- Properties of polypropylene
- Duration of guaranteed operation of polypropylene systems
- Pressure in pipelines
- Methods for installing polypropylene pipes
- Disadvantages of polypropylene systems
- Unusual properties of polypropylene
- Application of reinforced polypropylene pipes
It has long been no secret to anyone that polypropylene highways have firmly entered our lives. They are widely used for the repair and installation of plumbing and heating systems. They are especially actively used in new buildings, since open-minded people work there, and they try to introduce new technologies into life. But before you decide what to use in your home, it is important to find out what pressure the polypropylene pipe can withstand.
Of course, every reasonable owner, before installing polypropylene systems, should think about how reliable they are and whether there will be any surprises. The fact that old friends - steel and cast iron pipes - were definitely reliable, no one doubts this, but what is the situation with this new product - we need to figure it out.
Properties of polypropylene
To understand what pressure polypropylene systems are designed for, you need to take a closer look at the structure of the material itself.
Polypropylene is a soft polymer, so it does not perform reliably at very high temperatures. For him, a temperature of 140 degrees means that the surface of the pipe becomes soft, bends, and loses its shape. But if the temperature rises to 175 degrees, then the polypropylene will begin to melt.
Modern polypropylene pipes
However, it is unlikely that any of us at home have water at such a temperature in the systems at least sometimes. This means that polypropylene lines are quite suitable for use in a heating system and for supplying hot water.
Properties of polypropylene and temperature conditions of operation
Polypropylene is a product of the chemical industry, white powder. Polypropylene products are made from it by melting and pressing.
It is obtained through the polymerization of propylene under the influence of metal catalysts. Propylene is a gaseous substance, usually a by-product of ethylene or gasoline production and distillers.
Polypropylene softens at 140⁰C, and its melting begins at 175⁰C. This is exactly the temperature of superheated steam. Based on these parameters, it can be assumed that polypropylene is suitable for water supply with any temperature of this coolant, but not steam.
Everything would be just fine if not for one feature of polypropylene, namely its plasticity when heated. The higher the heating temperature of polypropylene, the greater its elongation under tensile load. In other words, if you hang a load on a heated pipeline, before it bursts, it will sag, stretching into a thin tube.
So a pipeline with cold water is quite hard and rigid, and pipes heated to 130⁰C can be easily bent to a right angle with a little effort.
It would seem that the plumbers' dream has come true; it is possible to make a pipeline with any turns without using fittings for these purposes. Unfortunately this is not possible. When a polypropylene pipe is bent by heating, its internal diameter becomes smaller, reducing the throughput of the water supply system, and the wall thickness on the outside of the bend will be significantly less.
READ ALSO: Which pipe for a water well is better to choose: HDPE or uPVC
Duration of guaranteed operation of polypropylene systems
The guaranteed service life for polypropylene pipes is about fifty years. This is provided that they will be used to supply water no warmer than twenty degrees Celsius. That is, during all these years the pipeline wall will experience a constant load. The force of the load will depend on the temperature of the water flowing in it and under what pressure. It is not at all surprising that after the expiration date, the pipeline system may simply burst.
In industry, it is common to use pressure units such as technical atmospheres. So, for polypropylene systems, the normal pressure in the pipe is from four to six atmospheres. That is, if water flows in the pipeline no hotter than 75 degrees at a pressure of no more than six technical atmospheres, then under such conditions the system will last all fifty years, as written in the advertisement. And maybe even more.
Operation of polypropylene pipes
This is a considerable period of time for heating systems made of polypropylene. This means that when using polypropylene lines in the right conditions, they will serve you for a long time and faithfully.
A little history
At the end of the Soviet era, despite the global shortage, microdistricts of houses were built in the regions of the Far East according to a standard design, popularly called Leningradsky.
During the construction of these houses, an attempt was made to reduce the cost of construction. The walls of the houses were made of panels, but the windows were triple glazed. The heating devices are convectors of a strange design, a curved pipe with an internal diameter of no more than 20 mm with thin steel plates tightly strung on it.
The Far Eastern climate is harsh, with winter temperatures dropping below -30⁰C. When there is a strong wind, the heat loss of a panel house becomes simply enormous and tiny convectors, designed for completely different operating conditions, simply cannot cope with the task. In order to somehow compensate for heat loss, it was necessary to increase the temperature of the coolant beyond 100⁰С, fortunately the parameters of the heating mains allowed this.
