Expanded polystyrene boards 50 mm thick
Foam plastic 50 mm thick is the most popular and affordable insulation for buildings. It consists of lightweight polystyrene foam beads bonded together. It is thanks to the large number of air pockets that PSB has the ability to retain the heat of protected structures. But, of course, it would not have become so popular if its advantages were limited only to low cost.
The properties of polystyrene foam are directly related to its closed-cell structure and the characteristics of the raw materials. They determine both its advantages and disadvantages, although the quality of execution also plays a role. The same polymer granules are used to produce any styrene boards. But to create solid products, they need to be “glued” together under certain conditions. Violation of the technology leads to weakening of the bonds between the hollow balls and reduces the quality of the insulation.
Technical characteristics of polystyrene foam:
- Light weight - air chambers account for 98% of the total volume of the sheet. As a result, even laying in two layers on the façade puts virtually no load on the foundation of the building.
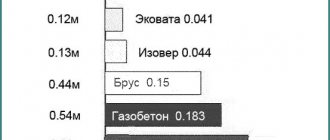
- Thermal conductivity (R) is in the range of 0.037-0.043 W/m °C. With such values, foam plastic with a thickness of only 5 cm is quite capable of replacing 95 mm of mineral wool. And a comparison with brick in masonry shows a 14-fold superiority of polystyrene insulation.
- Relatively low hygroscopicity at the level of 2-4% - closed cells are, in principle, unable to absorb water. Problems arise if the material has cracks or areas with poorly “welded” granules to each other.
- Vapor permeability - the foam allows no more than 0.05 mg/m·h·Pa of moist air to pass through it. This is a fairly low figure, so if you choose styrene to insulate the walls outside of a residential building, take care of good supply and exhaust ventilation of the premises.
Many people tend to attribute its toxicity to the disadvantages of polystyrene foam. Polymers actually evaporate styrene, which is harmful to the human body. In order for its content to decrease to safe concentrations of 0.002 mg/m 3, the insulation must be stored in a warehouse before it gets to the construction site or into the house.
But what you can’t turn a blind eye to is the low heat resistance of polystyrene foam - when heated above +80 ° C, it begins to melt, and at +210 it lights up. At this moment, it is not so much the flame that is dangerous, but the toxins released into the air, which have more than once led to human casualties - the smoke generation group of styrene corresponds to the maximum indicator D4. That is why the use of polystyrene foam is unacceptable in fire hazardous facilities.

Foam boards brand PSB-S-25
Among modern thermal insulation materials, the leading position is occupied by polystyrene foam (foam) of the PSB-S-25 brand, due to its optimal strength and thermal conductivity. It is universal and has a wide range of applications: walls, roofs, facades, loggias, floors. PSB-S-25 foam is produced from styrene granules filled with carbon dioxide, which after heating are sintered together and significantly expand in volume (almost 50 times), which provides it with low weight with good strength indicators and low production costs.
Features and Properties
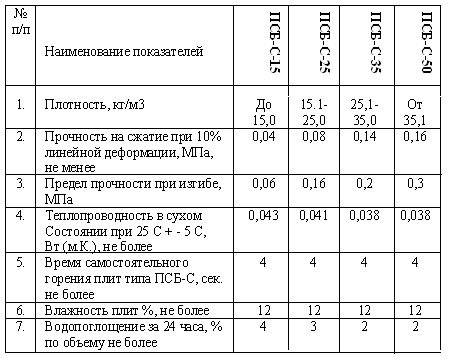
The abbreviation PSB-S-25 stands for “expanded polystyrene foam, pressless, self-extinguishing.” The number 25 means the maximum density of this brand. The material is durable, environmentally friendly, has low water absorption and does not attract rodents. About 98% of air in the composition provides it with high heat and sound insulation properties. Main technical characteristics of PSB-S-25:
| Index | Units | Meaning |
| Density | kg/m3 | 15–25 |
| Compressive strength (at 10% linear deformation) | MPa | 0,10 |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m⋅K | 0,039 |
| Bending strength | MPa | 0,18 |
| Operating temperature range | °C | -60 to +80 |
| Vapor permeability | mg/(m⋅h⋅Pa) | 0,05 |
| Moisture absorption in 24 hours | % | 2,0 |
| Self-burning time | With | 3 |
- Flammability.
