice
Connecting the computer to external temperature sensors and boiler control terminals allows you to configure independent changes in the operation of the burner.
For such a controller, it is necessary to install a voltage stabilizer and an uninterruptible power supply to ensure the operation of the boiler during voltage surges in the network or in its absence.
Advantages provided by an automation kit for a solid fuel boiler
There are no accidents or coincidences in our world, and people had to automate the process of burning solid fuel in a heating boiler for a reason - there are a number of good reasons for this. The most important of them is safety. Anyone who uses solid fuel to heat a home probably knows the consequences of overheating the coolant - boiling water in the boiler can even lead to an explosion with serious consequences. First of all, automatic control allows you to control exactly this moment - a person is a forgetful creature by nature, and automation works according to a program, and there is no such thing as “forgetting” for it.
In addition, automation of a solid fuel boiler provides a number of other benefits to humans.
- Optimizing the climate inside the house. It eliminates sudden changes in temperature - when the boiler is just loaded and combustion reaches its peak, the house is hot, and when the firebox is empty, the house becomes cold. Automation removes the first rise in temperature towards an increase.
- Fuel economy. This occurs due to the operation of the thermostat. Having brought the temperature of the coolant to the set value, the automation stops burning, switching the boiler to smoldering mode - slow heating occurs, which consumes much less fuel.
- The task of controlling the combustion process is removed from the person. That is, you loaded the firebox full and went about your business - all that remains is not to miss the next loading of the boiler.

Automation for solid fuel boilers photo
This concerns the primary tasks that automation for a solid fuel boiler is designed to solve. In addition to them, depending on its complexity, automatic control of fuel combustion may have additional options that expand the capabilities.
Design and operating principle
The automation that controls the operation of a gas boiler consists of many elements, conditionally divided into two subgroups. The first includes mechanisms that ensure the full and safe functioning of the boiler itself. The second includes devices that make it possible to operate the heating system in the most convenient and user-friendly mode.
READ MORE: Installation of MDF plinths - methods of fastening and procedure for performing work
Several modules are responsible for the operational safety of the unit.
- Flame controller - consists of two main parts - a solenoid valve and a thermocouple. Shuts off gas promptly and reliably and prevents leakage.
- Thermostat - maintains the set temperature of the coolant and protects the system from overheating. When the coolant cools down to minimum temperatures, the module starts the boiler into operation, and after recording peak-high readings, it turns it off, completely relieving the owners of the need to constantly pay attention to the system.
- The draft control sensor is responsible for stopping the gas supply to the burner in the event of a change in the basic position of the bimetallic plate, thus preventing gas leakage.
- Safety valve - monitors the amount of coolant in the circuit.

In addition to all the above useful qualities, the automation has a number of additional functions that increase the comfort of using the equipment.
The device performs automatic ignition of the gas burner, selects the most effective operating mode, promotes rational consumption of energy resources and conducts independent diagnostics, saving the owners from all these activities.
Current regulatory documentation says that the safety system for gas boilers must be equipped with a device that stops the operation of the entire system and shuts off the gas supply in the event of an unexpected breakdown or any other force majeure circumstances.
To carry out this task, automation must keep under control such parameters as:
- gas pressure in the system;
- presence of an optimal size flame in the burner;
- full, high-quality traction;
- working coolant temperature level.
When the gas pressure in a non-volatile mechanical system drops to a critical level, the resource supply immediately stops. This happens automatically due to the presence of a valve mechanism set to a certain value.
Volatile electronic devices are designed slightly differently. In them, the above function is performed by a minimum/maximum pressure switch.
As the number of atmospheres increases, the membrane with the rod bends, opening the power contacts of the boiler itself. Gas stops flowing and is not supplied until the pressure level is restored.
It is prohibited by law to independently troubleshoot problems and somehow interfere with the basic functionality of the equipment. Only a qualified specialist - an employee of the gas supply company - can correct any problems that arise.
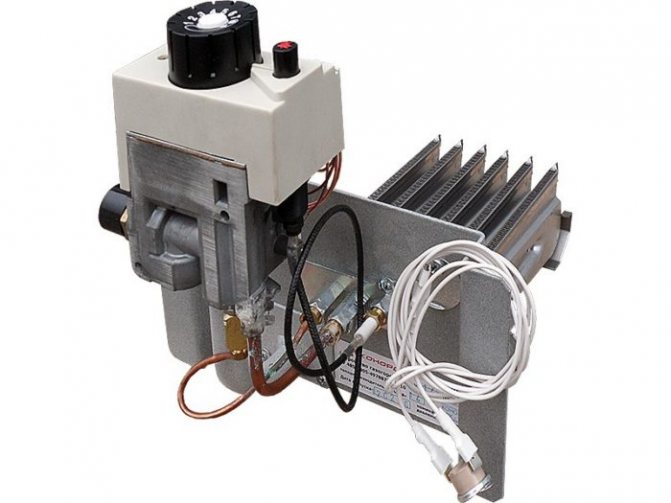

