Foamed polyethylene (or in other words polyethylene foam PPE) is a gas-filled thermoplastic polymer with a closed-porous structure, a soft and elastic material with excellent shock-absorbing properties. The production of foamed polyethylene has made the thermal insulation of building and instrument-making elements, as well as the packaging of a whole range of products, much simpler and more convenient.
Kinds
Based on foamed polyethylene, many types of insulation are produced with different purposes: heat, hydro, and noise insulation. There are several options that are most widespread.
- Polyethylene foam with foil on one or both sides. This type is a variant of reflective insulation, most often sold in rolls with a sheet thickness of 2–10 mm, cost per 1 sq. m – from 23 rubles.
- Double mats made of polyethylene foam. They are classified as basic thermal insulation materials and are used to cover flat surfaces, such as walls, floors or ceilings. The layers are connected to each other by thermal soldering and are completely sealed. Sold in the form of rolls and slabs with a thickness of 1.5–4 cm, cost per 1 sq. m – from 80 rubles.

- "Penofol" is a branded product from a well-known manufacturer of building materials of the same name. Polyethylene foam of this type has good noise and heat insulation. It consists of a sheet of polyethylene foam with perforation and a self-adhesive layer, ensuring convenient installation. Sold in rolls 3–10 mm thick with a length of 15–30 cm and a standard width of 60 cm. The cost of 1 roll is from 1,500 rubles.
- "Vilatherm" is a heat-insulating sealing harness. It is used for thermal insulation of door and window openings, ventilation and chimney systems. The operating temperature of the product ranges from -60... +80 degrees C. It is sold in skeins with a rope cross-section of 6 mm. Cost per 1 linear meter – from 3 rubles.

