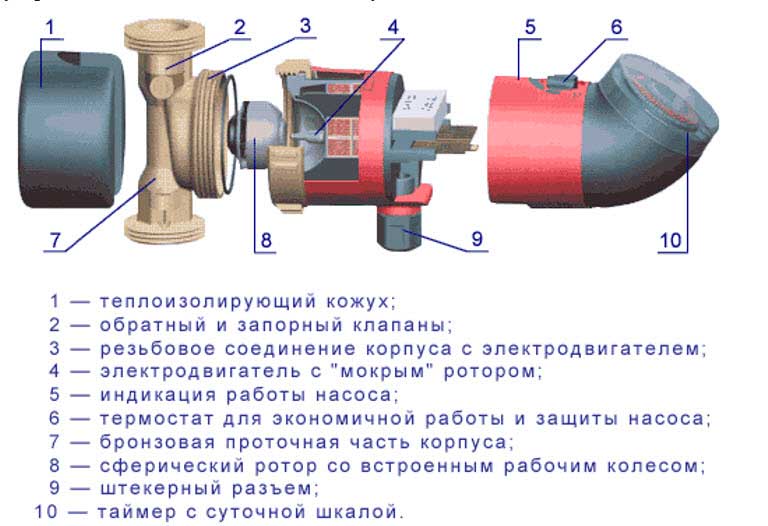
Main characteristics of circulation pumps
The main characteristics by which the choice of circulation pump is made:
- pressure
, showing the ability of the device to raise water to a certain height; - performance and flow
, showing how much fluid the supercharger delivers per unit time.
These parameters are key in calculating the heating system. The pressure will allow you to understand whether the blower is capable of serving a pipeline network with a certain height difference. And the flow rate is calculated according to the requirements of the heating boiler for the planned volume of coolant.
All the data the user needs is contained in the markings on the front panel
. The numbers on the circulation pump mean:
- type of device (most often it is UP - circulation);
- speed control type (not specified - single-speed, S - step switching, E - smooth frequency control);
- diameter of the pipes (indicated in millimeters, means the internal dimension of the pipe);
- pressure in decimeters or meters (may differ among different manufacturers);
- installation dimensions.
The pump marking also contains information about the types of connections of the inlet and outlet pipes. The complete coding scheme and word order looks like this:
Responsible manufacturers always follow standard labeling rules. However, individual companies may not indicate some of the data, for example, installation dimensions. You need to find it out directly from the documentation for the device.
The choice of a circulation pump is always made after a careful calculation, which takes into account the type of heating equipment, the volume of coolant, elevation differences, and the minimum required blower performance.
Advice! You cannot buy products from unknown companies that copy products from reliable and popular brands. Such a pump is an ineffective investment. The use of low-quality materials, impellers, and turbines with limited service life leads to rapid failure of the supercharger. On specialized forums you can find many scary stories in photographs about the kind of technological nihilism that the housings of Chinese “no-name” products contain.
Therefore, you should choose a pump only from trusted brands. Reliable devices are also available in the mid-price category
And if you need the highest quality and have the opportunity to pay one and a half to two times more, you should pay attention to products from the brands GRUNDOFS, WILO
Calculations
The circular pump device is a mechanism in the form of a rotor placed inside a metal casing. A wheel with several blades (impeller) is attached to the rotor shaft. When the pump motor is turned on, the wings rotate and move the liquid throughout the heating system.
The principle of operation is the forced transportation of water within a closed loop of the heating system, in other words, ensuring the circulation of coolant through pipes and radiators. Proper selection of such a unit ensures its correct operation without unnecessary costs.
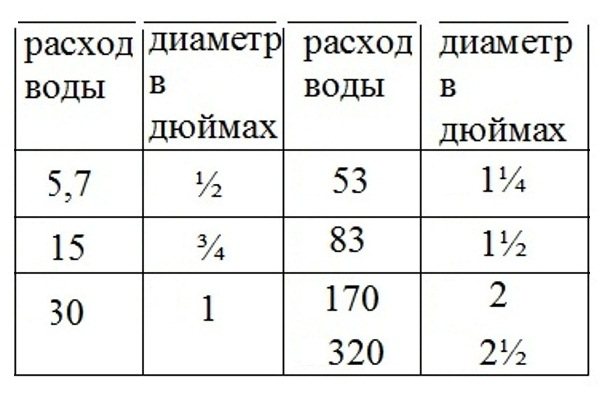
Pump power calculation table.