The fire safety of polystyrene foam PSB-S-25 is due to its manufacturing features: instead of flammable substances, the granules are filled with carbon dioxide and fire retardant additives are used. According to the regulatory and technical documentation, the insulation is marked G1, which means “low-flammability”. However, there are standard requirements for the operation of expanded polystyrene, including PSB-S-25: GOST 15588-86 prescribes that the permissible temperature of the insulated surface is no more than 80 ° C, the slabs should not come into contact with the interior of the premises (usually they are protected layer of cement-sand plaster 30 mm).
- Dimensions.
The length, height and thickness of PSB-S-25 are also specified in GOST 15588-86. Other sizes are allowed only by agreement with the manufacturer. The standard length of expanded polystyrene slabs has a range of 900-5000 mm, and widths - 500-1300, the interval in both cases is 50 mm. Thickness - 20–500, in increments of 10. The designation on the packaging should look like this: brand, dimensions and name of the standard, for example, PSB-S-25 1000x1000x50 mm GOST 15588-86.
Scope of application and benefits
The main purpose of the material is heat and sound insulation of walls, ceilings, roofs and attics. Thanks to its good strength characteristics, it successfully withstands loads when the roof rests directly on the slab. It is used in the manufacture of sandwich panels and as a middle layer in enclosing structures. In addition, thermal insulation boards made of expanded polystyrene are popular for protecting water pipes from freezing and as packaging. In cases where the structure is lightly loaded, it is more advisable to choose PSB-S-15, since it can be purchased at a lower price.
The advantages include:
- Wide range of applications.
- Resistance to any influences: temperature, mechanical, chemical.
- The price of PSB-S-25 foam is lower than that of brands with higher densities, and the strength characteristics are the most optimal.
- Ease of installation: lifting to a height without using a crane, cutting with a simple knife, ability to give any geometric shape.
- Low flammability, self-extinguishing.
Expenses
Depending on the manufacturer, density and size, it is realistic to buy polystyrene foam of the PSB-S-25 brand at a price from 1680 to 2400 rubles per 1 m3. The number of sheets in the specified volume ranges from 50 (with dimensions 1000x1000x20) to 5 (1000x1000x200). The cost of 1 piece, 20 mm thick, is about 50 rubles, and 200 - 440. Material consumption is calculated using special calculators, which are available on the manufacturers’ websites.
Foam brands
Density is the main indicator on the basis of which polystyrene boards are classified - the thermal conductivity of the foam, as well as its strength characteristics, largely depends on it. Materials are assigned a specific grade, usually indicating the maximum specific gravity:
- PSB-S15 (from 11 to 15 kg/m 3 ) - has the ability to conduct no more than 0.037-0.04 W/m·°C of heat and withstands compression up to 40 kPa.
- PSB-S25 (from 16 to 25 kg/m3) - here the R coefficient corresponds to 0.038 W/m °C, and the strength is about 100 kPa.
- PSB-S35 (not less than 25 kg/m 3 ) – has a thermal conductivity of 0.035-0.039 W/m °C and can withstand up to 140 kPa.
- PSB-S50 - here is a slightly non-standard range of density values 40-45 kg/m3, high thermal conductivity (0.04-0.043 W/m °C) and good strength indicators at 160 kPa.
The letter “C”, which marks 50 mm foam plastic, indicates that fire retardants were introduced into the polystyrene mass during production. As a result, the sheets acquired the property of self-extinguishing. But it only appears when the source of fire is removed after only 3-4 seconds.
There are other marking indicators:
- A - the geometry and dimensions of the foam are most accurate, and the edges are completely smooth.
- B – sheets with a profiled “step”, which allows you to create a dense, continuous layer of insulation, devoid of visible seams and gaps.
- N – moisture-resistant material for outdoor use.
The dimensions of the sheet are always standard: it is either 1x1 or 1x2 m (it is extremely rare to find a convenient width of 1200 mm). The reason is that in production, foam plastic comes in the form of a cube with a side of 2 meters and only then is it dissolved into slabs 50 mm thick. However, you can get products of other sizes and even shapes yourself by cutting them with a hacksaw or a hot metal string.
Application, pros and cons of different brands
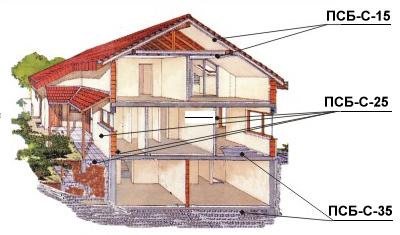
Fifty millimeter thick foam can have different uses, depending on the density. Sheets PSB-S15 and 25 are in demand because they are the most effective. As for their low strength, it is usually not taken into account - such foam plastics are mounted in non-load-bearing structures.