Foamed polyethylene is harmful to health after 50 years
Info
The purpose of the foil is to create the effect of distributing heat evenly over the entire surface and, using the reflective effect, to retain heat in the room. Therefore, foil heat insulators are used both in private construction and in industrial construction, this is rational. Foil foamed polyethylene Foil foamed polyethylene or foamed polyethylene is the most common heat, noise and moisture insulator.
Photo 1. Foil insulation of the Izolon NPE brand.
What is isolon and its advantages What is isolon and its advantages June 10 When carrying out major renovations of premises, one of the most pressing issues is the issue of sufficient thermal insulation.
This is made possible due to the closed texture of the fiber. Briefly about the technical characteristics Production is carried out by adding air to molten polyethylene and then hardening it.
Manufacturing includes the following stages: polyethylene granules are melted in a special container; liquefied gas is supplied into it, acting as a foaming reagent; due to it, the structure of the insulation is formed. The resulting material is supplied in rolls, slabs or sheets. It also has different densities, dimensions, and thickness, which allows you to select polyethylene for specific purposes of insulating a particular room. The material does not contain toxic substances, therefore, along with the industrial sphere, the lining of pipeline systems, air ducts, ventilation, and refrigeration chambers is used for thermal insulation of industrial and residential facilities. As a rule, manufacturers apply aluminum foil film to the surface on one or both sides, the purpose of which is to effectively reflect heat. To maximize it, the film is polished. Merilon foamed polyethylene For insulation of pipes with a small diameter, located in residential premises or in the ground at a depth of up to 1 m, insulation made of foamed polyethylene is used. The material is environmentally friendly, therefore it does not harm human health and is an excellent solution for residential and industrial premises.
Basic properties
The technical characteristics of foamed PE are a synthesis of the properties of polyethylenes, soft elastic materials with a low melting point, and foamed substances with their light weight and low thermal conductivity:
- Like regular polyethylene, foamed PE is a flammable material, the maximum operating temperature of which should not exceed +102°C. At higher rates it will melt.
- At low temperatures, even when dropped to -60°C, foamed polyethylene will retain all its properties, including strength and elasticity.
- The thermal conductivity of this product is very low, it is 0.038-0.039 W/m*K, which gives products made from it a particularly high thermal insulation coefficient.
- In direct contact with water, foamed PE absorbs it by no more than 1-3.5% of its volume per month.
- Foamed polyethylene is very resistant to chemically active environments, in particular to oil and gasoline products.
- Does not degrade in a biologically active environment (does not rot, is not susceptible to the action of bacteria and fungus).
- It absorbs sounds perfectly, so PPE can be used for sound insulation.
- Absolutely non-toxic, even during combustion.
- Easy to transport and install,
- Wear-resistant and durable up to 80 - 100 years of service.
Flaws
A negative property of foamed PE is its intolerance to ultraviolet rays. Direct exposure to sunlight has a destructive effect on it, therefore both storage and use of foamed polyethylene should take place in places protected from light. Otherwise, the material itself must contain protection, at least in the form of an opaque film.
Features of polyethylene foam
- Low thermal conductivity. This allows it to be used for arranging thermal insulation layers of buildings and structures.
- Variety of assortment. Polyethylene foam can be “simple”, foil-clad, reinforced (for example, with fiberglass, used for greenhouses), or included in other materials. By introducing various components into the initial composition, the final product can be given the required characteristics (strength, frost resistance and a number of others).
- From an environmental point of view, the material is clean, since the use of freon is not provided for by the manufacturing technology.
- Good water-repellent properties. Foamed polyethylene is well suited for protecting surfaces that are constantly exposed to liquids.
- Ease of working with the material.
- High soundproofing qualities.
- Polyethylene foam can reduce the likelihood of ignition of other materials. For example, it is often used to protect wood.
- Some types of products can be operated in the temperature range = 240 0C (from - 60 to + 180).
- Possibility of lamination with almost any material (films, lavsan, paper and others). Thanks to this, it is used everywhere.
- Durability, elasticity, wear resistance. Not damaged by insects, rodents, mold or mildew.
- The low price of the product makes it accessible to families with any income.
comparison of thermal insulation properties
Application
For packaging goods for various purposes, as a cushioning layer
This is especially important to ensure the safety of goods transported. The material is available in thicknesses from 0.5 mm to 2 cm, which allows it to be used universally. As screens to reflect heat
This property is used, for example, when finishing saunas (steam rooms) and refrigerators. At defense enterprises. This seemingly fragile material is, for example, an “integral part” of body armor. Well, the most common use is to reduce heat loss by various structures (thermal insulation): buildings and structures, pipelines and utility wells, tanks and caissons, ventilation ducts and technological shafts.
By the way, products with one-sided foil are excellent for mounting on the wall behind heating radiators, since this increases heat transfer into the room (the efficiency of the devices increases by 1/3). But foiling on both sides is an excellent option for roof insulation. They reflect both the heat rising from inside the building and the thermal energy of the sun's rays.
Given the diverse range of products, it is impossible to list all types of products. But it is appropriate to give approximate prices for some of its varieties.
Sold in roll form. The thickness of the material ranges from 2 to 10 mm.
Price – from 23 rubles/m2.

Duplicated mats
Thickness from 1.5 to 4 cm. Suitable for thermal insulation of flat surfaces over large areas. They are connected thermally, which eliminates the need for further sealing of the seam.
Price – from 76 rub/m2.

Penofol
For arranging layers of heat and vapor barrier. In rolls, with perforation. There is a self-adhesive coating. The thickness of the material is from 3 to 10 mm, the length per roll is from 15 to 30 m with a standard width of 60 cm.
Price – from 1,200 to 1,500 rubles/roll.

Vilaterm
Thermal insulating sealing harness with a cross section of 6 mm. It is used in the temperature range from - 60 to + 80 0C. For sound and heat insulation of ventilation ducts, window and door openings (for example, in Swedish insulation technology), smoke removal systems and much more.
Price – from 3.12 rubles/l.m.

