Residents of the private sector, owners of country houses and cottages today are showing increased interest in heating devices running on solid fuel. There may be several reasons for such attention to solid fuel boilers, starting with the desire to achieve independence from a centralized energy supply and, conversely, due to the lack of it. The pace of suburban housing construction today is significantly faster than the speed of work on gasification of populated areas, so the only way out of this situation is cast iron heating boilers using solid fuel.
Why cast iron boilers when there is a wide selection of models of steel solid fuel boilers? We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the design features of solid fuel cast iron boilers and answer the question accordingly.
Features of modern cast iron solid fuel boilers
For a country house, solid fuel heating boilers made of cast iron are the best option for a heating device. Residents of private houses install similar units as a backup heat source in case of extreme circumstances. Both options are justified from the point of view of expediency. Gas heating, despite its availability, is constantly becoming more expensive. There are frequent cases of pressure drop in the gas line. A cast iron boiler burning coal, wood or pellets will help out in such situations, providing your home with the necessary heat and hot water.
For residential buildings located far from power supply lines, solid fuel becomes the main source of heating. This is especially true in the central and northern regions of our country, where they still dream of a central gas supply, and heating stoves and boilers with wood is considered a common activity. The heating boiler, made of cast iron and running on solid fuel, is experiencing a rebirth today. Having become a successor to the traditional Russian stove, the solid fuel boiler is a high-tech device.
The main advantage that modern models of cast iron heating equipment have is the high power of the units. Some models have power up to 2000 kW. Everything that is at hand goes into the firebox of a solid fuel boiler: firewood, coal, coke, peat, wood products and waste. The only point that you should pay attention to is that cast iron boilers are inert devices. The power range of such units is not significant, but in operating mode the boiler can produce maximum performance.
Thanks to the introduction of various engineering and technical innovations into the design of boilers, manufacturers managed to increase the efficiency of units of this type to 80%. Only pyrolysis boilers have higher efficiency, but that’s a different story.
For reference: a modern cast iron solid fuel boiler is a multi-sectional device. Each section is made of cast iron. By the number of sections you can judge the power of the heating device.
All structural elements have a threaded connection. Seams and joints are treated with high-temperature sealants. The production of cast iron boilers and the assembly of equipment is carried out in high-tech production. Such products are made using a special metallurgical method. The casting process produces a cast iron alloy in which the percentage of carbon is 2-4.5%. By adding special additives, it was possible to obtain a high-strength alloy that is resistant to high temperatures.
Due to its design and physical and chemical properties of cast iron, the equipment has a long service life - up to 30 years. This fact captivates many consumers. Compared to other types and types of solid fuel heating devices, a cast iron boiler is more reliable and has a longer service life.
Long service life is explained by the high resistance of cast iron to corrosion. Cast iron can only become covered with dry rust on the outside, under the influence of external factors.
The solid fuel boiler models on sale are multifunctional. The cast iron heat exchanger has high heat transfer and maintains the required coolant temperature for a long time. The inertia of cast iron boilers eliminates this advantage, making it difficult to regulate the heating temperature of the coolant. Despite this drawback, a boiler with a cast iron heat exchanger can operate normally at low temperature operating conditions, which makes it convenient for domestic use.
For reference: In most cases, such heating units are installed in open heating systems, where the circulation of boiler water is carried out naturally, due to gravity. A solid fuel boiler made of cast iron can be installed in heating systems with forced circulation, however, the operating pressure in the system should not exceed 1.5 Bar.
Home renovation, landscape design, DIY garden
Author: Stanislav Dovydenko
Cast iron gas boilers are deservedly considered throughout the world to be the most reliable, powerful and at the same time economical heating systems. And it is not without reason that when in our country most of the owners of country houses begin to seriously think about choosing the most powerful heating system, gas boilers come to the fore. And here, the undisputed favorite is gas boilers made from the most durable metal - gray cast iron.
So what advantages do they have anyway? And why should you choose only them?