The main use of lightweight slabs is small objects in private construction. A sheet with a density of up to 15 kg/m3 retains heat perfectly, but due to its low strength, it makes sense to purchase it only for interior work:
- in the basement;
- on the balcony and loggia;
- when insulating the roof.
For large objects and outdoor work, it is better to buy a more durable PSB-25. Also, for facades and floor insulation, PSB-35 is used under a concrete screed, and the heaviest foam plastics are even laid under the road surface. But the cost of one sheet of this brand is quite high, so the material is not in great demand on the market.
Finished products of different sizes also have their pros and cons - regardless of their density. Large slabs with sides of 1x2 m are inconvenient to use when installing them yourself, and they are more difficult to buy. And foam plastic 1000x1000x50 mm often creates problems during the fitting process in a standard sheathing.
A serious drawback of all foam plastics without exception is their instability to UV radiation, as well as to solvents. The insulated surface must be protected from the sun, but contact with paintwork materials must not be allowed. In addition, low vapor permeability makes foam plastic an undesirable neighbor for wooden buildings. But the low price per sheet is a definite plus, since effective insulation cheaper than PSB has not yet been invented.
Technical characteristics of polystyrene foam
Indicator name
Expanded polystyrene boards are produced in accordance with TU 5767-001-93254741-2006 Certificate of Conformity No. РСС DE.СЛ51 Н00009 Certificate of Conformity No. РСС DE.СЛ51 Н00010 Sanitary and epidemiological conclusion No. 43.52.04.576.П.000011.04.07 Ser certificate of conformity ROSS RU. SL51. N00054 Fire safety certificate SSPB. RU. OP044. N. 00138 Extruded polystyrene has fairly high chemical resistance to most materials used in construction. Some organic substances can cause slabs to soften, shrink, and even dissolve. High chemical resistance to the following substances:
Low chemical resistance to the following substances:
When choosing adhesive compositions, you should be guided by the manufacturer's instructions regarding suitability for gluing polystyrene foam. Table of standard sizes of polystyrene foam
Sheet dimensions 1200×600 mm Bundle height ~ 400 mm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
www.polyshim.ru
Polystyrene foam plates m50 technical characteristics
FOAM POLYSTYRENE THERMAL INSULATION PLATES
Polystyrene insulating slabs. Specifications
Date of introduction 2015-07-01
The goals, basic principles and basic procedure for work on interstate standardization are established by GOST 1.0-92 “Interstate standardization system. Basic provisions" and GOST 1.2-2009 "Interstate standardization system. Interstate standards, rules and recommendations for interstate standardization. Rules for development, adoption, application, updating and cancellation"
1 DEVELOPED by the non-profit organization "Association of Expanded Polystyrene Manufacturers and Suppliers"
2 INTRODUCED by the Technical Committee for Standardization TC 465 “Construction”
3 ADOPTED by the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (protocol dated December 5, 2014 N 46-2014)
The following voted for adoption:
Short name of the country according to MK (ISO 3166) 004-97
Abbreviated name of the national standardization body
Gosstandart of the Republic of Kazakhstan
4 By Order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology dated December 12, 2014 N 2034-st, the interstate standard GOST 15588-2014 was put into effect as a national standard of the Russian Federation on July 1, 2020.
Information about changes to this standard is published in the annual information index “National Standards”, and the text of changes and amendments is published in the monthly information index “National Standards”. In case of revision (replacement) or cancellation of this standard, the corresponding notice will be published in the monthly information index “National Standards”. Relevant information, notifications and texts are also posted in the public information system - on the official website of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology on the Internet
INTRODUCED: amendment published in IUS No. 2, 2020; amendment published in IUS No. 5, 2020
Amendments made by the database manufacturer
Fire safety of polystyrene foam - technical information

The use of expanded polystyrene in construction is objectively limited by its flammability. Plates belong to the group of combustible materials. Based on fire safety certificates, polystyrene foam boards have a flammability group - G-1 according to GOST 30244, a flammability group - B2 according to GOST 30402...

The use of expanded polystyrene in construction is objectively limited by its flammability. Plates belong to the group of combustible materials. Based on fire safety certificates, polystyrene foam boards (manufactured in accordance with GOST 15588-86) have a flammability group - G-1 in accordance with GOST 30244, a flammability group - B2 in accordance with GOST 30402, a smoke-generating ability group - D3 in accordance with GOST 12.1.044. We should not forget that, based on GOST 15588-86, it is used “as the middle layer of building envelopes and industrial equipment in the absence of contact of the slabs with the interior,”
and, therefore,
the fire safety of the structure as a whole is ensured by the use of structural protection,
i.e. using gypsum fiber board sheets, ceramic bricks, plaster compositions, etc.