READ ALSO: 3 rules when using HDPE pipes with a diameter of 32 mm

Unfortunately, many residential buildings do not have an automated water supply control system. And the prospects for its appearance are vague. When the outside temperature drops to 35⁰C, the thermal power plant, to maintain the temperature regime, raises the coolant readings to 130⁰C. Thanks to pressure, water continues to flow through the pipes, not steam (about
Pressure in pipelines
The system of codes and regulations strictly regulates the correct indicators for water supply systems, but when testing the start-up of new houses, more pressure is applied. As a rule, it can reach 12 atmospheres, which is twice the norm. How do polypropylene pipelines fare in such an environment? A short-term change in pressure will not affect the quality of the pipeline. In addition, when testing systems, they usually use not only water, but also air, which significantly lightens the load on the pipe walls.
Obviously, it is not recommended to use the maximum pressure of polypropylene pipes, since under such conditions the service life of the pipeline is sharply reduced. And if, along with increased pressure, increased water temperature is used, then the pipeline may even rupture, bringing a lot of inconvenience and problems. That is why, when installing polypropylene pipelines, it is necessary to carefully monitor the maximum permissible pressure on the system.
Is the water hot?
Is it a lot or a little?
Let's see what current regulatory documents have to say about this.
SNiP 2.04.05-91 (“Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings”) directly states that the water temperature for all systems of the house should not exceed 95 degrees. And in the case of preschool children's institutions - it’s 37.

Theoretically, such devices should be in every elevator unit

If so, you can safely install polypropylene pipes: the operating temperature is suitable. Right?
It would seem that now all the questions have been resolved and we can go home. But, as is customary, there is a nuance. Even two.
In late Soviet times, shortly before the change of regime to a democratic one and the disappearance of sausages from stores, in the Far East (undoubtedly, not only there, but it was in the Far East that the author had the opportunity to observe this disgrace personally) entire microdistricts of houses were built according to the so-called Leningrad project .
Triple glazing and triple doors in the entrances are combined with panel walls and very unique heating devices. Water heating convectors are simply a coil of heating riser with a diameter of 3/4 inch with transverse fins made of thin steel plates tightly fitted onto it.
In theory, everything should have worked...
To understand the full scale of the tragedy, you need to have a good understanding of the Far Eastern climate. Temperatures of -40 - -45 there are not exactly every day in winter, but they do not surprise anyone, and -30 with strong winds is more than an ordinary occurrence. The volume of heat loss from a panel house is easy to estimate. Now let’s compare it with the heat that 50-80 centimeters of pipe with pathetic plates leave in the apartment.
To ensure an acceptable temperature regime in these houses, it was necessary to raise the temperature of the coolant in the heating system well above a hundred degrees. Fortunately, the parameters of the heating mains allowed this in the winter cold.
We live in Russia
There is no automated control of water supply in residential buildings in our country and there will not be a widespread system for a very long time. And now oil on canvas. Winter. It's -40 outside. By maintaining the temperature schedule, the thermal power plant raises the temperature of the coolant in the supply pipeline to 130 C. The water in the pipe does not turn into steam only due to pressure.

To ensure that residents' tap temperatures do not exceed 95 C, the water supply must be switched to a return pipeline. Manually. In the elevator unit in the basement of each house.
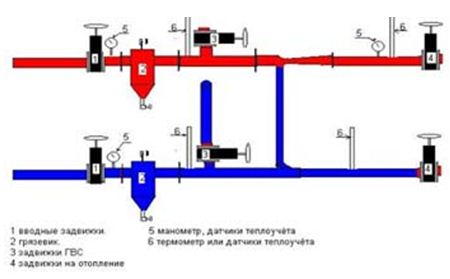
Hot water valves are marked with number 3
And the mechanic is sick. Or on a binge. Or just shortened. There is no need to tell you what the state of housing and communal services is in the outback.
And what?
If the water is at this temperature, should polypropylene pipes drain down?
Fortunately, this doesn't happen. Up to the point of 140-150 degrees, even unreinforced polypropylene pipes are not yet deformed. But their service life is actually reduced.
The fact is that manufacturers are big reinsurers. If a pipe bursts at a temperature of 94 degrees, for which the stated operating temperature is 95, the manufacturer will be sued. Since the thickness, strength of plastic and other physical properties of pipes inevitably change slightly from batch to batch, all reputable manufacturers indicate very underestimated parameters for products, which are guaranteed to fit all batches of goods.
Methods for installing polypropylene pipes
Features of pressure pipes
The advantage of polypropylene pipelines is that they can be connected to each other in different ways. There are two main connection methods:
- Dozens of types of fittings are regularly produced. They are used when it is necessary to branch a highway into several channels, or when the highway turns sharply;
- a particularly popular connection of polypropylene systems by creating a monolithic system. Using a soldering iron or a special welding machine, it is easy to cut the pipe in the right place and solder it. This method of fastening pipelines is considered the most reliable, since then there is no doubt whether the polypropylene pipe will withstand the given pressure.