If the flame disappears in the burner, the thermocouple cools down and stops producing current. After this, the electromagnetic damper in the valve no longer functions and gas stops flowing to the burner.
When the thrust drops, the bimetallic plate heats up intensely, changes shape and acts on the valve, causing it to stop supplying fuel.
The coolant temperature is kept under control by a thermostat. It ensures that the user-selected heating mode is maintained, while preventing the system from overheating and failing.
Volatile electronic automation operates based on information received from sensors. The microprocessor and internal controller analyze this data, process it and provide the system with commands that are optimally suited for a particular situation.
In order for electronic automation to function normally for a long time, it is necessary to call a technician annually to inspect the equipment, diagnose the microprocessor and view memory module reports
Mechanics have a slightly different principle. When the boiler is turned off, the internal gas valve is completely closed. At the moment the equipment is started, the washer on the valve is squeezed out and the passage for the fuel resource to the igniter is forced to open.
Ignition stimulates heating of the thermocouple and voltage is generated across it.
This resource uses an electromagnet to maintain the valve in the open position. By turning the washer manually, the user can effortlessly adjust the level and power of his heating equipment.
All internal equipment of automation for gas boilers, which is used when installing a heating system, can be divided into categories, there are only two of them:
- the first category is those devices that ensure the safe and proper operation of all boiler equipment;
- the second category is those devices that can significantly increase the comfort when using the boiler.
Safety automation for gas boilers consists of the following elements:
- the module that provides flame control. It consists of a thermocouple and a gas valve that works like an electromagnetic valve and shuts off the fuel supply;
- there is also a device that protects the system from overheating and maintains the required temperature; this task is performed by the thermostat. It independently, if necessary, turns on or off the boiler at those moments when the temperature approaches the specified peak levels;
- the sensor that controls traction. This device works based on vibrations depending on how the position of the bimetallic plate changes. It, in turn, is connected to a gas valve, which stops the gas supply to the burner;
- there is also a safety valve, which can be responsible for discharging excess coolant (for example, air or water) in the circuit. Some manufacturers immediately provide an element that helps dump excess.
The devices included in the security system are divided into the following types:
- mechanical;
- and operating from a power source.
They operate either under the influence of a drive and a controller that controls them, or are coordinated electronically.
Automation provides the user with more comfortable functionality, which is additional:
- automatic ignition of the burner;
- flame intensity modulation;
- self-diagnostic functions.
But such functionality is not limited to the internal design of the models.
Some design features of the models include additions such as sending data and processing it by an electronic system on equipment equipped with controllers and microprocessors. Then the following situation occurs: based on the received data, the controller itself begins to adjust the commands that activate the machine’s system drives.
Mechanical automation of a gas boiler also requires detailed consideration.
- The gas valve is completely closed and the heating installation is inoperative.
- In order to start a mechanical gas boiler, the washer is squeezed out, allowing the fuel to start and opening the valve.
- The valve opened under the influence of the washer and gas flowed to the igniter.
- Ignition is in progress.
- After this, gradual heating of the thermocouple begins.
- The electric shut-off magnet is supplied with a voltage that ensures its open position so that fuel access is not blocked.
- Mechanical rotation of the washer regulates the required power of the gas heating device, and the fuel in the required volume and with the required pressure is supplied to the burner itself. The fuel ignites and the boiler unit begins to operate.
- And after that, this process is controlled by a thermostat.
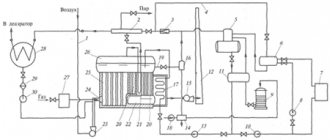
Automation scheme for solid fuel boilers: expanding possibilities
Man has learned best to control electricity - it is electrical signals and impulses that are used to control everything that is needed, including other equipment involved in the operation of the heating system.
- Heating circulation pump. Automatic control allows for constant and, most importantly, uniform distribution of heat throughout all rooms of the house.
- Circulation pump for domestic hot water. At a minimum, this is control of the water temperature, and at a maximum, it is supplied on a schedule, which, again, allows you to effectively manage the received heat.
- Water temperature in the boiler. The most important thing here is to prevent overheating and prevent the consequences of this.
Automation for solid fuel boilers: diagram
And that’s not all - modern automation for a solid fuel boiler can do many different things. For example, it allows you to program it, so to speak, remotely, using a GSM module. It is also possible to program the heating operation daily, daily and even hourly. By and large, correctly selected automation for a solid fuel boiler even makes it possible to integrate it into a global smart home system.
Boiler design for servicing two circuits
Today there are two types of automatic devices for heating boilers: volatile and non-volatile. Which of the two groups of automatic controls for a gas boiler is better, we will consider in detail.
Non-volatile
This group includes mechanical devices for controlling work processes inside the boiler. Advantages of this group:
- these devices have a lower price;
- manual adjustment is not difficult to operate the device;
- The device units are completely autonomous and do not depend on electricity.