Before choosing a pump, it is necessary to determine the volume of water that will pass through the heating boiler in one minute. These are the parameters that manufacturers set, balancing the liquid consumption with the boiler power. If a 20 kW heater is installed, then in one minute it will pass 20 liters of coolant.
Next, it is necessary to calculate the water flow in each ring of the heating system (knowing the power of the radiators, this process will not be difficult). The coolant flow in the pipes directly depends on their diameter. Inch pipes transport 30 liters of liquid per minute, two-inch pipes - 170 l/min. The average speed of water movement through the heating system is 1.5 m/sec. The power of the circular pump can be selected taking into account the length of the pipeline. For a ten-meter section of the heating main, a pressure of 0.6 m is sufficient. Therefore, in order to establish a water supply through a 100-meter heating system, it is necessary to select a pump capable of delivering a pressure of 6 m.
You can also calculate power using the following formula: Qpu=Qn/1.163xDt [m3/h], where
- Qpu (measured in m3/hour) – coolant supply at the design point;
- Qn (measured in kW) – heat consumed in the heated area;
- Dt – temperature difference in the forward and return pipelines (on average 10-20 °C);
- 1.163 – specific heat capacity of water.
Such calculations are not absolute, but rather standard. There are complex formulas for more accurately determining the required power of the circulation pump, but understanding them without certain knowledge in the field of physics will not be easy. And the units are mass-produced, so it is only possible to adjust their operational parameters to individual heating systems only approximately. Therefore, experts advise selecting a pump with a power reserve of 5–10% of that obtained as a result of calculations. There are devices with several setting modes. During their operation, you can select optimal operating parameters.
Having such simple knowledge and enlisting the help of the seller, you can choose a circulation pump of the optimal power that will provide heat throughout the entire room.
Installation of the pump: stages and nuances during installation
The first thing to do is drain all the liquid from the heating system. Then, if necessary, the pipeline must be cleaned. In accordance with the connection diagram, work on installing equipment and fittings must be carried out. When the installation of the heating system is completed, fill the water. after which excess air is removed from the pump. This is done by opening the central screw
Please note that before each time the unit is turned on, it is necessary to carry out air removal work
When a circulation pump for heating is purchased, you need to decide on the place where it will be installed. Experts recommend installing this equipment on the return line in front of the boiler. The thing is that air can collect at the top of the boiler during operation if the pump is installed on the supply side. This may cause it to be drawn out of the boiler, causing a vacuum to form, causing that part of the boiler to boil.
If the pump is installed in front of the boiler, then water will be pushed into the heating installation. The consequence of this will be the creation of air space and the installation will be completely full. In addition, with this installation option, the pump will operate at lower temperatures, which will have a positive effect on its service life.
Having selected the installation site for pumping equipment, then create a bypass or outlet. The need for it is due to the fact that in the event of a breakdown or when the electricity is turned off, thanks to it, the operation of the entire heating system will not stop and there will be an opportunity for the coolant to pass through the main pipeline thanks to an open tap. When installing a bypass, it is necessary to remember that the diameter of the pipe should be smaller than the diameter of the main pipeline. When the bypass is ready, proceed to the main stage of work on installing the unit.
The heating pump shaft must be completely submerged in water. If it is only partially immersed in the coolant, this will lead to a reduction in equipment performance by 30%. In the worst case scenario, the work area becomes faulty.
In addition, the installation also includes the installation of a terminal box with a top location.
In addition, ball valves are installed on both sides of the pump. During the operation of the equipment, they will be required to perform maintenance on the pump and dismantle it if necessary.
