Body Material: Brass
Regulation range: from 0 to 9 Bar.
Maximum operating temperature: 130 ˚С.
Nominal pressure: 16 Bar
Factory preset: 3 Bar
Closed-type heating systems are characterized by the temperature of the coolant and a parameter such as operating pressure. The efficiency of heat transfer depends on the volume of the working medium circulating in the circuit. The pressure regulator in the heating system, offered in wholesale quantities, compensates for the expansion of the coolant as a result of its heating to a high temperature. Using a regulator allows you to avoid emergency situations that could lead to damage to the heating or hot water supply circuit.
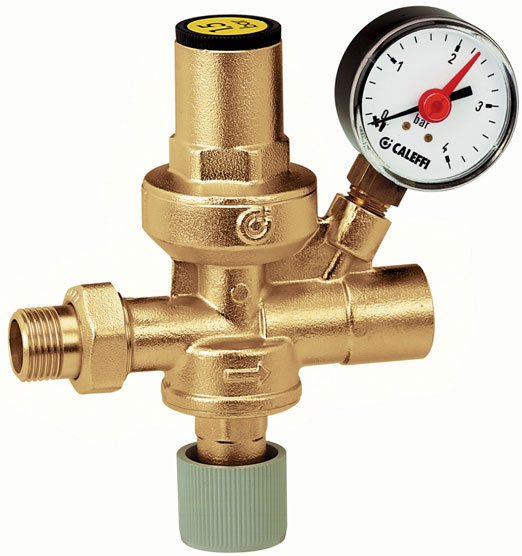
Operating principle of the Ogint water pressure regulator
The coolant, circulating in the heating system, increases in volume due to heating. Internal pressure increases significantly and requires timely stabilization. If the normalized value is exceeded, the pressure reducing valve opens, and the excess volume of hot water is pumped into the return branch of the main line. The product provides effective adjustment in the range from 0 to 9 atmospheres. To compensate for the volume when the working medium cools, water is pumped back into the circuit thanks to the valve. The regulator allows:
- maintain constant pressure in the system;
- prevent pipeline emergencies;
- ensure efficient coolant circulation;
- prevent damage to devices for which the operating pressure cannot be exceeded.
What is the temperature in the return pipe system
The temperature of the return pipeline is clearly stated in the construction regulations.
Warming up should be from 120 to 150 degrees. Most often, networks operate up to 110 degrees, since the pipes in the systems of most buildings are worn out. They simply cannot handle higher heat and pressure.
Any heating circuit operates at certain pressure and coolant temperature values, which are calculated at the design stage. However, during operation, situations are possible when the pressure drop in the heating system deviates from the standard level up or down and, as a rule, requires adjustment to ensure efficiency, and in some cases, safety.
Application area
In addition to the heating system, the Ogint pressure reducing valve has a wide range of uses. This device can be mounted at the inlet of boilers, boilers and other hydraulic equipment, which is designed for operation with limited coolant pressure. It is advisable to install a regulator on the inlet pipeline of hot and cold water supply.
The valve is made of brass and is designed to operate at high temperatures of water or other coolant circulating in the system. Guarantees constant stable pressure in the circuit, ensuring the safety and durability of heating equipment, as well as hot and cold water supply. The product is certified and approved for installation even in drinking water supply systems.
Pressure drop and its importance for the functioning of the heating system
For optimal functioning of any heating circuit, a stable and defined pressure drop is required, i.e. the difference between its values at the coolant supply and return. As a rule, it should be 0.1-0.2 MPa.
If this indicator is less, this indicates a disruption in the movement of the coolant through the pipelines, as a result of which water passes through the radiators without heating them to the required degree.
If the difference exceeds the above value, we can talk about “stagnation” of the system, one of the reasons for which is airing.
It should be noted that sudden changes in pressure negatively affect the performance of individual elements of the heating circuit, often disabling them.