The principle of manual adjustment: the arrow on the temperature scale sensor is set to the desired temperature. After turning on the boiler in operating mode, the thermostat controls the set temperature. A thermocouple, which is a transducer that measures operating temperature, is two metal rods (an alloy of iron and nickel) that respond to changes in temperature.
Two sensors have been added to modern mechanical automation units: thrust and flame.
A volatile device is an electronic device that regulates the gas supply using a tap. What are the functions of this type of automation for a gas boiler:
- close and open the gas supply valve;
- set automatic boiler mode;
- monitor the operation of the burner using a temperature sensor;
- in case of an unusual situation or a programmed shutdown, stop the boiler operation;
- visually demonstrate the operation of the boiler, water temperature, etc.
In the most modern electronic devices, the functions have been expanded, adding:
- control and monitoring of pump operation;
- protection of the heating system from low temperatures;
- protection of the heating system in case of valve failure;
- independent diagnostics and identification of defects in individual elements of the device.
Thanks to this innovation, there is a guarantee of uninterrupted operation of the boiler in compliance with conditions and temperatures. And the fault diagnosis system will help keep the device working much longer, because it is easier to prevent than to make major repairs. These are compelling arguments when asking: which automation is better for gas boilers.
A double-circuit gas heat generator differs from a single-circuit analogue in that instead of one heat exchanger, it has two, which in technical terminology are called primary and secondary.
READ MORE: What to consider when calculating a single-pipe heating system
The first one, i.e. The primary heat exchanger is located directly in the flame combustion zone. Its task is to heat the coolant for the functioning of the heating network. The secondary heat exchanger is responsible for the operation of the hot water supply.

Stable operation of the heating device is possible with coordinated operation of all its components. Information about the main functional units will help you understand the operating principle of the equipment

The design of any two-circuit unit includes the following standard elements:
- Combustion chamber with burner block;
- Heat exchangers;
- Equipment control and protection devices.
To understand the design features of double-circuit gas boilers, we will dwell in detail on each of its structural elements.
The burner of a gas boiler is responsible for obtaining a sufficient amount of heat necessary for the functioning of the heating and hot water supply circuit. Thermal energy is obtained by burning fuel. Place the burner in the combustion chamber, into which air is pumped in addition to gas. It is needed for the combustion process.
Depending on the operating modes, burners can be classified into the following types:
- Single level burner. A unit with such a burner can operate in only two modes - “Stop” and “Start”. Such boilers, despite their low efficiency and reduced service life, are popular due to their simplicity of design and low cost.
- Two-level burner. A heater with such a burner can operate at full or half power. Its advantages are noticeable in the warm season, when there is no need to operate the device at full power to heat water that is not too cold.
- Modulating burner. A smart boiler system with a similar burner allows you to configure and regulate power. Such a boiler is characterized by a high service life and efficiency, but at the same time it costs an order of magnitude higher than units with single-level and two-level burners.
Burners are divided into open and closed designs. When the burner is open, the air required to burn the fuel comes directly from the room in which the boiler is located. To remove combustion products, a chimney is required, which must provide sufficient natural draft.
Atmospheric heating units are usually equipped with a regular metal pipe, while turbine units are equipped with a coaxial chimney. Depending on the technical conditions of the room, the smoke duct is placed vertically or built at an angle. Corner options lead through the wall to the street or connect to a public chimney shaft.