Unsupported Browser
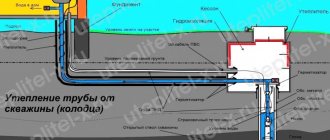
Areas of application of pipe thermal insulation. The importance of insulating pipes is obvious, since most have encountered the problem of freezing. To prevent such unpleasant situations from occurring, special insulation for pipes is used.
Home Foamed polyethylene is harmful to health Foamed polyethylene is harmful to health Products are considered optimally convenient for thermal insulation of large areas with a relatively flat surface.
- With foil on one or both sides, it is used in places where not only direct retention of warm air is required, but also reflection of thermal radiation and fire protection properties (roofs, walls, places behind heating radiators, internal surfaces of reflector heaters, etc.)
- In the form of tubes, polyethylene foam is used as a protective shell for water pipes, sewers, heating and air conditioning systems.
- In the form of a rope, it is used to cover seams and gaps in walls, window and door openings, etc.
Each type of polyethylene foam insulation can have self-adhesive surfaces for ease of installation.
IMPORTANT! For modern polyethylene foam insulation, finishing can be provided not only from film, but also from materials such as paper, lavsan and denser plastic.
Attention
Foamed polyethylene insulation - types and characteristics Progress does not bypass even construction, where more and more advanced materials are used to insulate buildings. One of them is foamed polyethylene, mass production of which has only recently begun. The material is applicable to almost any area of the house, be it the foundation or partitions between floors and rooms.
The increase in demand for it is due to the fact that insulation made of foamed polyethylene has a low thermal conductivity coefficient, and can serve for almost three decades without deterioration in properties.
Types of foamed polyethylene
Today, several types of this material are produced, which allows you to choose the best option for each specific case.
Thus, in the production of this heat and sound insulator, high or low pressure polyethylene can be used. The finished material may have a slightly different structure:
- foamy;
- cell phone;
- porous.
Depending on the scope of use, the material can be produced in different forms:
- sheet foamed polyethylene is indispensable for insulation and sound insulation of walls, ceilings, roofs, and foundations;
- tiled;
- tubes are used when it is necessary to perform heat and sound insulation of ventilation ducts, door or window openings, etc.;
- films are excellent for greenhouses;
- coated. So, the material can be foiled on one side, and then it is excellent for insulating walls located behind a heating radiator in order to reflect all emitted energy. If the foil coating is double-sided, then the material is good to use for roof insulation, because in this case the sun's rays and heat will be reflected from the heating elements, and an optimal microclimate in the room will be easy to maintain both in winter and summer.
But most often, foamed polyethylene, depending on its molecular structure, is divided into non-crosslinked and crosslinked.
Non-crosslinked polyethylene completely preserves the structure of the molecules and molecular bonds of polyethylene. It is made from polyethylene using the extrusion method by adding a blowing agent, which foams the original product. Previously, freons were used as a gas generator, which, due to their high heat of evaporation, were ideal for this process. Now, after the ban on the use of freons, which destroy the ozone layer, a propane-butane mixture or isobutane is used instead. All transformations occur in the extruder, after leaving which, with a sharp drop in pressure, the gas begins to expand, forming bubbles. And since the temperature outside the extruder is much lower, the finished mass hardens quickly. The final product is a translucent material with many large pores. Its strength is inferior to cross-linked polyethylene, since the intermolecular bonds here are much weaker. This dictates the scope of application of non-crosslinked polyethylene foam.
This type of foamed polyethylene is widely used as a heat and sound insulator in residential and industrial construction, as well as an insulator against water and condensation, but only in those rooms where it will not be exposed to heavy loads and high temperatures. In European countries, this material is used as packaging for a wide variety of items, even fragile ones, as it absorbs shock loads. It has found application in the food industry due to its complete hygiene and inertness.
Cross-linked polyethylene is produced by chemical or radiation methods. The chemical method involves melting polyethylene under high pressure along with reaction initiators and antioxidants. Peroxides, which often act as the initiator of the reaction, undergo a number of transformations, forming bonds between individual polyethylene molecules. A similar effect can be obtained by exposing polyethylene to a beam of energy, which is the radiation method of producing the material. As a result, foamed polyethylene acquires a fine-grained structure, which determines its greater resistance to loads, chemicals, moisture and temperature.