The system must also include a filter. It will protect the unit from mechanical particles. Once inside its structure, they can adversely affect the operation of the pump.
A manual or automatic valve must be installed on top of the bypass pipe line. It is necessary to release air pockets at certain intervals.
Wet pumps
Wet-type pumps are chosen for steam heating of private houses with an area of no more than 300 m2, and for heating garages. They are used for heating large greenhouses, poultry houses, and animal farms. The pump circuit is standard.
We recommend: How to make steam heating in a country house?
The rotor and starter are located in a protective cup to prevent water from getting on them. Seals prevent liquid from entering the glass. All other parts come into contact with water. This has its advantages.
Water, washing all pump components, lubricates them, thereby making them work more efficiently. Wet pumps, when used correctly, will last about 50 years. Care must be taken to ensure that no air accumulates in the pump. It will increase the load on the working parts, which will lead to their rapid wear.
Special outlets are provided in the design to remove air. They are located at the top of the motor and on the front wall of the housing. Air escapes through the upper pipe when the system is operating. If repair work is necessary, open the screw on the front wall.
Purpose of circulation pumps
The operating principle of a standard closed-type heating system is quite simple. The boiler heats the water, which passes through the radiators, releasing the accumulated heat
In the case of natural circulation, it is very important to maintain accuracy in design, maintaining a certain angle of inclination of the pipeline. However, due to the low speed of movement of the coolant, it quickly cools down, and cold liquid returns to the boiler, forcing it to constantly operate at full load.
To eliminate this drawback, different types of circulation pumps are used. Their purpose is to create the coolant pressure necessary to ensure uniform heat distribution between all elements of the system. First of all, this helps to reduce the requirements for compliance with slopes and pipeline cross-sections. At the same time, the difference in temperature of the liquid at the outlet and inlet of the boiler is only a few degrees, which significantly reduces the load on the heating equipment and reduces energy costs.
Video: choosing a heating pump
The potential of an autonomous heating system for several floors is not always enough. The pressure in it does not exceed the line of 0.6 MPa. To increase pressure and improve the water circulation process, you need to either create a closed line consisting of pipes of a rather large cross-section, or add a pumping unit to the equipment. Since pipes are expensive these days, it is better and more profitable.
The circulation pump is an excellent heating assistant
Only in the twenties did one German mechanic manage to assemble a sealed engine. After some time they prepared it at its base. For almost 30 years, such structures worked regularly, taking part in heating homes in Western Europe and the United States.
A clear drawback of the “primitive” water circulation pump was the poor gland seal, the rapid wear of which manifested itself with minor flaws, scratches on the shaft, and the gland material “did not suffer” in strength. The equipment needed sealing, the shaft needed grinding, so repairing a circulation pump was not uncommon for that time.
Look at the pump design and everything will become clear
70 years ago the “wet” circulation pump was born. It was concocted by an engineer from Switzerland. The motor in this unit was placed on an elbow along which water pumped, and the water simultaneously lubricated the oil seal.
Later, the knee was replaced with a snail, familiar to today’s realities, and the centrifugal apparatus acquired modern features in appearance.
Design of pumps for heating systems
Depending on the design, all pumping units of heating systems are divided into two types:
- dry circulation pumps;
- wet rotor pumps.
Both types of devices are quite effective in heating pipelines and have both advantages and disadvantages.
Dry pumps

In such units, the rotor does not come into contact with the working fluid, since all elements of the electric motor are separated from the working chamber of the device by a special type of sealing system. It consists of polished metal rings carefully fitted to each other. To eliminate friction, there is always a thin film of liquid between the sealing elements, which acts as a lubricant. This is what prevents damage to the seal rings.
Depending on the location of individual structural elements, dry pumps for heating systems can be divided into three types:
- console type pumps;
- vertical centrifugal pumps;
- block pumps.
The suction pipe of cantilever circulation pumps is located on the outer edge of the volute, while the discharge part is placed in the opposite direction. A feature of the second type of units is the location of the electric motor in a vertical plane, which can significantly increase the productivity of the devices.
