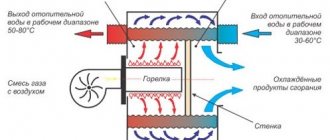
A steam boiler is one of the most popular and widely used types of heating units. The main structural part of the unit in question is the combustion chamber. It burns the loaded fuel with intense release of thermal energy. The generated heat is used to heat water with further release of steam. Steam is used for various industrial and domestic needs, in particular for home heating. At the same time, you can easily handle making a simple boiler with your own hands.
DIY steam boiler
Design Features
The design of the boiler in question is based on a kind of drum. Pre-prepared water is supplied to this piece of equipment through a system of pumps and pipes. The lower compartment of the boiler contains down pipes. These elements have different diameters and do not heat up during boiler operation. Through a pipe system, liquid from the drum passes into the collectors. The latter are most often located at the bottom of the boiler.

Steam boiler
The collector is connected to the drum using a lifting pipeline. Due to the pipeline, heating surfaces are created at the place of combustion of the loaded fuel.
A pipeline system operating according to the mechanism of communicating vessels is connected to the steam generator. A mixture of liquid water and water vapor circulates in hot pipes. This mixture has a fairly low density, which allows it to easily flow into the separator compartment, where steam and water are separated. The liquid component is sent to the steam boiler drum.
The steam passes into the steam line, and then into special heaters, where the pressure and temperature of the steam increase to the required parameters. Finally, the steam is sent to the appropriate steam turbine.
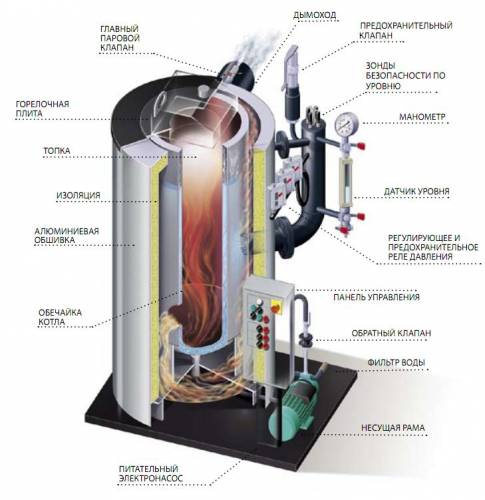
Making a steam boiler
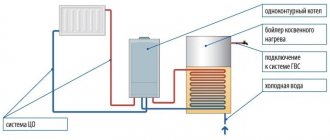
Types of boilers: hot water, steam pyrolysis
Depending on whether the device will heat a hangar or a small warehouse, two heating supply options are provided - steam or hot water. To heat indoor production areas, hot water boilers are most often used. And the steam pyrolysis option is well suited for residential buildings and small premises. Which of them is more economical and which is more expensive should be calculated individually, based on the parameters of the area, principle and design of each model separately.

Heating boiler Protherm Bizon NO 100
Types of steam boilers
There are several modifications of steam boilers. They are divided according to the following characteristics:
- a method of moving a mixture of steam and water. In accordance with this parameter, the equipment is divided into boilers with forced and natural movement;
- condensate return method: open and closed devices;
- nature of coolant movement: gas-pipe and water-pipe units.
Gas-tube and water-tube heating equipment have different designs and efficiencies. The category of gas-pipe equipment includes boilers in which the movement of gas is carried out in flame and smoke tubes. As they move, the gases heat the water in the system. The tubes rest on the side faces of the combustion chamber.
In water-tube equipment, water circulates through tubes. In this case, gases wash the pipes from the outside.
The boilers in question can use solid fuel, as well as fuel oil and gas.
