You can insulate a room using various methods. For example, use polystyrene foam. Its distinctive characteristic is its high performance. The most basic advantage of polystyrene foam is its low thermal conductivity. This quality helps to retain heat well. In addition, polystyrene foam has other advantages.
- Practicality.
- Environmentally friendly.
- Ease.
- Easy installation.
- Ability to withstand temperature changes.
- Affordable price.
Factors affecting thermal conductivity
Foam boards are manufactured in various thicknesses . Therefore, there are numerous factors that affect the thermal conductivity of a material.
- Layer thickness. To achieve high-quality energy saving, it is necessary to make the layer thicker. For example, a 5 cm layer will transmit less heat than a 1 cm layer.
- Structure of the material. Its porosity enhances its insulating properties. This is because the cells contain air. And it retains the thermal conductivity of the foam well.
- Humidity. During storage, the foam must be protected from moisture. It adversely affects the characteristics of the material, even vice versa.
- Average layer temperature. If the temperature increases, there will be consequences. The efficiency of using the insulator will become worse.
How does the density of foam affect its cost?
Production of foam plastic.
There are several points of view related to the concept of density. The unit of measurement for this parameter is kilogram per cubic meter. This value is calculated from the ratio of weight to volume. It is impossible to determine with one hundred percent accuracy the qualitative characteristics of polystyrene foam related to its density. Even the weight of the insulation does not affect its ability to retain heat.
When thinking about purchasing insulation, buyers are always interested in its density. Based on these data, one can judge the strength of the material, its weight and thermal conductivity. Foam density values always fall within a certain range.
During the production process of expanded polystyrene boards, the manufacturer determines the cost of production. Based on the formula for determining density, the weight of the insulation will affect this value. The greater the weight of the material, the denser it is, so its cost is higher. This is due to the fact that polystyrene, as a raw material for heat insulation boards, plays an important role. It accounts for about 80% of the total cost of finished products.
Return to contents
How does changing the thermal conductivity of foam affect its density?
Polystyrene foam is made from polystyrene foam balls containing air.
Any thermal insulation material contains air in its pores. The improved thermal conductivity index depends on the amount of atmospheric air contained in the material. The higher it is, the lower the thermal conductivity coefficient. The production of polystyrene foam is carried out from polystyrene foam balls containing air.
From this we can conclude that the density of polystyrene foam does not affect its thermal conductivity. If this value changes, then changes in thermal conductivity occur within percentages. One hundred percent air content in the insulation is associated with its high heat-saving ability, since air is characterized by the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient.
Due to the low thermal conductivity of the insulation, a high degree of energy saving is ensured. If we compare polystyrene foam with brick, their energy-saving ability will differ significantly, since 12 cm of thermal insulation thickness corresponds to 210 cm of thickness of a brick wall or a 45-centimeter wooden wall.
The thermal conductivity coefficient of foam plastic, expressed in digital values, belongs to the range 0.037 W/mK 0.043 W/mK. This value can be compared with the thermal conductivity of air equal to 0.027 W/mK.
Return to contents
Type and characteristics of polystyrene foam
The construction market offers a large selection of insulating materials. Polystyrene foam has low thermal conductivity . But this indicator may vary depending on the type of polystyrene. When compared with other insulation materials, certain conclusions can be drawn. For example, a sheet of foam plastic with a density of 50-60 mm can be replaced with a large volume of mineral wool. Material with a density of 100 mm can be replaced with foamed polystyrene with indicators of 123 mm. The characteristics of these types of insulation are slightly similar. Therefore, the difference is small. The performance of foam plastic exceeds that of basalt wool.
What should you buy?
The building materials market offers a huge selection of polystyrene foam boards. The high thermal conductivity of insulation boards depends on their type.
For example: a sheet of polystyrene foam PSB-S 15 has a density of up to 15 kg/m3 and is 2 cm thick. For a sheet from 2 to 50 cm, the density is no more than 35 kg/m3. When comparing polystyrene foam with other similar materials, you can easily trace the dependence of the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam boards on its thickness.
So, for example: the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is 50 mm, twice that of mineral wool of the same volume; in this case, the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam with a thickness of 150 mm will generally be 6 times higher than these indicators. Basalt wool is also very inferior to polystyrene foam.