According to paragraphs 2.16.1 and 2.16.2 of GOST 30244, the toxicity indicator of combustion products is the ratio of the amount of material per unit volume of a closed space,
in which gaseous products are formed when the material burns. The ratio of these indicators is strictly standardized and controlled, starting from project documentation and ending with delivery to the state commission. The value of the toxicity indicator of combustion products should be used for a comparative assessment of polymer materials, and also be included in the technical specifications and standards for finishing and thermal insulation materials.
Leading industry institutes (JSC "TSNIIPROMZDANIY", Moscow) are developing Albums of standard technical solutions for the use of polystyrene foam in construction, an album of standard technical solutions for the use of polystyrene foam (FTT - PLASTIC, Izhevsk). Materials for design and working drawings of units for using polystyrene foam of JSC Polymer-Pack SPb were developed and approved in accordance with the established procedure.
When determining the scope of application of polystyrene foam slabs, the results of tests of fragments of walls with polymer insulation, the letter of the State Fire Service of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia and the Ministry of Construction of Russia “On the insulation of external walls of buildings”, as well as reference data “Manuals for the design of fire resistance limits, limits of fire spread by structures and groups” are taken into account flammability of materials TsNIISK im. Kucherenko.
According to the certificate, PSBs belongs to low-flammable (group G1) materials.
In SNiPs 21-01-97 “Fire safety of buildings and structures”, 31-01-2003 “Residential multi-apartment buildings”, II-26-76 “Roofs. Design standards”, regulating the requirements for flat roof structures, there is no ban on the use of flammable insulation materials.
Moreover, SNiP II-26-76
“Roofs. Design Standards” (Appendix 2) has already determined the composition of the roof covering for reinforced concrete floors - P4, where
polystyrene foam slabs can also be used
). This confirms that thermal insulation does not have to be non-flammable. In addition, in this SNiP there is no roof structure with mineral wool slabs on a reinforced concrete slab.
On the issue of using PSBs in flat roofs, consultations are also given at the institutes that participated in the preparation of SNiPs on roofing and fire safety - TsNIIPromzdanii (responsible executor, Ph.D. T.E. Storozhenko) and TsNIISK im. Kucherenko (responsible executor, head of the topic, candidate of technical sciences V.N. Zigern-Korn). A positive response was received:
as part of the roofing coverings of the objects proposed above, polystyrene foam boards PSBs can be used, and the determining factor in the choice of roofing structure for categories of residential buildings f1.3 fire resistance class II and I class of structural fire hazard C0 is the presence of a reinforced concrete floor slab of thicknesses under the roof. 160mm. On top, the fire-resistant insulation is protected by a cement-sand screed, which is the base of the roofing roll carpet. This is allowed in accordance with the letter of the GUPO Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia No. 20/22/1343 dated June 24, 1997 and the Technical Standardization Directorate of the Gosstroy of Russia No. 13-443 dated June 24, 1997.
TsNIIPromzdanii has developed and certified design documentation for the use of polystyrene foam boards in construction (Certificate of Conformity No. ROSS RU.CP46.C00017), including for roofing structures. In our practice, there are many examples of the use of polystyrene foam in roofing coverings. Among them are housing construction projects in Moscow and Moscow Region, designed by various design organizations, private and public. And polystyrene foam is also used to insulate the roofs of neighboring Zvenigorod facilities.
Media contact Yulia Gamzina Press attaché of the Association of Expanded Polystyrene Manufacturers and Suppliers Mob. (921) 918 3615 Email
Reference
The Association of Manufacturers and Suppliers of Expanded Polystyrene is a non-profit organization that unites leading Russian and foreign manufacturers and suppliers of polystyrene foam in the Russian Federation. Objectives of the Association:
- carrying out measures to ensure the quality of expanded polystyrene products in accordance with generally recognized quality standards;
- encouraging honest entrepreneurship in the production of expanded polystyrene products, preventing the emergence of unfair competition in the market for expanded polystyrene products;
- regulation of the identification of expanded polystyrene products that meet quality requirements by applying the Association logo
The goals of the Association are to coordinate the entrepreneurial activities of its members, represent and protect common property interests, form a positive image of expanded polystyrene, and assist in the promotion of thermal insulation materials and molded products made of expanded polystyrene on the Russian market.