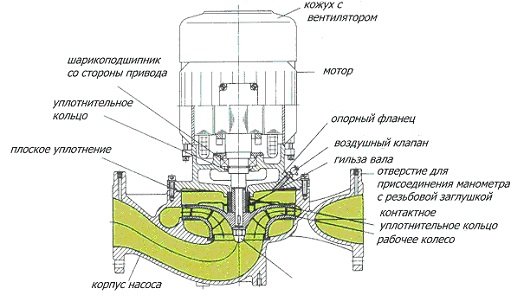
Design of a circulation pump with a dry rotor
Dry rotor pumps have numerous advantages:
- long service life;
- high performance;
- Efficiency is close to 80%;
- ability to work in case of coolant leak;
- high maintainability;
- relatively low cost;
- reliability;
- Possibility of installation in any position.
At the same time, the increased noise level of units of this type does not allow their installation in residential premises. Disadvantages also include requirements for cleanliness of the coolant and the need for periodic maintenance and lubrication of the moving seal.
Glandless circulation pumps

The rotor and impeller of pumps of this type are located in the pumped coolant, which copes well not only with its main function, but also with cooling the electric motor parts. The stator of the pump electric motor is separated from the rotor by a sealed glass made of non-magnetic steel or carbon fiber. “Wet” type units are designed to operate in systems with stable, rarely changing fluid flow. The presence of a control unit allows you to vary the number of connected windings, and accordingly, change the pump performance. The choice of the optimal operating mode has a positive effect on the efficiency of the unit.
The advantages of “wet” type units include:
- low noise level;
- no need for lubrication;
- effective cooling method;
- ease of maintenance and installation;
- relatively low price of the unit and spare parts;
- long service life.
Pumps with a wet rotor are not without disadvantages in the form of low efficiency (a little more than 30%), the inability of the unit to operate without coolant and the requirements for horizontal orientation of the rotor shaft during operation.
Design features by connection method

In utility and industrial pipelines, circulation pumps with a dry rotor are most often used as more efficient and powerful devices. Their connection is carried out mainly by flange connection, and for installation either a common support frame or a specially equipped foundation can be used. At the same time, manufacturers also produce devices designed for integration into autonomous heating systems. As a rule, they all have increased power and performance, and their installation does not require special mounting.

The delivery package for pumps with a coupling type of connection necessarily includes fastening elements.
Coupling connections of circulation pumps are typical for low-power wet-type units with direct-flow coolant movement, which can be built directly into the pipeline. Such devices are represented by a wide range of household centrifugal pumps, while powerful industrial units with a flange connection require additional pipeline support using a console and foundation.
tekras.ru
The use of rotary pumps requires pumping a large volume of liquid. There are several types of rotary pumps, differing in operating principles and design features. Let's look at the main types of rotary pumps and their design below.
Rotary pumps operating principle and characteristics
The principle of operation of a rotary pump is to transport liquid by placing it in a chamber from which it is expelled using rotational and translational manipulation. The main working mechanism of these pumps is the rotor. Depending on their design, rotary pumps are divided into different types.
Some people apologize to government employees for these misappropriations, saying their wages are too low. How can you honestly justify illegal activity? If a landlord steals goods, even ten dollars' worth, he will probably be dead.
If the salaries of civil servants are too low, then they need to be adjusted to market value less the amount of additional benefits they receive, such as increased risk, housing subsidies, etc. their privileged position in government should not be a reason to ignore illegal activities, especially those that involve important material resources for the poor. Low wages should never be used as an excuse to explain away theft and dishonesty.
The working mechanism of rotary pumps constantly rotates, but despite this, the operating principle of this equipment is individual and is not similar to dynamic pump options. In the process of pumping liquid, it enters the chamber, and it is displaced using a discharge pipe.
They are more common where there is no transparency in government spending. Unlike the previous situation, when the pit is digested using local labor, and when the pump is completely used using local materials, the leak is more difficult to hide and therefore more difficult to achieve.