In order to apply one of the insulation methods, it is necessary to select the correct dimensions of the material. The following algorithm can be used to calculate:
- It is necessary to clarify the overall thermal resistance. This value depends on the region in which the calculation needs to be performed, namely on its climate. To calculate the thermal resistance of a wall, you can use the formula R = p/k, where its thickness is equal to the p value, and k is the thermal conductivity coefficient of the foam. From constant indicators we can conclude what resistance the insulation should have. The required value can be calculated using the formula p=R*k; the value of R can be found based on the previous step and the thermal conductivity coefficient.
Features of thermal conductivity
Expanded polystyrene retains not only heat, but also cold well. Such possibilities are explained by its structure. The composition of this material structurally includes a huge number of sealed multifaceted cells. Each has a size from 2 to 8 mm .
And inside each cell there is air, consisting of 98%. It is this that serves as an excellent heat insulator. The remaining 2% of the total mass of the material is made up of polystyrene cell walls. You can verify this if you take, for example, a piece of foam plastic. 1 meter thick and 1 square meter in area. Heat one side and leave the other side cold. The difference between temperatures will be tenfold. To obtain the coefficient of thermal conductivity, it is necessary to measure the amount of heat that passes from the warm part of the sheet to the cold part .
People are accustomed to constantly asking sellers about the density of polystyrene foam. This is because density and heat are closely related. Today, modern foam plastic does not require checking its density. The production of improved insulation involves the addition of special graphite substances. They make the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material unchanged.
Thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam in comparison
If you compare polystyrene foam with many other building materials, you can draw colossal conclusions.
The thermal conductivity of foam plastic ranges from 0.028 to 0.034 watts per meter/Kelvin . If the density increases, the thermal insulation properties of extruded polystyrene foam without graphite additives decrease.
A 2 cm layer of extruded foam can retain heat like a 3.8 cm layer of mineral wool, like a 3 cm layer of regular polystyrene foam, or like a 20 cm thick wooden board. For brick, these abilities are equivalent to a wall thickness of 37 cm. For foam concrete – 27 cm.
Thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam is 50 mm in comparison with other thermal insulators
A little about insulation.
Let's look at the thermal conductivity of 50 mm foam in comparison. We will not present the entire table; we will only outline some of the main points. Why is it advisable to consider the thermal conductivity of foam plastic in comparison with other types of heat insulators? And why was a 50 mm thick product chosen for analysis?
The answer to the second question is simple. Sheets of this thickness are most popular in low-rise construction. Moreover, the product is used to insulate both internal and external walls. It should be said that such sheets, in addition to performing their main function of thermal protection, also perfectly reduce the transmission of unwanted noise.
What does this have to do with comparison with other types of insulation? It clearly shows that 50 mm foam plastic is significantly superior to other competitors.
This happens due to the fact that this material consists almost entirely of air. And air, as is known, has extremely low thermal conductivity, about 0.027 W/mK.
The average values of this value for foam plastic range from 0.037 W/mK to 0.043 W/mK. If you depict a comparison of heat-insulating materials in graphical form, the picture will look something like this.
Our product is clearly unrivaled.
But what is the thermal conductivity of 50 mm polystyrene foam compared to other insulation materials in digital terms? In tabular form?
After all, this format is the most visual?
If you prioritize by heat transfer coefficient, the table will look like this.
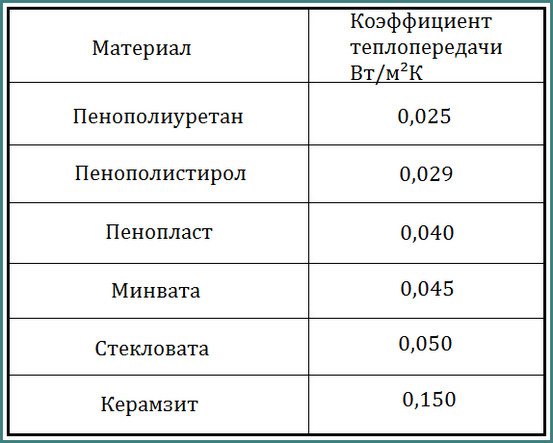
But all this is, so to speak, theory. Which is not interesting for an ordinary developer to go into. He is interested in the practical values of the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam (say, 50 thick) in comparison with other insulators. Let's talk about a few numbers.
- A 50 mm foam plastic sheet (according to RF SNiP) has thermal insulating properties equivalent to 850 mm thick brickwork.
- The same sheet will be equivalent to twice the volume of mineral wool.
- A 100mm foam board is equivalent to a 123mm layer of expanded polystyrene foam.
You can, of course, still rummage through tables and reference books, make comparisons, and draw conclusions. But we will express the essence of the issue in one sentence.