Methods for regulating operating pressure and ensuring the stability of its differential on the supply and return
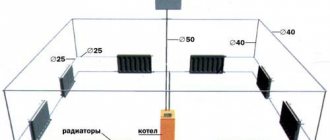
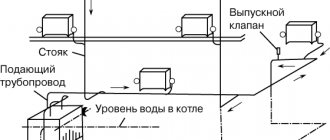
- First of all, it is necessary to remember that optimal operation of the heating system, incl. the creation of the required pressure in it depends on the correctness of the design, in particular, hydraulic calculations, and installation of lines and pipelines, namely: - the supply line in most schemes should be located at the top, the return line, respectively, at the bottom; - for the production of bottlings, pipes with a diameter of 50-80 mm should be used, for risers - 20-25 mm; — connections to heating devices can be made from the same pipes from which the risers are made, or one step less.
It is allowed to underestimate the cross-section of radiator piping only if there is a jumper in front of them.
Figure 3 – Jumper in front of the heating radiator
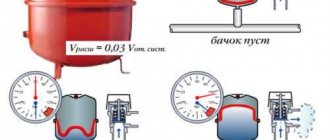
Figure 4 – Diaphragm expansion tank
The expansion tank, the volume of which is usually taken to be about 10% of the total volume of the system, can be installed in any part of the circuit. However, experts recommend installing it on a straight section of the return pipeline in front of the circulation pump (if available).
To prevent a situation where the device’s capacity is insufficient with a continued increase in pressure, the circuits provide for the use of a safety valve that removes excess coolant from the system.
Figure 5 – Pressure regulator
Finding the reasons for the drop and increase in pressure drop
Deviation of pressure more or less from the norm requires establishing the cause of this phenomenon and its elimination.
Pressure drop in the heating circuit
If the pressure in the heating system drops, then with a greater degree of probability we can talk about a coolant leak. The most vulnerable are the existing seams, joints and connections.
To check this, turn off the pump and monitor changes in static pressure. If the pressure continues to decrease, it is necessary to find the damaged area. To do this, it is recommended to sequentially disconnect different sections of the circuit, and after determining the exact location, repair or replace worn elements.
Key nodes
- , electric or solid fuel
Each of them has certain characteristics. The volume of liquid that it is capable of heating, as well as the permissible pressure, depend on these values.
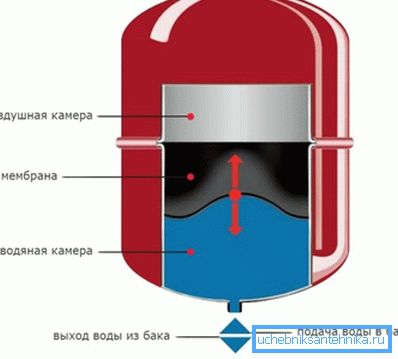
- Expansion tank
Used in dynamic closed-loop systems. It consists of two chambers: one contains air, and the other contains liquid. The chambers are separated by a membrane. There is a valve in the air compartment through which, if necessary, bleeding occurs. The main purpose is to regulate pressure drops in the heating system.
- Electric blower
- Heating control devices
- Filters
Types of pressure in the heating system
Pressure in a heating system is the force with which liquids and gases act on the walls of the heating system elements, determined by the ratio to atmospheric pressure.
Working pressure is the pressure that is present in a working system with normal operating characteristics. Working pressure is the sum of two quantities - static and dynamic pressure. (See also:) Static pressure is a value measured when water is stationary, taking into account its height.
Dynamic pressure is the effect on the walls of equipment of moving liquids or gases.
The pressure difference is the pressure difference in the coolant supply and return zones of the pumps.
The operating pressure varies depending on the temperature of the coolant. For example, at a temperature of +20 0 C this pressure is 1.3 bar, and at +70 0 C – 1.9 bar.
If in a single-circuit system the pressure is lower than required, the coolant will stagnate and will not provide effective heat transfer from heating devices.
Installation of differential pressure regulators
In heating circuits with varying coolant flow - on risers and horizontal sections of branches - the installation of differential pressure regulators makes it possible to eliminate the influence of changes in the hydraulic mode of the system on the branches.
They also help prevent noise formation on control valves at high pressure. (See also: ) Installing regulators allows you to optimize regulation by increasing the role of control valves. Connecting impulse pipes before and after the control valve allows you to set the exact amount of coolant flow and prevent it from being exceeded.