Government agencies and local businesses will also have more reason to identify shortcomings in an alternative technology solution and advocate against its use. Like most things in life, a rope pump is not perfect. There are some restrictions on its use. These include limited water depth and possible water contamination.
A closed space is created inside the working chamber of the rotary pump, to limit which movable and stationary parts of the device are used. During work, this space changes in volume. In the process of moving movable parts, the working chamber changes in size, thus pumping the working fluid.
Although the rope pump is effective for shallow wells, it is less effective for deep wells. Unfortunately, it is not easy to predict how deep this might be good for rope pump operation. The inability to predict this is due to the fact that local materials are used to make the pump, which do not have universal standards. Both the diameter and thickness of valves, for example, affect the depth of the well where the pump can be used. Because the inner tubes and skin may vary in thickness, and because the valves are handmade by local craftsmen, they are not uniform.
Depending on the main movement in a rotary pump, they are of two types - rotary rotation and rotary inflow. The first option is based on the exclusive rotation of the moving parts in the pump, and the second is based on a combination of both rotation and delivery.
Rotary rotary pumps are of gear and screw type. The first option is distinguished by the presence of a working chamber, the body of which remains motionless, and the gears move in a certain direction. The working chamber changes in size precisely due to the movement of the gears. This pump option can have both external and internal gearing.
If the valve is too thin and flexible, it becomes crooked and water flows toward the bottom valve instead of up. The deeper the wells, the water that presses against the bottom valve can be so heavy that it flows all the way back before it reaches the surface of the well. Likewise, even if the valve is not too flexible, the inner diameter of the pipe cannot be cut too accurately and water flows back to the bottom valve. And this problem is accentuated in proportion to the depth of the well. Instead, if the valve is cut so that it is too tight inside the pipe, it may be more effective at lifting water through the pipe, but this may also increase the difficulty of handling the wheel at the top of the well.
Screw pumps are characterized by the presence of a working chamber, with a fixed body and movable screws. The screws rotate around their axis, thereby creating a temporary working chamber that injects and pumps liquid. When considering this version of pumps, we should highlight the vane and rotary-plunger versions.
At some point the wheel will be too stiff for manual control. Since all of these factors are variable, it is impossible to say what the maximum depth of a well is where a rope pump can be effective. Another limitation is the possibility of well contamination. The above rope pump does not indicate that the well must be covered. People tend to forget this because more time, money, effort and will are spent. If the well is not covered, small animals or their feces can get into the water.
Human waste and vermin can get into the water if those operating the wheel do not keep their hands clean. A well with a suitable cover will allow the pipe to reach above the cover before deflecting where the water is stored in the container. A simple hole in the cap may be enough for a rope to run down the shaft. Of course, it would be better to place a small piece of pipe, somewhat larger than the main pipe, over the cover so that the valves can easily penetrate it along with the rope inside the well.
The vane version of the rotary pump is distinguished by the presence of a rotor with longitudinal slots, inside of which there are vane parts. The rotor rotates inside a cylindrical housing, while the axes of the rotor and the housing part do not coincide with each other.
To limit the working chamber in cylindrical pumps, the casing part and gates are used. In order to close the working chamber, the gates fit tightly to the body using centrifugal force or special spring mechanisms installed in the inside of the rotary pump. In relation to the design features of a rotary cylindrical pump, they have a single or double action.
If community residents are not overly concerned about hygiene and have limited resources, they may be more tempted to skip the pit, increasing the likelihood of infection. The consequences of these deficiencies can be limited by providing adequate training and an effective information campaign on hygiene standards.
Although these are recognized disadvantages of using a rope pump, they are not serious problems. Experts who have invested in hand pumps will exaggerate all of these problems without noting that solving these problems comes at a much lower cost than using hand pumps.
Rotary plunger pumps are divided into radial and axial. The operating principle of this pumping equipment is comparable to a pump and a hydraulic motor. These pumps work due to a combination of movements of both rotational and translational types.
Advantages and disadvantages of a rotary pump
Despite the fact that rotary pumps differ in design, all types of this equipment have the following advantages:
Unskilled local workers may be used to drill surface wells and install rope pumps. Skilled workers, such as self-employed craftsmen, can produce used tires, build used and abandoned bicycle pumps, and fix valves on rope.