If to maintain a certain value of energy saving, a layer of wood 45 cm or brick 201 cm , then foam plastic - only 12 cm , due to its low thermal conductivity.
Classification of expanded polystyrene
Regular foam
Thermal insulation material obtained by foaming polystyrene. As mentioned above, its volume is 98% air , which is sealed into granules.
This speaks not only of its excellent thermal insulation qualities, but also of its sound insulation properties. The main advantage of the material is the lack of ability to absorb moisture. In addition, it does not rot or biodegrade. Durable material, light weight and easy to use. It can be glued to any building material.
Expanded polystyrene is easy to burn, but it contains a substance called a fire retardant. This is what gives the foam the ability to self-extinguish. In addition, expanded polystyrene cannot be used to insulate facades. This is due to its low vapor permeability . And in order to carry out work with foam plastic under the roof, you should carefully consider the ventilation system.
Use depending on the brand of material
- PSB-S 15. The marking of polystyrene foam indicates that it can be used to insulate structures that are not subject to mechanical stress. For example, insulation of the roof, the space between the slings and the ceiling.
- PSB-S 25 and 25F. Common markings for polystyrene foam. It says that any surface can be insulated. Walls, facades, ceilings or flooring, roofing.
- PSB-S 35 and 50. This material can be used to insulate objects that are under constant high load.
What is the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam boards?
Energy saving is the main task for which thermal insulating materials are used in construction. When comparing different types of insulation with each other, first of all, compare their thermal conductivity. It is measured in W/(m K) and shows how much heat will pass through an object 1 m thick per unit time. The lower the thermal conductivity coefficient, the lower the losses.
What do thermal insulating properties depend on?
The low thermal conductivity of expanded polystyrene is due to its structure: the volume of solid matter is usually less than 3%. The many cells that form the structure of the sheet contain air inside, which perfectly retains heat. There is a simple rule: the smaller the granules and the more uniform their sizes, the better the performance of the slab.
Depending on the manufacturing technology, polystyrene foam can be:
- pressless: EPS, PSB, PSB-S;
- press: PS-1, PS-4;
- extrusion: XPS, Penoplex, Stirex, Technoplex, TechnoNIKOL, URSA XPS;
- autoclave: Styrofoam;
- autoclave-extrusion.
Extruded polystyrene foam is produced by mixing granules at high temperature and pressure. The result is a particularly uniform, closed-porous structure, with cells of 0.1–0.2 mm. Therefore, the thermal conductivity coefficient of extruded polystyrene foam (0.028–0.034 W/(m K)) is lower compared to that made using other technology.
Polystyrene foam is obtained by processing raw materials with dry steam; the granules in it join together due to thermal expansion. It has large heterogeneous cells that are not held together very rigidly, so the insulation is significantly inferior in strength and density to that produced by extrusion. At the same time, the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam, especially in high-density grades (35 and 50), is slightly inferior to extruded polystyrene foam (on average by 0.002 W/(m K)).
How does the thickness of the slab affect?
The value of this parameter varies in the range of 10–200 mm:
- a sheet up to 30 mm has a thermal conductivity of no more than 0.035 W/(m K), it is suitable for insulating interior partitions;
- slabs up to 100 mm are used for finishing internal and external walls; with their help, heating costs can be significantly reduced. The indicator in this case is somewhat lower, for example, for a 50 mm sample it is 0.31–0.032 W/(m K);
- expanded polystyrene with a thickness of more than 100 mm is used in regions with severe frosts, as an option - as a foundation frame. Its thermal conductivity is no more than 0.3–0.031 W/(m K).
How to independently calculate the required insulation layer?
To do this you will need:
- Find out R - the value of heat transfer resistance of the external wall of the house. The data is permanent, individual for each region and is publicly available on the Internet.
- Determine k - the thermal conductivity coefficient; it is indicated in the characteristics of the material.
- Calculate thickness by dividing R by k.
It should be remembered that this calculation takes into account both the thermal insulation properties of polystyrene foam and similar data for all layers of the wall, including brickwork, plaster, and so on.
Stamps
The production of different types of expanded polystyrene is dictated by the differences in the materials of the buildings being constructed. Non-flammable insulation PSB-S is fireproof, which is why it is often used in finishing the facades of residential buildings. The number in its marking means maximum density.
| Brand | Thermal conductivity, W/(m K) | Application |
| PSB-S 25 | 0,041 | insulation of walls, facades, roofs and floors of buildings and structures |
| PSB-S 35 | 0,038 | production of sandwich panels and reinforced concrete concrete using permanent formwork |