And here it is worth emphasizing several of their obvious advantages:
Firstly,
Cast iron gas boilers have a phenomenally long service life. There are options for cast iron boilers that have lasted 35-40 years and continue to serve their owners faithfully to this day! Such durability is understandable - all parts of these types of boilers, even their heat exchangers, are entirely traditionally smelted from good old cast iron alloy.
Secondly,
All cast iron boilers are characterized by an exceptionally high level of performance. Even in the oldest versions of boilers of this type, efficiency can reach 89-91%. And this is a significant number. Especially considering that most cast iron boilers still operate in the gravity cycle. That is, in order for the coolant to begin circulating throughout the entire heating system, it must first be heated to at least 100 degrees Celsius. Such boilers are usually called gravity boilers.
But they have their main drawback - they begin to sharply lose productivity if the gas pressure in the gas line becomes critical. And modern cast iron boilers, which have pre-installed circulation pumps with a magnetic coupling, activated by a thermostat command, can come to the aid of the owner of a country house. The entire system begins to operate in a single mode even in cases where the coolant temperature is far from 100°C.
Third,
modern types of cast iron gas boilers have built-in cold water heating systems (DHW). And if you install either a flow or storage system in your home, then any household will always have hot water in any volume. If a flow-through water heating system is installed, then even the lowest-power (up to 10 kW) cast-iron gas boiler can heat up to 6-7 liters of water per minute! Boilers of this type are most often called double-circuit, because an additional heat exchanger made of either cast iron or steel is installed in the combustion chamber.
In some cases, when it is necessary to obtain an impressive amount of hot water, an additional capacitive tank (up to 50-80 l) is installed, in which hot water, so necessary for most households, will be constantly accumulated.
Fourthly,
Most of the cast iron boilers that have recently appeared on the domestic market have another positive advantage - electronic ignition. You no longer need to constantly keep the wick burning or use ordinary newspaper to ignite the burners. And why is this anachronism needed? After all, you can and should use a modern cast-iron gas boiler, which has in its design electronic fuel ignition, powered by batteries. And even if the electricity in the house is turned off, such a boiler will be able to work properly in autonomous mode.
Post tags: GAS BOILERS, Private house, Cast iron boilers
What models of cast iron boilers are produced
Cast iron boilers, according to their design features, are divided into two generally accepted types:
- single-circuit;
- double-circuit.
The first option is a type of heating unit limited in functionality. Single-circuit boilers provide only autonomous heating.
Important! Hot water supply is not possible in this case. The way out of this situation would be to connect a water heating tank to the boiler or install an additional heat exchanger with a large and constant water flow. For normal operation, the installed DHW elements must be linked to the heating boiler automation system.
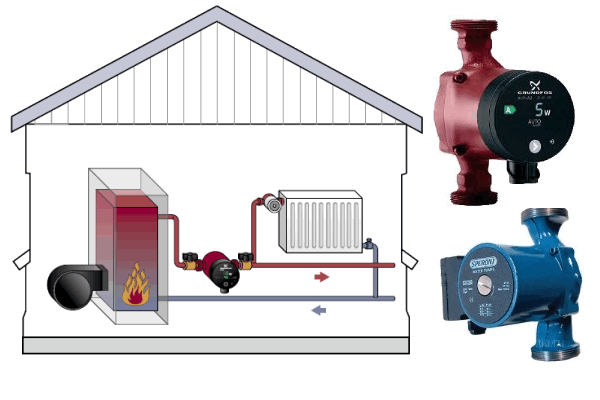
The second option is the most common. Many residents of private houses are interested not only in heating, but also in hot water for domestic needs. In this case, cast iron solid fuel boilers are connected to an additional circuit through which DHW is provided. An additional circuit can be replaced by installing an indirect heating boiler.
Note: for domestic purposes, a boiler with a capacity of 80-100 liters is selected. The limited volume of hot water and the massiveness of the structure itself are a significant drawback of this engineering solution.
