One of the best materials for insulating facades is expanded polystyrene (foam), invented more than 180 years ago. The structure of polystyrene was first discovered by the Russian scientist I.I. Ostromyslensky, but France patented a method for obtaining this element. The first production of polystyrene took place there in 1937. Since then and to this day, its production has been rapidly developing and improving.
Types of expanded polystyrene
At the moment, there are several brands of expanded polystyrene on the building materials market, differing in their production method and properties:
- Pressed expanded polystyrene - produced in various countries under different brands (brands of domestic expanded polystyrene - PS-1, PS-4). This grade of material has a high density (60-600 kg/m3) and is used in various fields of radio engineering.
- Pressless expanded polystyrene (EPS) – brands of domestic material PSB, PSB-S are distinguished by high physical and chemical properties. This material is used for insulating facades.
- Extruded polystyrene foam (XPS) - domestic analogues of EPPS - Penoplex, TechnoNIKOL XPS. This material is also used for insulating facades, but has some disadvantages in comparison with the previous type of polystyrene foam.
- Autoclaved polystyrene foam - this material is not used for insulating facades, so there is no point in considering it in more detail.
Features of the use of polystyrene foam
The scope of application of this building material is wide. Since expanded polystyrene has excellent thermal insulation properties, strength, low price, and ease of processing, it is used as packaging and insulated containers, as an auxiliary means for imparting buoyancy, as a material for modeling, advertising and casting. In addition, it is actively used in agriculture and construction.
In recent years, expanded polystyrene has been actively used to insulate building facades. This technology for insulating facades is called “wet facade”. The insulation process includes many stages. Changing the order of work or excluding one of the stages will negatively reduce the quality and durability of the insulation. The method of “wet” insulation of facades with polystyrene foam is most suitable for houses made of brick, cinder blocks, and reinforced concrete.
The entire process must be carried out by qualified personnel in good weather, since high humidity, precipitation or scorching rays of the sun can slightly change the properties of unprotected materials.
Pay attention to the article about roof insulation with polystyrene foam, in which we will talk about another area of application of this universal material.
This article will help you understand all the intricacies of insulating the roof of a house from the inside.
Technology of insulating facades with foam plastic
The procedure for thermal insulation of a facade using modern polystyrene foam is simple. It is important to know the main stages and stock up on the necessary working tools and materials. When purchasing, it is important to pay attention to their purpose, namely, external finishing work . It all starts with the preparatory process. The first thing you need to do is prepare materials for work:
- Glue for gluing foam plastic.
- nails for thermal insulation (dowel-umbrella);
- primer and plaster to treat the surface;
- nylon rope to calculate irregularities on the surface of the facade.
You also need to stock up on a hammer drill and screwdriver, a stationery knife, a hacksaw, a level and a spatula. First, it is important to find out the required amount of polystyrene foam to insulate the facade. This can be easily determined by measuring the outside area of the building. But, in this case, you need to accurately calculate the zero point for a specific option.
If the zero point is incorrectly calculated, the interior may be constantly damp, which leads to the formation of mold, unpleasant odors and high humidity . To insulate facades with polystyrene foam of a residential building, experts recommend polystyrene foam up to 45 mm thick. You definitely need to pay attention to the density of the material.
Surface preparation
Before you begin insulating with polystyrene foam, you need to level the façade surface of the walls.
In order not to disrupt the bonding strength of the slabs, it is important to remove all protrusions and bumps. Small depressions and depressions are acceptable. Before pasting, all uneven surfaces must be cleaned and the façade walls primed with a special impregnating compound. The primer promotes good adhesion of the sheets to the wall and impregnates it with an antiseptic, which protects against the formation of fungus. And also having moisture-resistant properties, it creates an outer hydrolyzed layer.
Pasting process
Foam boards are glued end to end in rows. The first row starts at the bottom and goes up. To obtain a staggered gluing order, in subsequent rows the first slab is cut in half. According to building codes, it is advisable to apply special adhesive to the entire area of the slab. However, most often the mixture is applied pointwise, along the entire perimeter of the insulating surface.
Or glue can be spread on the facade wall. Then it is applied in strips up to 10 mm thick, leaving empty spaces so that the adhesive mass spreads under the slab . Adhesive for polystyrene foam should not contain acetone or solvent, since they dissolve the thermal insulation material, making holes in it. A universal glue is considered to be a dry cement mixture diluted with water.
Fastening with dowels
After the solution has dried and hardened about a day after gluing, the foam boards can be strengthened.