The gas burner is the main element of a double-circuit gas boiler; it is responsible for burning fuel and obtaining thermal energy in the required quantity
Turbine boilers are equipped with closed combustion chambers into which air cannot flow spontaneously. They are safer and more reliable in operation, but more expensive and more difficult to operate. Boilers with closed burners, in addition to a smoke exhaust, require a channel through which the oxygen required for combustion is supplied to the chamber.
That’s why they equip turbine boilers with coaxial pipes, because in addition to removing smoke, they also draw in fresh air flow from the street. It happens that for normal operation, two coaxial chimneys are connected to a closed combustion chamber. In addition, the entire structure is supplemented with an air supply pipe.
All similar boiler models are equipped with fans that provide smoke movement, multi-level protection systems, and automation. The listed devices and systems require electricity to operate. Their disadvantage is their energy dependence, which increases operating costs.
If a burner burns fuel to produce heat, the heat exchanger provides this heat for further transfer to water. As already mentioned, the double-circuit design contains primary and secondary heat exchangers.
The primary heat exchanger is located directly above the burner and is a finned tube bent in the shape of a snake. Under the influence of the flame, the water in the heat exchanger heats up and moves through a three-way valve further into the heating system wiring.
The secondary heat exchanger is a system of wavy plates, which are assembled into a single block with two pairs of holes. Each pair of holes has its own functions.
Water from the water supply flows through one of the pairs, and the coolant flows through the second, entering the heating circuit. A similar system of plate and tubular heat exchangers is called dual.
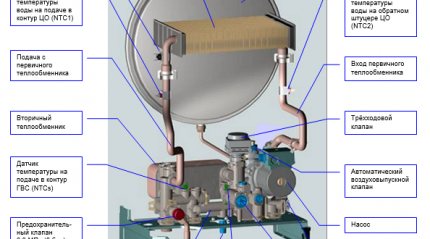
The primary and secondary heat exchanger are combined into one system, the correct operation of which is ensured by a special three-way valve
There are heating devices that use a bithermic heat exchanger of complex configuration instead of a dual system. This heat exchanger is made of copper; it consists of a pair of tubes located one inside the other. Coolant flows through the outer tube, and water flows through the inner tube to ensure the operation of the hot water supply.

The bithermal heat exchanger of the coolant and water heater has a complex configuration, when the tube of one circuit is placed in the tube of another circuit
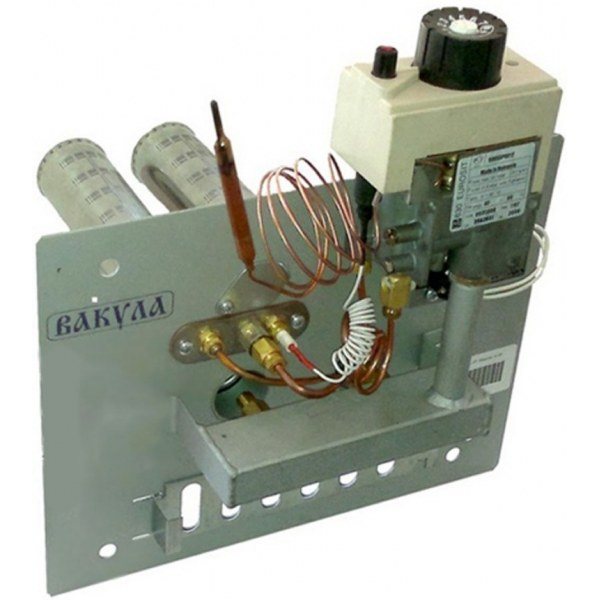

Boilers with a bithermal heat exchanger are more difficult to operate, since both heat exchangers are represented by a single unit, which makes it difficult to descale. But such heating devices are in demand, as they are characterized by small overall dimensions and high water heating speed.
The boiler automation is responsible for safe and stable operation. It monitors the water temperature in the DHW components and maintains the temperature of the coolant in the heating lines. The automation of a gas boiler does not allow the heating device to operate in the event of dangerous situations.
The unit interrupts operation or does not turn on in the following cases:
- Reduced pressure in the gas system;
- Lack of traction;
- Absence or critical overheating of coolant.
The control unit, which controls the operation of protection and process automation devices, is represented by a set of switches, microcircuits, or a combination thereof. In addition to ensuring safety and temperature control, it monitors the operation of the circulation pump and fan.
Modern gas boilers are distinguished by the presence of intelligent controls, the software of which contains various operating modes.
The operating features of gas equipment are largely determined by the design version of the heating device. Modern boilers are available in two form factors - floor-mounted and wall-mounted.
When choosing a design option, you need to focus on the size of the heated area and the activity of using the hot water system. You need to understand that wall-mounted boilers are more compact, but at the same time they have much less power.

The double-circuit wall-mounted gas boiler has a compact size and modern design, but is only effective when heating small areas with moderate hot water consumption
The choice of a wall-mounted double-circuit boiler may be justified if the heated area does not exceed 200 sq.m, and the total productivity of the hot water system does not exceed 14 l/min.
The small size of a wall-mounted boiler, although it seems like an advantage, actually hides many disadvantages. Compactness is achieved through the use of thinner heat exchanger tubes. In addition to the fact that they have a shorter service life, there is a possibility of clogging.
In floor-standing installations, more massive and reliable cast iron heat exchangers are used. This not only increases the reliability of the heating device, but also extends its service life.