If your water consumption is constant and in small volumes, a double-circuit cast-iron solid fuel boiler is quite suitable.
Structurally, heating boilers made of cast iron are divided into units with natural draft and with forced ventilation. In the first case, the air inside the residential building is supplied naturally to the working area of the boiler. Combustion products, soot and soot exit through the chimney in the same natural way. The system is designed for low-power boilers and is suitable for installation in small buildings.
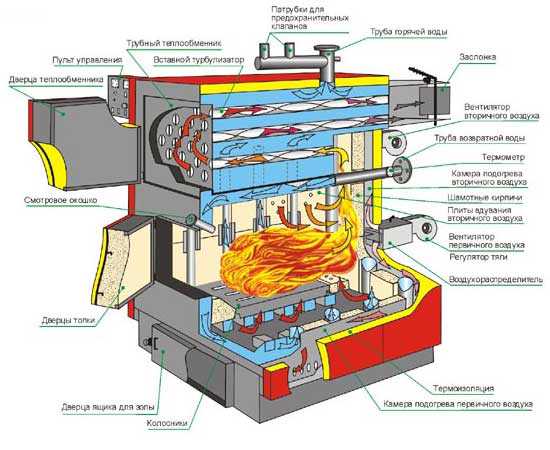
Forced ventilation is a more advanced and reliable design. With the help of a fan, atmospheric air enters the firebox, ensuring combustion of the loaded fuel. The hood works on the same principle. The fan additionally creates a low-pressure zone, due to which combustion products are sucked into the chimney.
Construction of a cast iron solid fuel boiler
The production of cast iron boilers is carried out using expensive special equipment, and the assembly process is very labor-intensive. A cast-iron boiler consists of a sectional body covered with facing panels, thermal insulation, a chimney pipe and heating system connection pipes, doors for loading fuel and for cleaning the firebox, an ash tray, and, if the design allows for it, a boost fan.
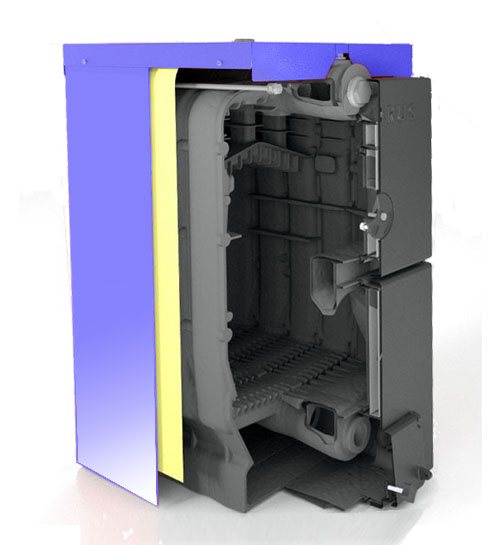

The body of a cast iron boiler consists of sections made by casting from a high-strength alloy consisting of iron and carbon. The sections are connected to each other using threaded connections and sealed with high-temperature sealants. Thus, it is possible to replace sections in case of damage and failure.
The power of a cast iron boiler is determined by the number of sections - the more sections, the higher the power. The increased resistance of cast iron to coolant quality and high temperatures allows the use of almost any type of solid fuel, including coke, coal, wood and pellets.
Cast iron solid fuel boilers - advantages:
- corrosion resistance and durability, service life reaches 25 – 50 years, thanks to the very long service life of cast iron;
- insusceptibility to scale formation on the internal surfaces of the heat exchanger, which has a positive effect on efficiency. Scale is easily removed with water.
- more compact dimensions compared to steel boilers, since the surface of the cast iron heat exchanger absorbs and retains heat better.
- maintainability (possibility of replacing cast iron sections of the boiler);
- it is possible to increase power by adding additional sections.
Cast iron solid fuel boilers - disadvantages:
- The fragility of cast iron causes low resistance to sudden changes in coolant temperature, which can cause cracks in the heat exchanger (loading cold firewood from the street, filling the boiler with cold water, etc.)