Differential pressure regulators can be installed on the pump bypass line. Used in systems with varying coolant flow. Reducing the coolant flow will increase the pressure drop between the suction and discharge pipes. The regulator reacts to the increased difference by opening and bypassing the coolant from the pressure to the suction pipe, as a result of which the coolant flow through the pump remains constant.
Installing pressure regulators creates stable barometric operating conditions for the boiler and the heating system as a whole.
Use of materials is permitted only if there is an indexed link to the page with the material.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
The functioning of any heating system requires certain indicators of temperature and coolant pressure, which are calculated during design. But sometimes during operation a pressure drop occurs in the heating system - a deviation to a smaller or larger direction is observed. This problem must be addressed not only to maintain heating efficiency, but also for safety reasons.
Control methods
You can control the pressure in the system using a sensor
For monitoring, water pressure sensors are installed in the heating system. These are pressure gauges with a Bredan tube, which is a measuring device with a scale and pointer. It shows excess pressure. It is installed at control nodes defined by regulatory documents. Using a heating system pressure sensor, you can determine not only a quantitative indicator, but also areas with possible leaks and other problems.
The flow of the working medium does not pass directly through the pressure gauge, since the measuring device is installed using three-way valves. They allow you to purge the pressure gauge or reset the readings. This tap also allows you to replace the pressure gauge with simple manipulations.
Pressure gauges are installed before and after elements that can affect pressure losses and pressure increases in the heating system. It can also be used to determine the serviceability of a particular unit.
Pressure drop value for heating system
For the normal functioning of the heat supply, a certain pressure difference is required (the difference between the supply and return values of the coolant).
Typically, pressure loss in a heating system is 0.1-0.2 MPa. When this indicator is less, this is a signal of a disruption in the movement of water through the pipelines, which is accompanied by ineffective heating (the coolant passes through the radiators without heating them to the required value). When the differential value is exceeded by more than 0.2 MPa, “stagnation” of the system begins, resulting from airing.
A sharp change in pressure does not have the best effect on the functioning of individual elements of the heating structure, often causing their breakdowns.
The installation of pipelines and highways is also of considerable importance:
- It is recommended to place the supply pipe at the top and the return pipe at the bottom;
- for spills, pipes with a diameter of 50-80 millimeters should be used, for risers - 20-25 millimeters;
- The lines to the radiators can be made from the same pipes that are used for risers, or a little less.
The cross-section of radiator piping can only be underestimated if there is a jumper in front of them.
In addition, it is known that as the temperature rises, the coolant increases in volume, and accordingly, the pressure in the heating system rises. For example, at 20 degrees it increases by 0.13 MPa, and at 70 degrees – by 0.19 MPa. Therefore, to regulate the pressure, you can simply change the water heating level.
To increase the coolant pressure, and this is important for providing heat to multi-storey buildings, it is necessary to use circulation pumps.
To automatically regulate operating pressure and differential in small buildings, expansion tanks (usually membrane type) are used.
They begin to function if the pressure in the system rises to 0.2 MPa. These devices remove excess hot water, which ultimately helps maintain the pressure at the required level. The expansion tank can be installed in any part of the circuit. Its volume is approximately equal to 10% of the total displacement of the system. However, experts advise installing it on a straight return pipe in front of the circulation pump, if present.
The schemes provide for the use of a safety valve that removes excess coolant from the system - this is necessary to prevent a situation in which the tank capacity is not enough to stop the pressure increase.
In complex and large heating structures, which are often found in multi-story buildings, regulators are used to maintain the required pressure. They prevent airing even during sudden pressure surges in the mains and noise generation on control valves. They are installed on the jumper between the supply and return pipelines, or on the bypass line of the pump.
There is another way to regulate pressure in multi-storey buildings - this is the use of shut-off valves. For example, if there is a drop in pressure in the heating system, then to increase the indicator, the cross-section of the return pipeline is reduced using a valve. If the pressure deviates less or more from the norm, it is necessary to find out the cause of the problem and eliminate it.
Pressure drop monitoring
In order for the heating system to operate normally and the risk of an accident to be minimized, it is necessary to monitor the temperature and pressure of the coolant from time to time.