Cross-linked polyethylene is a more versatile material, a reliable heat and sound insulator that can be used in a wide temperature range, which determines its distribution. It is excellent for insulating walls, ceilings, ceilings, floors, pipelines; it is often used simply as a sound insulator or for waterproofing foundations, cellars and basements. In addition, this material has become extremely widespread in mechanical engineering, automotive industry, and medicine. To insulate an apartment, it is better to choose cross-linked polyethylene foam in order to obtain a more durable, strong and reliable coating that can certainly cope with any load.
Description and properties
This material is divided directly according to its structure into two main, main varieties:
- NPE or simply - unstitched;
- X(F)PPE, simply stitched.
A non-crosslinked type of material is a material produced using an extruder from solid polymer products and butane and propane gases. This variety is a linear chain of molecules without the presence of intermediate bonds, so it easily wrinkles, crumples and does not straighten after the cessation of mechanical action.
The cross-linked type of material is in turn divided into two large types:
- with physical “firmware”, denoted by the abbreviation FPPE;
- with chemical “firmware”, sometimes designated by the abbreviation KhPPE.
The main difference between this type and the first from the point of view of any chemist-technologist is that the molecules have not only a linear, but also a cross-link, that is, they are “wired” with each other.
The difference between physical and chemical cross-linking methods is that in the first case, the establishment of cross-links occurs due to the action of electrons, and in the second - chemical reagents, namely free radicals.
The cross-linked material has noticeable external differences - it has smaller bubbles, that is, cells, it is much denser and holds its shape much better.
Cross-linked and non-cross-linked types of material also differ in their properties - the cross-linked type is characterized by low thermal conductivity, it is vapor-proof, easily compressible and returns to its original shape, and also perfectly absorbs sound, for example, music, or any noise. Unstitched, accordingly, has lower performance, but also has a number of unique advantages.
The properties common to both types of material that characterize them include:
- absolute water resistance;
- resistance to the activity of any microorganisms;
- resistance to alkaline and other chemical influences;
- absence of any interaction with the environment;
- ease of installation in any area of application of the material.
A cross-linked type of material is more expensive than a non-cross-linked one, therefore, when planning to use it, it is worth considering whether polyethylene with “cross-linking” is really necessary or whether a more economical, non-stitched option will suffice.
Both types of material are covered with foil; commercially this type is called “foiled polyethylene foam.” Aluminum foil is welded to polyethylene using a thermal welding procedure, and its surface, outer layer is polished.
The use of foil not only increases the thickness of polyethylene foam, but also significantly enhances its characteristic properties:
- thermal insulation increases to 97% compared to the base;
- vapor barrier also increases significantly, due to the elimination of condensation formation;
- there is practically no effect on sound insulation, although the describing instructions allow for the effect of “reflection” of sound.
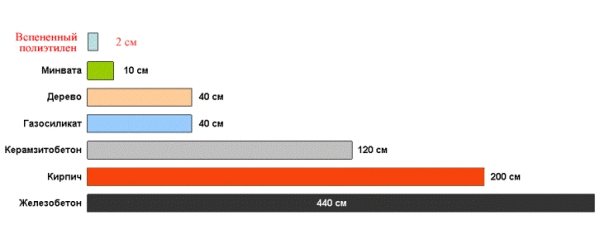
The main advantage of combining the material with foil is the increase in thermal insulation; for example, just a 10 mm layer of polyethylene foam insulation retains the same amount of heat as brick (red brick) masonry 15-20 cm thick.
Thermoflex polyethylene foam with foil is available in the following types:
- one-sided, this type of material is glued to the insulation item or wrapped around it, with a layer of foil facing out;
- double-sided, ideal for interior spaces and partitions, polyethylene foam insulation on both sides “wrapped” with foil, performs its functions equally, regardless of changes in the direction of heat flows, sound waves or noise;
- single-sided with an adhesive base, this is an “improved” single-sided type, the only difference is that you do not need to purchase glue for it;
- single-sided with film lamination, the same one-sided, but the foil layer is reinforced with a film sheet that reliably protects it from mechanical damage;
- with forced perforation is an attempt to combine the qualities of a complete insulator and a “breathable” material; reviews about it are extremely contradictory, but this type of polyethylene foam is best suited for heating and water pipes.
Also, it should be mentioned that the installation of this material is the simplest of all installation works on insulation and insulation of premises, the material weighs very little, and one pair of hands is enough to cover a room with foamed polyethylene sheets.
What to look for when buying polyethylene foam?
When purchasing any building materials, it is important to take into account some nuances that will not only save money, but also not skimp on quality.
Pay for what you buy
Most often, foamed polyethylene is sold in rolls; winding can be completely different. Most manufacturers manufacture the material according to specifications, which may specify ranges of undercuts. This is not a deliberate deception, but a feature of production. Therefore, before purchasing, be sure to check the possible shortage of material, this way you will not only purchase the amount of material you need, but will also be able to compare prices per square meter.