- due to the fragility of cast iron, the boiler is sensitive to shocks and shocks (inconvenience during transportation);
- lower efficiency (than that of steel boilers), due to the design limitations of the heat exchanger (production technologies do not allow making a multi-pass heat exchanger from cast iron).
In conclusion, we can summarize briefly:
- steel solid fuel boilers are more efficient (higher efficiency, longer combustion time per load of fuel), but due to low wear resistance and susceptibility of steel to corrosion processes, they have an average service life of 10 -15 years;
- cast iron solid fuel boilers are less efficient (more heat loss, less efficiency), but they are unpretentious to fuel, due to the fact that cast iron is practically not subject to corrosion and have a long service life - 25 - 50 years.
- Heating a private house
- Condensing boilers
- Pyrolysis boilers - design and principle of operation
Construction of a solid fuel boiler in a classic configuration
A classic solid fuel cast iron boiler is a complex mechanism in which each element has its own purpose and performs certain functions. High structural strength and reliable connections of individual structural elements ensure safe operation of the unit.
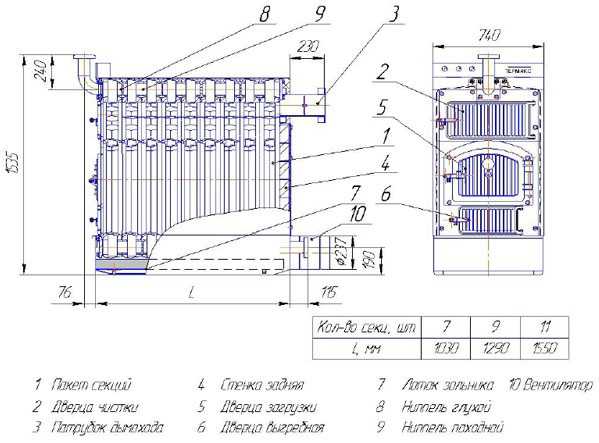
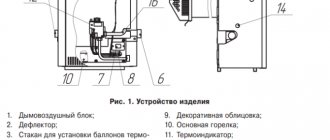
The number of sections in cast iron solid fuel boilers is always fixed. The diagram below shows the structure of a cast iron boiler and the location of the main structural elements. The main components of a cast iron boiler are:
- sections;
- pipe (chimney outlet);
- nipples;
- combustion chamber with door;
- ash tray;
- fans.
Almost all parts and components of the structure are interchangeable, which makes the cast iron boiler very convenient and practical to maintain. The absence of complex structural products and devices simplifies the operation of the boiler in domestic conditions. The design of the boiler is simple and understandable even to the layman who is not initiated into boiler equipment.
As for the control mechanism, the situation here is ambiguous. Cast iron boilers using coal or other fossil fuels in most cases have a mechanical control system. The main control mechanism is the draft regulator, which is responsible for controlling the decrease or increase in the heating temperature of the coolant. Modern devices, produced mainly by foreign companies, are equipped with controllers and blower fans
For reference: blower fans are installed on solid fuel cast iron boilers to eliminate the resistance that arises in the air duct.
Such devices have little impact on the boiler’s ability to be adjusted; however, due to additional equipment, the efficiency of the boiler increases. The combustion chamber and cast iron sections are not picky about fuel quality. Unlike pyrolysis boilers, which require dry (maximum 20% humidity) fuel, long-burning cast iron boilers can handle any type of fuel, in any condition.
Disadvantages of cast iron boilers
Now let's look at the disadvantages of cast iron boilers, which are revealed during their practical use.
Let's start with the fact that few buyers and installers can professionally operate and maintain cast iron boilers. As a result, boiler ruptures are common due to cold water entering them. This is the main “minus” of cast iron boilers. And if you wire such a boiler, as required by manufacturers and regulations, it will cost significantly more than a steel boiler.
In addition, it is often technically impossible to direct the return flow of waste water into a cast iron boiler so that it is preheated before entering.