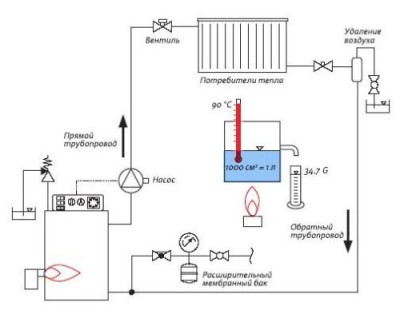
An example of organizing steam heating
Differences from fire tube boiler

The difference between these units lies in the configuration of the placement of the combustion chamber or, in principle, the source of thermal energy relative to the heat exchanger and water tank. Firstly, generating steam is not necessary at all. A fire tube boiler mainly works for heating with water, providing the function of a domestic hot water system. Secondly, in such boilers the firebox is located in the center of the structure, and the containers with water circulation circuits are of an applied nature. They come into contact with the heat exchanger on the outer surface of the structure.
But this is not the only difference between fire-tube and water-tube boilers. The difference also occurs in the means of regulating the heat exchange process. The design of the water-tube unit includes an economizer, thanks to which the initially cold water is preheated. Accordingly, further heat exchange reactions occur more intensely and with less energy consumption. On the other hand, the advantages of fire tube equipment include structural simplicity and a minimum amount of maintenance activities during operation.
How does a typical steam heating boiler work?
Heat is generated in the combustion chamber. Subsequently, it arrives at the heating surfaces. There are 2 types of heating surfaces: convective and radiation.
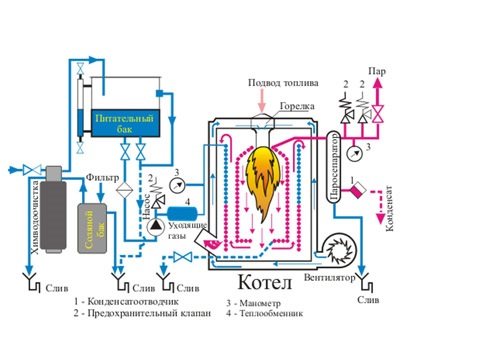
Operating principle of a steam boiler
The composition of convective surfaces includes the following elements:
- air heaters;
- economizers;
- heat exchange devices.
The listed additional equipment is needed to increase the efficiency of the boiler, rationalize fuel consumption and reduce the level of heat losses.
It is important that the water used to operate the boiler is extremely clean - impurities are unacceptable. Therefore, before being fed into the boiler, the liquid must be cleared of gases and various impurities, ultimately becoming nutritious.
The purified liquid is sent to the economizer. A special pump helps her with this. The economizer heats the coolant liquid under the influence of gases. Next, the liquid passes into the upper compartment of the drum compartment. Here the boiler water is mixed with the nutrient liquid.
A certain amount of water passes from the upper compartment of the drum compartment to its lower compartment. The movement of water occurs through boiling tubes.
At the top of the steam boiler, the gases have a lower temperature, which gradually increases as they approach the lower compartment of the unit.
The water is heated and, together with a mixture of steam and water, is sent to the upper chamber of the drum.
The second part of the liquid from the upper drum compartment goes for redistribution. The boiler water is heated. The resulting steam bubbles go to the upper compartment of the drum compartment.
In the upper chamber of the drum, due to the separator, the mixture of liquid and steam is almost completely separated. As a result, saturated steam is created, which further increases the efficiency of the boiler. It is this saturated steam that is used by the end consumer.
In order to increase the efficiency of boilers, their operation is organized in such a way that in the upper chamber of the drum compartment the level of “lower” and “higher” water fluctuates. Between the mentioned liquid levels there is a reserve supply of water designed to maintain the operation of the heating unit in the event of a loss of liquid flow into the system.
The permissible “highest” liquid level in the drum compartment is determined with the expectation that water does not enter the superheater.
The maximum permissible “lowest” liquid level in the drum is calculated so as to prevent overheating of the upper compartment of the drum, as well as the boiler bundle. It is important that water enters the downpipes in a stable volume.
To further increase efficiency, the design is equipped with an air heater.
The liquid in the system can circulate forcibly and naturally. Natural movement is based on the difference in density between the liquid and the vapor being created. The mixture of water and steam in the rising tubes has a lower density than the same composition in the descending tubes. However, the pressure and temperature remain the same throughout the tube. As a result, the steam, which is a gas in nature, rushes upward.