Nails with a wide head, which are also called “dish-shaped dowels” or “umbrellas,” will help with this. Additional reinforcement with dowels is necessary: when the slabs are not completely coated with glue, the walls are crooked, or the insulation needs to be pressed tightly against the wall. It happens that they fix the corners of a building to avoid tearing off the foam. The fastener is driven in with a hammer. Tile joints are coated with polyurethane foam without expansion or glue. Interestingly, it is possible to insulate the facade without using glue, only with the help of umbrella dowels.
Plaster
To apply plaster, the walls are reinforced with reinforcing mesh. First, the mesh must be attached to the corners of the building. Then over the entire surface. But it is necessary to take into account that the mesh must be glued in pieces and not all at once, since in sunny, dry weather the installation adhesive solution dries quickly.
The mesh must be partially submerged in the mixture, which is added when the canvas is smoothed. In the end, you need to achieve the result - the mesh fabric is visible quite a bit.
An important point: it is convenient to start installing the reinforcing mesh from the top left corner. Then there is a chance to avoid horizontal joints when unwinding the roll.
The surface can be plastered in one or two reinforcing layers. For the first layer, a moisture-resistant material is used, which provides waterproofing. This can be cement with active waterproof components . And the second layer serves as finishing or decor and is not applied when finishing siding.
External cladding
External cladding is performed in several ways. This can be plastering with painting, laying facing bricks, fixing siding. Insulating a facade with expanded polystyrene technology is a simple operation that can be accessible to anyone, without special training or special knowledge.
Distinctive properties of expanded polystyrene
Among the positive qualities of this thermal insulation material it is worth listing:
- low thermal conductivity;
- high moisture resistance;
- biological and chemical neutrality;
- durability;
- harmlessness to human health;
- ease of installation;
- self-extinguishing of the material.
Let's look at each of its properties in more detail:
- Low thermal conductivity.
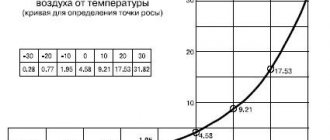
This indicator is very important for thermal insulation materials. The lower the thermal conductivity of a material, the less thickness of insulation will be required to ensure the required level of thermal and sound insulation of the building. The thermal conductivity coefficient of expanded polystyrene foam is 0.039, so a thickness of 0.11 meters is sufficient to insulate a house. And to obtain the same thermal insulation properties of sand-lime brick masonry, you will need to build a wall more than two meters thick. - High moisture resistance. The maximum percentage of moisture absorbed by polystyrene foam is only 6%. And at the same time it will retain about 92% of its original characteristics. In addition, expanded polystyrene can withstand about 50 cycles of alternating freezing and thawing without changing its physical and mechanical characteristics, which allows this material to be used even in northern climatic zones.
- Biological and chemical neutrality. Expanded polystyrene is not susceptible to the influence of microorganisms (mold, fungi, bacteria). This also speaks in its favor, since other building materials use harmful compounds to combat microorganisms.
- Durability. According to Russian tests, the service life of expanded polystyrene boards reaches 80 years. This material does not crumble, rot or decompose. He is not afraid of ultraviolet rays. It also does not turn yellow over time.
- Harmless to human health. Polystyrene foam is an inert and non-toxic material. During the production of this material there are no harmful emissions into the environment. Confirmation of the harmlessness of the material is its use for storing certain types of food products and the production of children's boards from it for learning to swim.
- Convenience and ease of installation. This thermal insulation material can be processed with any available means. During processing, it does not generate dust and does not lead to the formation of allergies. During installation, the material retains its original dimensions. It is lightweight, which makes it easy to install. Foam plastic can be used on objects of any complexity and configuration.
- Self-extinguishing during combustion. To insulate facades, only self-extinguishing polystyrene foam is used. This property of the material indicates its ability, when exposed to an open flame, not to burn, but to slowly char and melt. And when the flame is eliminated, the material will not ignite again.
Reviews about insulating facades with foam plastic
Approximate prices for foam plastic for facade insulation
For insulating facades, the following brands of polystyrene foam are most often used (the table shows dealer prices per unit of measurement, end of 2013/beginning of 2020):
| Name | units change | Cost, rub |
| Polyfoam PS-1-150 | 1 kg | 780-3500 |
| Foam plastic PSB-S-15 | m3 | 1045-1500 |
| Penoplex Comfort 50*600*1200mm | PC. | 168 |
| Penoplex Comfort 50*600*1200mm | package | 1200-1320 |
| TechnoNIKOL XPS Technoplex 1200 x 600 x 20 mm | m3 | 1300-4180 |
Advantages of polystyrene foam insulation
The advantages of insulation include:
- low thermal conductivity;
- health safety;
- environmental friendliness;
- biological inertia;
- durability;
- chemical resistance;
- fire safety;
- ease of processing and installation;
Low thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity of a material is the transfer of internal energy from more heated parts or bodies to less heated ones. Depending on the structure of the material, internal energy can propagate at different speeds (slowly or quickly). The thermal conductivity of a material is characterized by a thermal conductivity coefficient; the lower it is, the higher the thermal insulation properties of the material.