Advantages and disadvantages
Before choosing a boiler for an autonomous boiler system, you should weigh the pros and cons. Each type of heating device has its own advantages and disadvantages. Solid fuel boilers made of cast iron also have their advantages and their obvious disadvantages.
We have already said that heating equipment of this kind is very inert and difficult to adjust. It takes a long time for the boiler to cool down. When installing the device in a heating system, it is necessary to install an expansion tank, which acts as a temperature regulator of the coolant in the circuit.
A significant drawback, if the operating conditions are not met, for this heating equipment is the fragility of the cast iron heat exchanger. Such units suffer greatly from mechanical damage, sudden temperature changes and water hammer.
Important! When transporting the new boiler, care must be taken to avoid impacts or falls.
Damage to the heat exchanger can be avoided if you follow the operating rules. Do not load cold firewood into the firebox or fill the device system with cold water. For reliability, you can install mixing units that act as a mixture.

In technological terms, heating devices with cast iron heat exchangers are significantly inferior to gas units and other types of solid fuel equipment in terms of thermal efficiency.
Compared to steel appliances, heating appliances made of cast iron are more expensive. However, you should not bring all the listed factors together and give up on equipment of this type. The advantages of this technique are obvious:
- long service life;
- high resistance to corrosion processes;
- absence of scale inside the heat exchanger;
- maintainability and manufacturability of the boiler design itself;
- acceptable dimensions of equipment corresponding to living conditions;
- high resistance to electrochemical reactions and to sharp drops in boiler water temperature.
The main advantages of cast iron boilers:
- Durability of trouble-free operation;
- Low cost;
- Do not require a separate room;
- Convenience and ease of maintenance;
- No noise effects during operation;
Models using gas are highly popular due to the availability of this type of fuel in our country. Even low pressure in the gas central allows such devices to function quite well, delivering the required amount of heat, quite sufficient to create a comfortable environment. Therefore, during severe frosts, the use of this type of heating devices is quite advisable in the northern regions of Russia.
Let's sum it up
Solid fuel appliances steadily occupy one of the consumer niches among heating equipment. The wide technological capabilities possessed by the new models have brought heating devices made of cast iron to a new level.
Today, solid fuel units made of cast iron are becoming a mandatory attribute of a country house. The omnivorous nature of heating devices in terms of fuel, unpretentiousness in maintenance, and simplicity of design make these devices competitive products in the heating equipment market. The high cost of products should not confuse the consumer. The invested funds will pay off in full, taking into account the service life of the boiler equipment.
Features and advantages of cast iron boilers
A heating boiler made of cast iron is a structure consisting of separate sections. Its elements can be moved to the place of further operation and assembly and installation can be carried out there. This is convenient not only when it is necessary to transport equipment, but also in case of its breakdown. But this is far from its only advantage.
A heating boiler made of cast iron has the following positive characteristics:
- High corrosion resistance. A small layer of dry rust may form in the upper layers of cast iron, but it does not progress further. As for wet corrosion, it also affects cast iron material slightly less than steel.
- The thickness of the boiler walls is quite high, which has a beneficial effect on its durability.
- High levels of wear resistance and heat transfer.
But do not forget about the rules for operating heating equipment. A properly designed heating system should minimize the formation of condensation in the boiler furnace. Excessive humidity can occur when the temperature of the boiler walls drops below the dew point. For diesel-powered equipment this figure is 47-49°C, while for gas boilers it is slightly higher - 54-55°C.
If the basic rules for using a combustion device are not followed, condensation may accumulate on its walls, which in large volumes contains sulfur oxide and other impurities that form an aggressive environment. This moisture can gradually corrode the walls of the product.

Cast iron or steel heat exchanger?
Solid fuel boilers of both types have both advantages and disadvantages. It is impossible to say for sure which heat exchanger is better - steel or cast iron. But so that you can decide what is best for you, below I will list all the pros and cons of both types of solid fuel boilers.
Solid fuel boilers with cast iron heat exchanger.