Forced circulation is provided by special pumping equipment.
Scheme for transferring a steam boiler to hot water mode
Design and types of fire extinguishing boilers
Despite the fact that the boilers discussed below, strictly speaking, do not belong to energy-generating equipment, they structurally have much in common with water-heating steam boilers, and therefore are also discussed in this article.
The sequence of action of the fire extinguishing boiler (see Fig. 5) is that the gaseous combustion products formed during smoke or fire enter numerous pipes, which are completely immersed in water. Structurally, this receiving unit is designed in the form of a sealed vessel, the heat exchange of which with the environment is practically absent. As hot gases pass through the gas outlet pipes, the water inside the vessel is heated. As a result, steam is formed, which, due to the specific purpose of such a boiler, remains inside the unit. Such steam can be used to generate energy, but the efficiency of this process will not be significant, since there is no possibility of increasing the steam pressure in boilers of this type.
It has been proven that the heat-generating capabilities of fire extinguishing boilers are limited by steam pressure of no more than 1700...1800 kPa, with a productivity of no more than 9...10 tons of steam per hour. Steam boilers of these types are installed in metallurgical plants, where a sufficient amount of hot gases is produced. In addition to their main duty, boilers of this type also significantly reduce the risk of fire at facilities that use open flames (which is why they are called fire extinguishing boilers).
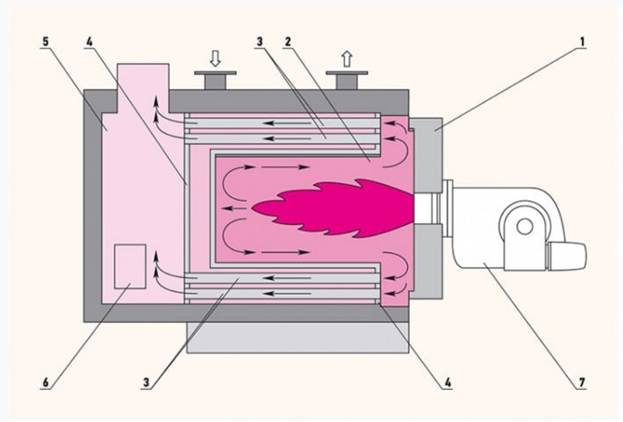
Figure 5 – Sequence of operation of a chimney-tube fire extinguishing boiler: 1 – Facade damper; 2 – Combustion device; 3 – Smoke pipelines; 4 – Pipe boards; 5 – Front part of the boiler; 6 – Inspection hatch; 7 – Block of fuel combustion devices
Types of fire extinguishing boilers
They can be with external and internal locations, and of three different types:
- Long-tubular with reverse counterflow (see Fig. 6);
- With a short fire tube (see Fig. 7);
- Compact.
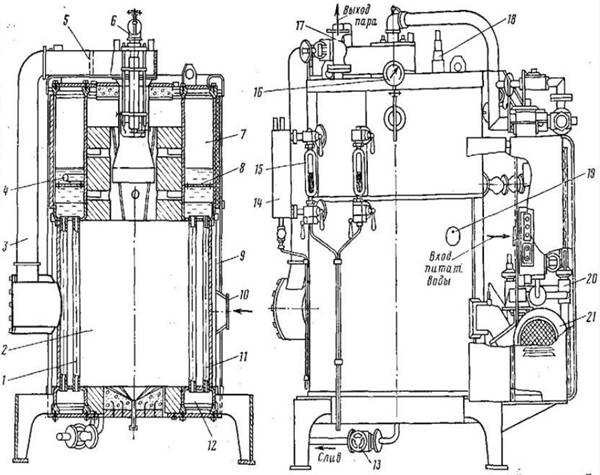
Figure 6 – Design diagram of an automated long-tube vertical boiler: 1 – Screen pipelines; 2 – Combustion space; 3 – Air duct for heated air; 4 – Feeder; 5 – Register for air; 6 – Fuel burning device; 7.12 – Upper and lower collectors; 8 – Grid steam distributor; 9 – Hull casing; 10 - Vent filter; 11 – Convector pipes; 13 – Drain valve; 14 – Level gauge grid; 15 - Water indicator; 16 – Pressure meter; 17 – Main valve; 18 – Safety valve; 19 – Observation hatch; 20 – Pumping unit; 21 – External air supply fan
Figure 7 – Layout solution for a boiler with short-length fire tubes: 1 – Fuel combustion device; 2 – Main pipe block; 3 – Explosion valve; 4 – Power supply; 5 – Gas box; 6 – Economizer; 7 – Portal frame; 8 – Maintenance area; 9 – Support; 10 – Drive; 11 – Supply pipeline
Steam boilers of the first type can have vertical or horizontal gas exhaust pipes. In boiler houses or low-power thermal power plants, boilers with pipes located horizontally are mainly used. They consist of the following nodes:
- Horizontal block.