The thicker the better?
Of course, when answering this question, it is important to understand for what purpose you are purchasing foamed polyethylene. If we are talking about the underlay for floor coverings, then this is a myth that will not only lead to wasted finances, but will also negatively affect the service life of the laminate or parquet board.
The optimal thickness of the substrate is 2-3 mm; this is the thickness of the product that allows you to hide the permitted defects in the screed, while the material serves as a kind of damper. Using 5-10 mm polyethylene foam as a substrate is not only impractical, but also destructive, since the base for the flooring becomes too “soft”, which will soon damage the locks of the laminate or parquet board.

The savings are obvious
How to save money without harm? Take a closer look at the most unpopular thicknesses, such as 4 or 8 mm. Perhaps saving 1-2 mm is not critical for your task, but it will help save money, since such materials are cheaper than classic 5 and 10 mm.
Is the foil material better?
In fact, there are a lot of varieties of foamed polyethylene. There are self-adhesive, foil, reinforced and other options. One of the most popular is polyethylene foam with one reflective side. This material is used to reflect heat from the surface. A reflective “substrate” is used in baths, saunas, in heated floor structures, as well as in the installation of heating radiators. In addition, such insulation acts as a barrier to moisture that can enter the structure.
Buy material with a reflective surface only when it is really necessary, because its cost is significantly higher than that of ordinary polyethylene foam.
Production and features of polyethylene foam
Polyethylene foam is made by processing high-density polyethylene (LDPE), to which dyes, refractory reagents and other hydrocarbon compounds are added. For manufacturing, the extrusion method is used, which results in foamed polyethylene with a large number of closed pores with air inside. After this, the material is subjected to heat treatment and foaming at a temperature of 180°, and, if necessary, the finished material is then cross-linked.
Cross-linked polyethylene foam is produced by radiation or chemical means. Polyethylene, reaction catalysts and antioxidant substances are melted, brought to a thermoplastic state, and then sheets are formed and stitched together. Non-crosslinked polyethylene foam is formed by foaming ordinary polyethylene with a propane-butane mixture or freons.
Features of the material
Among the main features of polyethylene foam, the following should be highlighted:
- Excellent thermal conductivity, allowing the use of polyethylene foam for thermal insulation. Thermal conductivity indicators of foamed polyethylene – 0.037 W/m*K
- Reduced hygroscopicity. This property allows the material to be used as a protective barrier against liquids and moisture.
- High-quality sound insulation. The physical properties of the material make it possible to use it as sound insulation not only in construction, but also in mechanical engineering.
- The permissible operating temperature range is 240 degrees.
- Strength and wear resistance. The material is not exposed to biologically aggressive environments, insects and other external factors.
Let us note an interesting fact: 1 cm thick polyethylene foam easily replaces a 15 cm brickwork or a 5 cm layer of mineral wool.
How does polyethylene inhibit the propagation of sound?
In order for polyethylene to acquire soundproofing properties, it is foamed. This is a special state of the polymer: a special foaming agent is introduced into its melt, under the influence of which small air bubbles form and harden. The physical mechanism of the material looks like this:
- The sound wave enters the structure of the polyethylene foam board through its surface.
- Inside, the wave begins to fragment and repeatedly reflect from air obstacles. The direction of movement of the wave changes many times, as a result, a significant part of the wave energy is lost.
- As a result, when passing through a layer of foamed PE, the sound becomes significantly quieter. Even with an insulation thickness of only 10 mm, the noise reduction level can reach 30% of the original volume.
Another important quality of the material is vibration damping ability. That is, the material is optimally suited for insulating moving systems in which noise occurs due to vibration. Therefore, car interiors are soundproofed with just such a polymer.
Properties and characteristics
First of all, you need to understand what the material is. Thus, foamed polyethylene (polyethylene foam, PE) is a material based on traditional and well-known polyethylene. However, unlike the standard variety, the foam type has a special closed-porous structure
In addition, it is important to note the fact that the foam material is classified as gas-filled thermoplastic polymers
If we talk about the time the material appeared on the market, it happened about fifty years ago. Since then, polyethylene foam has been gaining popularity among users. Today, the production of goods complies with all international standards that are prescribed in the relevant GOST.
Before you decide to purchase and use the material, you must evaluate and analyze all the available distinctive characteristics of polyethylene. It should be borne in mind that these properties are not only positive, but also negative. Nevertheless, they all constitute a set of distinctive features of the material.
So, the most important characteristics of foamed polyethylene include certain qualities.
First of all, it is necessary to say about the high flammability of the material. So, if the air temperature reaches +103 degrees Celsius, polyethylene will begin to melt (this indicator is the so-called “melting point”). Accordingly, during operation you must remember this quality of the material.
The material is resistant to low temperatures. Thus, experts report that even when the ambient temperature drops below -60 degrees Celsius, polyethylene still retains such important characteristics as strength and elasticity.
The level of thermal conductivity of polyethylene is very low and is at the level of 0.038-0.039 W/m*K. Accordingly, we can talk about a high level of thermal insulation.