Cast iron boilers are structures assembled from sections cast in the factory (and only in the factory). They are connected to each other by threaded elements. The seams are coated with high-temperature sealant. The design of a cast iron boiler itself is quite simple - it is a set of those same sections. The more sections, the more powerful the boiler. The removal of flue gases from the furnace is usually direct and does not have additional passages or heat exchangers.
Advantages of cast iron boilers:
1. It's definitely durable. Cast iron is less susceptible to corrosion, it is resistant to scale and weak acids (condensation), and its service life is many times longer than that of steel boilers.
2. Cast iron boilers are not afraid of high temperatures, so chipboard scraps and coal can be used as fuel without unnecessary fears.
3. For most cast iron boilers, you can add power if necessary, simply by increasing the number of sections to the size you need, although this procedure is not cheap, but it is possible.
4. Thanks to the prefabricated structure, cast iron boilers can be repaired. As far as you understand, repairs should be carried out by specialized specialists, preferably from an official service center. Only they may have special equipment. I don’t recommend trying to replace the section yourself.
Disadvantages of cast iron boilers:
1. Cast iron itself is a very hard material, which in turn makes it brittle. If, as an experiment, you take a hammer and hit an old cast-iron radiator, it will crack or split, losing its tightness, but a steel canister can be splashed into a cake with the same hammer and it most likely will not lose its tightness.
The same thing can happen to the boiler during transportation, unloading, etc.
2. The cast iron heat exchanger is afraid of sudden temperature changes. This is fraught with possible cracks. Therefore, it is strictly not recommended to throw firewood into a hot firebox from the cold, and I am already silent about filling an overheated boiler with water. More details about the safety systems of solid fuel boilers.
3. The efficiency of a cast iron boiler is usually less than that of a steel one. This is mainly due to the fact that in a steel solid fuel boiler, manufacturers try to use flue gases to heat the coolant, installing additional heat exchangers.
Solid fuel boilers with steel heat exchanger
The designs of steel boilers are more varied than cast iron ones. Classic, pyrolysis, top-burning, pellet. The manufacturing method itself is based on welding elements made of sheet steel. Most often, the heat exchanger is a “water jacket” around the firebox in which the coolant is heated. In some models, for better heat transfer, additional dampers with heat exchangers are installed along the exit path of flue gases, thereby increasing the efficiency of the boiler.
Advantages of solid fuel boilers made of steel:
1. Larger selection of models. As an example: A pellet boiler, if there is a large bunker or pneumatic feed, can be loaded once a month. With cast iron, such terms are not realistic. Or a solid fuel boiler that works on the principle of pyrolysis - it is at least 40% more economical than a cast iron one.
2. Steel boilers are more convenient to maintain. Their heat exchangers are much easier to clean. In addition, steel is not afraid of impacts, which greatly facilitates the work of removing carbon deposits, but it must be cleaned otherwise the efficiency of the boiler decreases.
3. Steel boilers have a more impact-resistant structure and therefore there is no need to worry about them being damaged during transportation and unloading.
4. It is much easier to repair a solid fuel boiler made of steel than a cast iron one. All damage can be repaired locally, of course, if it is not global in nature.
Disadvantages of steel solid fuel boilers:
1. Steel is susceptible to corrosion, so the service life of the boiler is shorter than that of cast iron.
2. If a steel boiler is not properly tied, as a result of which condensation forms in it, and this is a weak acid, its service life can be limited to 2-3 seasons. Cast iron can leak this brown liquid for decades.
3. Steel tends to burn out. So, before buying a solid fuel boiler, ask what steel the firebox is made of and what its thickness is. I recommend not to use boilers whose combustion chamber steel thickness is less than 4 mm. As for how much of a boiler it is, as some manufacturers claim, we’ll talk about that here.
3. The power of a steel boiler, unlike a cast iron one, cannot be increased.
REMEMBER:
The SAFETY, PERFORMANCE and DURABILITY of your solid fuel boiler depend on correct installation