Thermal insulation materials have low thermal conductivity coefficients, which makes it possible to retain heat indoors. Expanded polystyrene has low thermal conductivity, which makes it possible to use it for thermal insulation of buildings and structures for various purposes.
Environmental friendliness
Buildings and structures insulated with expanded polystyrene do not have a negative impact on
environment, they do not emit toxins and do not cause air, soil or water pollution. Moreover, harmful toxins are not released not only during the operation of polystyrene foam, but also during its production.
In the production of expanded polystyrene, substances such as chlorine and fluorine are not used, which have a negative impact on the environment and destroy the ozone layer.
Thus, during the production of insulation, no greenhouse gases are emitted, which makes it possible to talk about the high environmental friendliness of not only the material itself, but also its production technology.
Expanded polystyrene is produced using a simple and cheap technology that does not require significant energy costs. The waste generated during the production process of the material is used to make various building materials such as concrete and solid bricks.
Durability
Expanded polystyrene retains its performance characteristics over a long period of time. Thermal insulation boards are not subject to crumbling. The material is biologically and chemically inert, resistant to acidic and alkaline environments. Expanded polystyrene is not susceptible to rotting and mold. Expanded polystyrene boards, if their contact with ultraviolet radiation is excluded, retain their characteristics, original shape and color throughout the entire operational period.
Expanded polystyrene, used for insulation of buildings and structures, is a fireproof material; it is prone to self-extinguishing if an accidental spark hits the insulation. When exposed to high temperatures, the material does not emit toxic substances; in the event of a fire, polystyrene foam does not spread fire, therefore, the fire resistance of walls insulated with polystyrene foam depends only on the properties of the material used for their construction.
Health safety
Expanded polystyrene is a non-toxic material that does not emit harmful substances even when heated significantly. Expanded polystyrene has no negative impact on human health or the environment as a whole. The material is used for the manufacture of containers in the food industry and fully meets the requirements of sanitary and hygienic standards.
Ease of processing
P
Mechanical processing of polystyrene foam can be carried out with any available tool. Both scissors and a regular kitchen knife are suitable for cutting insulation. Foam thermal insulation boards are easily cut to the required size. During processing, polystyrene foam does not crumble and does not emit dust. When processing expanded polystyrene, there is no need to observe any specific safety measures; the material is hypoallergenic and does not cause irritation when it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes.
With proper insulation of the facade of a building using polystyrene foam, not only its energy efficiency increases, but also heating costs are significantly reduced. A building insulated with polystyrene foam requires less thermal energy, since the heat remains inside the room and does not penetrate outside.
Expanded polystyrene is a building material that does not lose its shape during installation and operation. The insulation is not prone to shrinkage and deformation. Dimensional stability makes it possible to insulate a room as efficiently as possible by carefully sealing the joints of sheets of material. Expanded polystyrene allows you to create a homogeneous thermal insulation layer, and careful sealing of seams and joints will prevent the formation of so-called cold bridges through which heat will leak from the room.
Expanded polystyrene is suitable for insulating buildings, even of very complex configurations. If you have the appropriate equipment, polystyrene foam can be given any desired shape in a few hours.
The material has exceptional soundproofing properties. Walls insulated with polystyrene foam will prevent the penetration of extraneous sounds from the street into the room. The noise absorption of polystyrene foam is explained by the low dynamic rigidity of the material.
The heat insulator is lightweight, so installation does not create additional load on the structure. The lightness of expanded polystyrene allows it to be mounted even on prefabricated industrial buildings and structures, the construction of which is carried out using lightweight metal structures.
The versatility of the material allows it to be used for insulating buildings and structures both inside and outside. Expanded polystyrene is used not only for insulating facades; it is used to insulate the floor, ceiling and foundation of a structure.
Expanded polystyrene can be used to insulate the facades of buildings operated in various climatic conditions. The insulation can withstand significant temperature changes well and is a frost-resistant and moisture-resistant material.
Based on numerous studies, it was concluded that with proper thermal insulation work, polystyrene foam can be used for 50 years, that is, the durability of the material itself is more than 50 years.
The advantages of the material also include low cost. Even the highest quality thermal insulation boards made of polystyrene foam have an affordable price. The low cost of insulation is due to the low costs of producing the material.
When insulating facades with polystyrene foam, the guarantee ranges from 25 to 30 years and directly depends on the quality of the source material.
Expanded polystyrene has low water absorption; the material absorbs only about 4% of moisture, since the insulation does not contain fibers that absorb water.
Next, learn about the benefits and applications of extruded polystyrene foam.