For this purpose, a special pressure sensor is used in the heating system, as in the photo. Most often, deformation pressure gauges with a Bourdon tube are used to measure pressure. When determining low pressure, a variety of them can be used - diaphragm devices. After water hammering, such models should be verified, since in subsequent measurements they may show inflated values.
In those systems that provide automatic control and regulation of pressure, various types of sensors are additionally used (for example, electric contact).
The placement of pressure gauges (tapping points) is determined by regulations.
These devices should be installed in the most important areas of the system:
- at its entrance and exit;
- before and after filters, pumps, pressure regulators, mud traps;
- at the exit of the main line from the boiler house or thermal power plant and at its entrance to the building.
These recommendations must be followed even when creating a small heating circuit and using a low-power boiler, since not only the safety of the system depends on this, but also its efficiency, which is achieved through optimal fuel and water consumption (read: " "). It is recommended to connect pressure gauges through three-way valves - this will allow you to purge, reset and replace devices without stopping the heating system.
Increased pressure
If the maximum pressure in the heating system is exceeded, the reason for this is slowing down or stopping the movement of water in the heating circuit.
This can lead to:
- contamination of mud traps and filters;
- the occurrence of an air lock;
- coolant replenishment due to automatic failure or incorrectly adjusted valves located on the supply and return (read: " ");
- a feature of the regulator or its incorrect setting.

Unstable pressure is especially common in recently installed heating systems due to the removal of air. This is considered normal if, after bringing the water volume and pressure to operating levels, no deviations are observed for several weeks.
Otherwise, most likely, pressure instability is associated with incorrect hydraulic calculations, including insufficient volume of the expansion tank. That is why, when installing a heating system, it is important to correctly perform all the calculations - in the future this will eliminate various problems with its functioning.
Why do you need pressure in the heating system?
In this article, you will learn about the importance of pressure, methods for increasing or decreasing it, and the reasons that cause pressure drops in a heating system. Also become familiar with the equipment that is used to regulate and control heating pressure.
How to create pressure in the heating system?
Pressure can be static or dynamic.
Static systems are installed without the use of pumps. Usually these are single-circuit circuits. Pressure is created as a result of a difference in altitude. Under its own weight, from a height of ten meters, water presses with a force of one bar.
Dynamic systems use pumps to increase the pressure in the heating system. These are more complex schemes that allow the installation of two and three circulation circuits. In other words, they simultaneously include:
- warm water floor;
- storage boilers.
The most important thing in heating is proper water circulation. To ensure that the liquid moves in the desired direction, check valves are installed. The check valve is a connecting coupling with a spring and a damper. It allows fluid to flow in only one direction, ensuring proper circulation and high pressure in the heating system.
Pressure in the autonomous circuit
The clear meaning of the word “difference” is a change in level, a fall. In the article we will touch on it too. So, what causes the pressure in the heating system to drop if it is a closed circuit?
First, let's look it up in memory: water is actually incompressible.
Excessive pressure in the circuit is created due to two factors:
- The presence in the system of a membrane expansion tank with its air cushion.
- heating radiators and pipe elasticity. Their elasticity tends to be zero, but with a large area of the inner surface of the circuit, this factor is also reflected in the internal pressure.
From a practical point of view, this indicates that the pressure drop in the heating system recorded by the pressure gauge in most cases is caused by a very small transformation of the volume of the circuit or a decrease in the amount of coolant.
Here is a probable list of both:
- When heated, polypropylene expands more than water. When starting a heating system assembled from polypropylene, the pressure in it may drop slightly.
- Many materials (as well as aluminum) are plastic enough to change shape under prolonged exposure to moderate pressure. Aluminum radiators can simply swell over time.
- Gases dissolved in water slowly leave the circuit through the air vent, affecting the actual amount of water in it.
- High heating of the coolant with a reduced volume of the heating expansion tank can lead to the operation of the safety valve.
Finally, real malfunctions cannot be completely ruled out: minor leaks along welding seams and section joints, etching nipple of a microcrack and expansion tank in the boiler heat exchanger.