When someone decides to furnish their home with polypropylene systems, they calculate the required length of the pipeline, determining how much material they will need. Then it is important to find out exactly what pressure is in the line on which it is planned to install polypropylene pipes. Having decided on the diameter, it is important to be able to independently determine whether a given pipe is suitable for the conditions of this particular home. It is worth noting that the normal operating pressure of polypropylene pipes is indicated in mega-pascals. The symbol for this unit of measurement is MPa. One technical atmosphere is equal to 0.0980665 MPa, which means that for a polypropylene line this value should not exceed 0.588399 MPa.
Installation of polypropylene pipes
What pressure can different types of polypropylene pipes withstand?
Many buyers who decide to install a polypropylene pipeline for cold water supply or heating are interested in what pressure they can withstand. The service life of polypropylene pipes will depend on this. This question is very important. Since the pressure in the plumbing system or in the heating system, which polypropylene experiences throughout the entire period of its use, affects the service life of the product. If the pipeline has a constantly high temperature but low pressure (or vice versa), then the pipe will last quite a long time. But if the system has both high pressure and high temperature at the same time, the service life will be sharply reduced.
In order for the pipeline to serve the 50 years promised by the manufacturer, the pressure in the system must be 4-6 atmospheres, and the coolant temperature must not exceed 75 degrees.
Disadvantages of polypropylene systems
Before using polypropylene systems, it is important to consider several disadvantages of such pipes:
- polypropylene pipes cannot be bent;
- fittings for pipelines made of polypropylene do not have a very aesthetic appearance;
- when heated to high temperatures, the pipes stretch and sag, thus creating an unattractive appearance;
- When installing such pipes, it is important to monitor the operating temperature, otherwise the overheated edges of the pipeline will change their size and will differ in cross-sectional diameter from the fittings reassigned for them.
High pressure polypropylene pipes are difficult to find. The manufacturing material itself is not intended for use in such conditions. If you regularly allow increased pressure, the communication line will definitely fail.
Unusual properties of polypropylene
By their structure, polypropylene pipelines tend to react strongly to sudden temperature changes.
When a pipe is exposed to too high temperatures, it expands. When the temperature drops, it returns to its original position.
Although in some ways this is a disadvantage, it is still a lifesaver in some situations.
Since plastic pipelines are sometimes laid underground in outdoor conditions, they are not completely protected from frost. For most systems, freezing is a disaster. However, with polypropylene lines the situation is completely different. If the water in such pipelines freezes, then nothing happens to the pipe itself. It's just expanding. When a thaw occurs, the water melts and the system returns to its original position.
Of course, whatever the consequences, freezing water in the main is an unpleasant phenomenon. Therefore, in the case of laying a polypropylene pipeline on the street, it is important to dig it to a depth that will be at least twenty centimeters more than the required norm.
When installing such pipes in multi-story buildings, it was noticed that the pressure on the first floor differs from the pressure on the last. However, this difference is small. For example, from the first to the fifth floor the pressure difference will be only 177 Pa. This is about 0.017 percent of one atmosphere. It turns out that the pressure on the first floor of a high-rise building will always be slightly higher than on other floors. However, this difference is so small that in order for it to become noticeable, a person must live from the fifth floor to the height of a skyscraper. But even there, sometimes special pumps are installed that stabilize the pressure on all floors.
Specifications
The technical and operational properties of the material are explained by the zigzag molecular structure of the polymer.
| Characteristics | PVC | CPVC |
| The proportion of chlorine in the composition | 44% | 56% |
| Density, g/cm3 | 0,95-1,46 | 1,47-1,6 |
| Melting temperature | 100-260 °C | 260-395 °C |
| Glass transition temperature | 70-80 °C | 105-120 °C |
| Decomposition temperature | 100-120 °C | 120-140 °C |
| Temperature minimum | -15 °C | |
| Modulus of elasticity, MPa | 550-1200 | 2400—2700 |
| Yield strength, MPa | 18-26 | 50-55 |
| Design strength, MPa | 6,3 | 10 |
| Tensile strength, MPa | 40-50 | 50-80 |
| Bending strength, MPa | 80-120 | |
| Thermal conductivity, W/(K∙m) | 0,14-1,63 | 0,13-0,22 |
| Specific heat capacity, J/(kg K) | 90 | |
| Linear expansion index | 1,2-1,4 | 0,62 |
| Gas permeability | 13 | 1 |
| Roughness coefficient | 0,006 | |
| Dielectric constant (at 50 Hz) | 3,5 | |
| Fire safety class | KM3 | |
| Flammability class | G2 | |
| Flammability class | AT 2 | |
| Flash point | 620 °C | |
| Flash point | 500 °C | |
| Auto-ignition temperature | 1100 °C | |
| Smoke emission class | D3 | |
| Toxicity class of combustion products | T2 | |
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=
PVC pipe products differ:
- High strength and resistance to significant hydraulic pressure, mechanical stress and deformation (especially unplasticized forms of the polymer).