During the operation of foamed polyethylene, one should take into account the fact that the material itself is capable of absorbing sound. In this regard, it is often used to equip recording studios, clubs and other premises that require mandatory sound insulation.
PE does not contain any components that can harm the human body. Accordingly, the material can be used without fear for health and life (both your own and your loved ones). In addition, even during combustion the material does not emit toxic components.
The most important characteristic of polyethylene, thanks to which it is popular and in demand among a large number of users, is the fact that the material can be very easily transported. Also important is the fact that polyethylene foam can be easily installed.
PE is a material that has a high level of wear resistance. Accordingly, we can conclude that it will serve you for a long period of time. If you try to roughly estimate the service life of the material, it is approximately 80-100 years.
During the operation of the material, it is imperative to take into account the fact that it is destroyed by exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Accordingly, direct use of the material must be carried out under protected conditions.
Great variety in terms of color, shape and type of design. The most popular and in demand are rectangular sheets in black and white.
The thickness of polyethylene may vary. This indicator plays a decisive role when choosing a material. So, depending on your needs and preferences, you can choose PE with a thickness of 10 mm, 50 mm, 1 mm or 20 mm.
In addition to the functional characteristics of PE, it is important to study in detail the chemical and physical qualities of PE (for example, properties such as density, ability to absorb moisture, etc. play an important role)
Among the distinctive chemical and physical properties of the material are:
- the recommended temperature range for use of the material is from -80 degrees Celsius to +100 degrees Celsius (at other temperatures the material loses its characteristics and qualities);
- strength can range from 0.015 MPa to 0.5 MPa;
- the density of the material is 25-200 kg/m3;
- Thermal conductivity index is 0.037 W/m per degree Celsius.

Features of insulation manufacturing
The highly elastic material is made from high-density polyethylene.
Polyethylene foam is a high-quality thermal insulation material with excellent technical characteristics. Today this insulation is rapidly gaining popularity and demand in Ukraine. It is made on the basis of polyethylene and has a closed porous structure.
This type of insulation belongs to the category of gas-filled thermoplastic polymers. It is considered an excellent insulator of heat, moisture, noise and steam.
The composition of polyethylene foam includes such components as: LDPE, gas-forming agent, antioxidants, and various additives. Available in rolls (1 m wide and up to 20 mm thick).
One of the most promising insulation materials of our time. It has a relatively low cost, so in terms of price the material is very affordable.
Properties of thermal insulation raw materials
Pipe thermal insulation performs a protective function for pipelines. Foamed polyethylene is used for various engineering communications:
- heating lines;
- cold and hot water supply pipelines;
- sewerage;
- air conditioning systems;
- air vents in ventilation.
For heating and hot water supply pipes, insulation is needed to reduce heat losses in the coolant and level out the thermal expansion of the material. For cold water pipes, the heat insulator serves as protection against freezing and condensation on the surface. Polyethylene foam protects sewer channels from freezing and reduces noise levels. Ventilation and air conditioning pipes are protected from ice and condensation.
Polyethylene foam performs thermal insulation functions due to its technical characteristics:
- thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.03-0.04 W/m*K;
- the density of products varies among different manufacturers from 25 to 40 kg/m3;
- water absorption – no higher than 2%;