- Several pipelines, usually located at a certain angle (this improves the conditions for the flow of flue gases).
- Bottom bypass valve.
- Upper bypass valve.
- Smoke chamber.
- Ribs separating individual pipeline tubes.
- Steam trap.
- Gas receiver.
- Cases.
Boilers of this type usually use as fuel the fuel that is used in the main metallurgical unit (for example, in metallurgical plants it is coke, in boiler houses it is coal). The fuel burns below this horizontal block, and the resulting combustible gases, using convection, move in countercurrent to the opposite part of the boiler body. There they enter the pipelines and are directed in the opposite direction into the smoke chamber. During this movement of gases through the pipes, they release the heat they have accumulated through the walls to the surrounding water. Initially, individual steam bubbles appear in it, and then intense steam formation begins, as a result of which the pressure in the internal tank of the steam boiler increases. To control this process, steam boilers are equipped with instruments and automation devices, the main ones of which are the lower and upper safety valves. The lower valve serves to regulate the combustion process of solid fuel, and the upper valve serves to limit the pressure of the generated steam.
The remaining steam (usually at a lower temperature than usual) is discharged into a condensate trap and is periodically removed from the boiler.
Fire extinguishing boilers of other types structurally have much in common with the above, but differ in the length of the pipelines and their location. However, with a vertical version of the unit, the conditions for steam generation deteriorate and the efficiency of the steam boiler decreases, so compact installations are designed only when there is not enough space in the boiler room.
Fire extinguishing boilers are universal, easy to manufacture and operate, and can be easily integrated into the existing heat supply system of an enterprise or even a small urban area. They can be effectively used to localize possible fires. However, the considered units also have significant limitations, which are as follows:
- The volume of water that is inside the body of such a boiler is quite large, so it will take a long time to heat a large mass of water. With increasing steam pressure, this time increases even more.
- Inside the housing, water and steam are in the same volume, therefore, for safety reasons, increasing the pressure above a reasonable level is unacceptable.
- The resulting steam is characterized by high humidity, which negatively affects its properties as an energy carrier.
Assembling a simple steam heating boiler
If desired, a basic boiler can be assembled with your own hands. A homemade unit will have a somewhat simplified design compared to factory-assembled equipment, but this will in no way affect its efficiency and efficiency.
Boiler assembly kit
Before you begin, prepare the following items:
- pipes of different diameters;
- stainless steel sheet;
- sheet asbestos;
- safety valve;
- hacksaw;
- ruler;
- roulette;
- chisel;
- hammer;
- welding machine;
- file.
Assembly of the unit
The work of making a boiler yourself is carried out in a few simple steps. Follow each step of the instructions sequentially, simultaneously focusing on the drawings and diagrams.
First step. Determine the optimal dimensions of the future steam boiler. Its performance directly depends on the size of the equipment. Please clarify this point individually, taking into account the specifics of your specific situation.