- Resistant to oxidation and rust.
- Immunity to most chemicals: alcohols, acids, alkalis, salts, mineral oils, solvents.
- Lightness, which makes it easier to deliver and work with the material, and also reduces the overall structural loads of the building.
- High plasticity (characteristic mainly of plasticized PVC), which facilitates mechanical processing of pipes: cutting, bending, welding.
- Low roughness index, which helps maintain the required hydraulic pressure and prevents sedimentation inside the circuit.
- Resistant to weather conditions and temperature changes.
- The dielectric properties of PVC, they do not conduct current and are resistant to stray currents. However, these qualities are lost when heated above 85°C.
- Biological inertness. Plastic pipes are not susceptible to microorganisms and are not a favorable environment for their development.
- Environmentally friendly, since during operation the circuits do not emit harmful substances into the atmosphere. However, if operating conditions are violated (heating above normal), the process of molecular decomposition of the material starts, accompanied by the release of hydrogen chloride.
- Wear resistance, allowing trouble-free operation of engineering systems made of polyvinyl chloride for 50-80 years.
- The ability to recycle pipes, which compensates for one of the most important disadvantages of PVC - the difficulty of disposal.
PVC pipes are fireproof. Unlike most plastics, the ignition temperature of PVC materials is much higher; in conditions of critically high indicators, they simply melt before reaching the maximum. Combustion is accompanied by the release of toxic substances, but the burning polymer itself does not lead to the spread of fire, since it lacks the characteristic flame of most polymers. As soon as the source of fire is eliminated, polyvinyl chloride materials self-extinguish.
Limited temperature conditions are perhaps the biggest drawback of polymer pipes.
PVC pipes are no exception:
- The operating temperature range of most PVC pipes is limited to the range from 0 to 65 °C (for chlorinated varieties - from 0 to 95 °C).
- At subzero temperatures, the material becomes brittle, and at temperatures below -15 °C, the pipeline with the carrier inside can simply break. As a result, when laying externally or immersed in the ground, a PVC pipeline requires careful insulation.
- Under conditions of excessive heating of the circuit (70-105 °C), the effect of “glass fragility” occurs.
- The moment when the PVC pipe loses its shape (“floats”) is considered critical, which occurs when heated to a temperature of 100-260°C.
However, depending on the conditions and formulation of PVC production, as well as the thickness of the pipe wall, these characteristics will be different for each thermoplastic model.
Application of reinforced polypropylene pipes
In addition to standard plastic pipelines, more durable connections have been invented - from reinforced pipelines. The difference from the usual ones is that between the layers of polypropylene there is a layer of aluminum or fiberglass. Due to this layer, the expansion capacity of the line is reduced, and it no longer sags when heated, does not expand during installation, and does not contract during cooling.
Some experts believe that it is better to use reinforced connections for heating systems. In addition, they have a more attractive appearance, which means they can be used in open heating systems.
Knowing what pressure a polypropylene pipe can withstand, you can confidently install it at home and not worry about the reliability of all connections.
Advantages of reinforced polypropylene
- The linear dimensions of these pipes are less susceptible to changes under the influence of temperature. This is true when pipes are recessed into the screed during work. The use of reinforced polypropylene pipes in the heating system avoids damage due to temperature deformations.
- The service life of a reinforced pipeline under conditions of constantly high operating temperatures is much longer.
- The melting point of polypropylene pipes with and without reinforcement is the same. But at a temperature just below the melting point, under the influence of pressure, a pipe without reinforcement will burst, but a pipe reinforced with glass fiber will not. The maximum pressure in polypropylene pipes is 10 bar. The higher the temperature of the coolant, the lower the pressure in the pipeline should be.
Conclusion: In systems with a constantly high coolant temperature, it is better to use reinforced polypropylene pipes than the same unreinforced ones.

There is a lot of debate among consumers about what temperature plastic pipes can withstand. Some say 95⁰С, while others say 120⁰С. This is explained by the fact that the group of plastic pipelines includes polyethylene pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene. Their operational parameters are somewhat different. The optimal operating temperature for this type of plastic pipe is exactly 120⁰C. The melting point of plastic pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene is 200⁰C.
READ ALSO: A simple way to fix cracks in plastic
The cost of cross-linked polyethylene pipes is several times higher than the price of polypropylene pipes. Therefore, the use of polypropylene pipes is economically justified in systems with suitable performance characteristics. They tolerate short-term increases in the maximum operating temperature declared by the manufacturer. In addition, cases of polypropylene water supply leaking after assembly are quite rare.