Spending on developing funds to pay local workers instead of importing capital has many advantages. He has previously argued that this reduces the possibility of misappropriation of funds for personal use, which plays the role of increasing transparency by involving more stakeholders. Transparency makes funds raised by the community and money received from donor institutions easier to track and therefore more difficult to hijack.
- the presence of a uniform supply of the pumped liquid, in relation to reciprocating pumping equipment;
- the ability to operate the pump in hydraulic motor mode due to the presence of reversibility;
- the absence of valves in the design of the pump, so the efficiency and power of the equipment are at a high level;
- the frequency of movement of the rotary pump is quite high, their speed is at the highest level compared to other alternative pumps.
However, rotary-type pumps have certain disadvantages, namely:
As part of the private enterprise consolidation process, local drilling and pumping stations could be created and trained. Organizing them can be part of the work of a community mobilizer. Development funds that flow out of the community if the imported hand pumps were manufactured elsewhere will thus be available to these private private enterprises. A drilling company may be formed with a core of managers and trainers who will employ teams of local workers for each client.
When the money is used to provide employment to local youth, the money generated by them will be spent on purchasing local consumer goods. The same thing happens when local craftsmen use worn-out rubber tires to cut and install plastic pipes to turn old and broken bicycles into pumps. Rope pump technology helps grow the workforce, increase local income, reduce unemployment and grow local businesses.
- the pumped medium must meet certain regression requirements and must not have an abrasive effect on the internal parts of the pump;
- a high level of equipment reliability entails high costs for its maintenance and operation.
This document, like others in this series, is intended specifically for community mobilizers. It does not purport to provide technical support for rope pumps, but rather to discuss the social and economic considerations of using these pumps. Your main goal as a mobilizer, animator, activist or social worker is to strengthen poor communities.
Self-reliance is not only the freedom not to depend on external funds, but also freedom from dependence on many other categories of external resources. There is no evidence that poor villages in less developed countries should unquestioningly accept the way of thinking, creativity and assumptions on which technology is based in Europe and North America. It is a form of mental dependency that helps perpetuate poverty.
Design and diagram of a rotary pump
Inside the flow part of the rotary pump there is one hollow rotating disk, which is responsible for performing rotational manipulations and pumping liquid between the nozzles.
Pumps with an empty disk inside are used in the process of pumping liquids with solid particles. However, they are distinguished by reliability, long service life, and low rotation speed. It is possible to install several hollow disks inside the pump. Among the advantages of this pump option, we note:
Providing expensive drilling equipment and expensive hand pumps also creates a form of dependency. Where the underground space is too deep, such dependence cannot be completely avoided. In areas with deep groundwater, there is a high likelihood that the water is salty and too difficult to pump, so it may be more appropriate to consider other technologies such as rainwater harvesting. In areas where the groundwater is not too deep, mechanical drilling equipment and hand pumps can be avoided.
By promoting the use of rope pumps by explaining the advantages and disadvantages to community members who need to decide whether to use them, the mobilizer helps reduce dependency and increases confidence in their strengths. If it works, the template will be copied.
1. Possibility of self-priming. The pump starts even if there is no liquid in it.
2. Ability to operate at low speeds. Thanks to this advantage, the pumps have the ability to pump high-viscosity liquids. Low speed operation ensures long-term operation of the equipment, a high level of reliability and resistance to wear.
Remember that the village, not the agency, must make the decision. While you can review the costs and benefits of each option with them, it is up to the community to decide which technology is best for them. Armed with the above arguments and considerations, you can help them consider the consequences of choosing a rope pump over other technologies. Your strategy should outline the possible alternatives, costs, benefits, and other considerations for each option so that community members can make an informed decision.
3. In order to clear the downstream pipes of liquid, the reverse flow function is used. There is no need to use a second pump or switch pipes.