At this stage, prepare all the necessary drawings. If you wish, you can order their preparation by a professional or use ready-made drawings from open sources.
Second step. Prepare the necessary materials. Previously, a list of required elements was given. First of all, buy pipes with a diameter of 32 mm and 12 mm. The stainless steel sheet should have a thickness of about 2-3 mm.
Third step. Prepare the boiler body. The best option is to weld the body yourself from sheet metal. Select the dimensions of the case individually, according to your needs.
Fourth step. Make the base of the boiler. It was previously said that the design of steam boilers is based on a system of interconnecting pipes. First of all, prepare a piece of pipe about 11 cm long with a wall thickness of about 3 mm.
Cut a pipe 11 cm in diameter into 12 elements - they will serve as smoke pipes. Cut a larger diameter pipe into flame tubes.
Select the length of the pipes in accordance with your diagrams.

Copper pipes
Fifth step. Make the required number of bulkheads and walls of the steam boiler. To do this, use stainless steel sheet.
Sixth step. Prepare holes in the walls of the unit to accommodate flame and smoke pipes. Attach the mentioned elements in flared form to the base of the boiler. A welding unit will help you with this. At this stage, also focus on the available drawings and diagrams.
Seventh step. Attach the safety valve and steam manifold to the unit body. You will subsequently release residual steam through the valve.
Eighth step. Insulate the boiler using asbestos sheet.
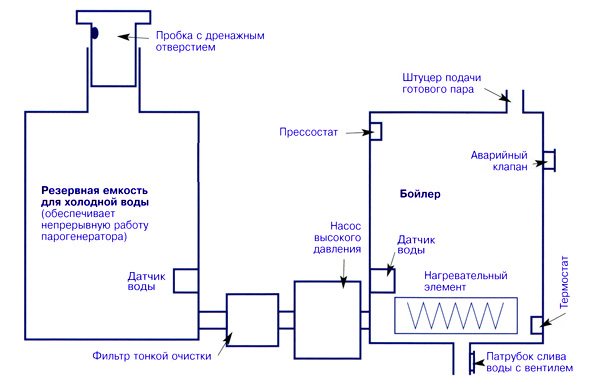
Steam generator connection diagram
Thus, having understood the basic provisions of the instructions, you can independently assemble a simple steam generator and include it in the heating system of your own home. At each stage of the work, be guided by the drawings you have, because It is impossible to understand the assembly procedure of the unit using textual recommendations alone.
Conditions for safe operation of the boiler
The boiler must be not only efficient, but also safe. The key to reliable and efficient operation of a steam heating boiler is maintaining a given level of heating of the metal elements.
In view of this, the coolant must constantly circulate inside the heated tubes while simultaneously cooling the heating surfaces. It is important that the coolant stably removes heat from the pipe material, which is heated under the influence of flue gases. If heat removal is insufficient, the metal will simply overheat, become less durable, and the efficiency and safety of the equipment will decrease. In the worst case, the pipes will simply burst.
Check the operation of the boiler regularly. Correct all problems immediately after they are discovered. Even the slightest defect can quickly lead to a significant decrease in the efficiency of the unit and a deterioration in the safety performance of the system. Water will come out of the drum, steam will penetrate into the drop tubes, the drum and tubes will heat up too much, and an accident will occur.
Also, you, as the owner, must ensure that all design elements and equipment used are of exceptionally high quality.
Differences from gas pipe equipment
In water-tube units, the direct transmitter of thermal energy is hot water, filling the circulation pipes of the heat exchanger. The result is an efficient and safe generator that promotes steam production. As for gas-tube boilers, the technical design, even externally, may partially correspond to water-tube structures. The only difference is that the carrier of thermal energy will be the gases exhausted in the combustion chamber. How does this affect the operational process? If the operating principle of a water-tube boiler allows for complete consumption of the exhaust products without residues until evaporation and further use of the steam, then a gas-tube boiler will have to release the working gaseous medium already in the heat exchanger system. Moreover, thick pipes are provided for this purpose to ensure the safety of the process.