- fire resistance class G2 in accordance with GOST 30244 (refers to moderately flammable material);
- application temperature – from -60 to +90 degrees;
- a vapor permeability of 0.001 mg/m*h*Pa allows the material to be classified as completely vapor-proof;
- minimum service life - 20 years, maximum - 80 years;
- strength is expressed in tensile strength at break up to 0.3 MPa and elastic modulus in dynamics up to 0.7 MPa;
- depending on the insulation layer, the sound absorption coefficient is from 25 to 55%;
- resistance to aggressive chemical influences.

High insulation properties demonstrate the features of insulation for pipelines for various purposes. Low thermal conductivity allows you to reduce the thickness of the heat insulator without changing the efficiency. Polyethylene foam exhibits waterproofing properties and protects metal pipes from corrosion. The material does not rot, has high hygienic indicators, fungi and bacteria do not multiply on the surface.
The disadvantages of the heat insulator are flammability at temperatures above 300 degrees, spontaneous combustion at 400 degrees. In addition, the material is not resistant to ultraviolet radiation.
Due to its elasticity, the material is resistant to deformation, but it can be damaged by sharp objects. Low cost and ease of installation allows the use of polyethylene foam at industrial facilities and in private engineering systems.

What it is?
Foamed polyethylene is an artificial elastic material consisting of bubbles filled with gas. Production takes place on special extruded lines, where polyethylene granules are mixed with reagents. During the process, the composition is heated to +140 degrees - a chemical reaction occurs, as a result of which the volume increases 20 times and the material acquires a cellular structure.

The uncooled mixture can be molded to obtain various types of thermal insulation:
- sheets wound into rolls for insulation of building structures and packaging;
- foil sheets with a reflective side;
- harnesses for sealing joints;
- mats for various purposes;
- hollow cylinders for pipeline insulation.
The size of closed bubbles does not exceed 1 mm, which increases the density and technical characteristics of the material. Pipe insulation is made from cross-linked and non-cross-linked polyethylene.
Foamed polyethylene is inert to various materials and mortars. Therefore, pipe insulation can be carried out underground and in the open. Polyethylene foam insulation is suitable for thermal insulation of pipes made of polypropylene, steel, cast iron, metal-plastic, and polyvinyl chloride. It is used in industrial engineering systems, city communications and private pipelines.
Application of non-crosslinked polyethylene foam

- Non-crosslinked polyethylene foam is convenient for packaging and, if necessary, softens pressure during loading. Has an unlimited shelf life. It cannot spoil and is beneficial when packing valuable goods and cargo. In the packaging market, NPE has no equal competitors, and occupies 90% of applications.
- Used as packaging material for electrical equipment, dishes, furniture, glass products. Perfectly protects the surface from dust and technical debris.
- NPE is excellent for insulating from moisture, water, steam, condensation and mechanical noise.
- Subject to minimum quality requirements, it is used in construction as thermal insulation and mechanical engineering. Not suitable for use when there are powerful loads or the air temperature is too hot.
- It is well used to reduce energy costs while saving heat in the house - thanks to reflective insulation. Widely used to level the surface, put under parquet, laminate, linoleum.
- It has a variety of release forms - in polyethylene mesh, in rolls, in sheets of different thicknesses. With a laminated or foil base, non-crosslinked polyethylene foam will perform protective functions depending on the requirements and the task at hand.
- In the European Union, there is a restriction on the use of NPE; it is used only for packaging.