4. Solid particles enter the liquid due to the high adaptability of the disc.
Rope pumps are not a one-size-fits-all solution to problems in the water sector. However, they improve the situation on many issues. Although there are strong investors who oppose the adoption and development of rope pumps, the benefits of using them, especially encouraging communities to use their own resources and build capacity, will far outweigh the disadvantages.
The Mobilizer is able to introduce rope pumps to facilitate their wider use, as well as help community members make their own decisions, help themselves and become stronger. From the specialized work it follows that the car, which is so necessary for all of us today, has a history full of vicissitudes, marked by important events. Who knows how many enthusiasts, courageous, inventive spirits, skilled technicians, who sometimes gave up their lives and spent wealth and even sacrificed their interests on the altar “divine machine”.
5. The suction height value of the rotary pump is more than eight meters.
6. Low noise production and low vibration levels ensure easy operation of the pump.
7. A high level of efficiency and performance is also one of the advantages of these pumps. The performance of the device does not depend on the viscosity level of the liquid it pumps.
Discoveries, inventions, steps forward were made almost side by side, at high speed or very slowly, often with great difficulty, because the automobile included so many and varied achievements of science and technology that were at first unimaginable. The car has penetrated unhindered into the farthest corners of the globe, being loved and loved by the vast majority of people, but also being blown up by a few. It is produced today about 40 million pieces per year.
The car has become a friend of the person he is in no mood for, regardless of the weather; Sometimes fueled by the wrong fuel, subjecting the engine to abnormal technical and mechanical demands, sloppy on the part of some owners, "tattooed" into new tires or normal, it has become much more important than it was ever intended to be.
8. The versatility of the pump is ensured primarily by its ability to pump various types of liquids.
9. The design features of the pump are simple, since it contains compact elements that can be easily replaced or repaired.
10. Under certain circumstances, sediment is able to work without liquid.
The principle of operation of this pump is the rotation of a hollow disk, which gradually comes into contact with internal areas on the body part. As a result, a line is created that is responsible for sucking liquid from the system. Thanks to this, the liquid begins to move. A membrane is used to control the disk, in the process creating two separate sealed chambers. The vacuum space is responsible for the suction of liquid into the pump.
Due to the fact that rotary disk pumps contain only a few components, they have a long service life, do not break down and are easy to repair. The scope of use of this type of device extends to:
- both volatile and viscous liquids;
- lubricating oils and liquids with increased dryness;
- liquids containing abrasive substances;
- aggressive and corrosive liquids;
- food industry products.
Classification of rotary sediments and features of their application
There are two main classes of rotary pumps:
- rotary rotary pumps;
- rotary-progressive pumps.
The first version of pumps is characterized by the presence of only rotational movements during the process of pumping liquid. There is a type of rotary pump called a toothed or gear pump.
This pump option can have internal or external gearing. A pump with external gearing is used for pumping liquids with a high level of viscosity that have lubricating properties. The self-suction capability of such pumps is no more than five meters. The operating principle of this mechanism is based on the constant connection of the driving and driven parts of the mechanism. Next comes the process of setting it in motion. As the sediment rotates, the teeth begin to suck in liquid due to the formation of a vacuum space. Due to the formation of contact between the teeth, fluid is transferred from one part of the mechanism to another.
The second version of the gear pump has internal gearing and is more compact in size. However, the manufacture of this device will require a lot of effort, so its cost is a little more expensive. An electric motor is required to drive the drive gear. Since its shaft with the help of teeth grips the leading section of the device, the rotation of the wheel begins. During the rotation process, volume is released, as a result of which liquid enters the inside of the pump. The medium moves under the influence of its injection.
Rotary progressive pump options are divided into:
- vane type rotary vane pump;
- rotary piston pump.
A vane pump is also called a rotary vane pump; this equipment is self-priming and differs in volumetric dimensions. The main function of this pump is to pump liquids that have lubricating properties, such as oils or diesel. The pumps are capable of sucking liquid in a dry position and do not require a working type liquid.
The operating principle of this device is based on the presence of a rotor with eccentrically located plates, inside of which there are grooved sections of longitudinal variation, called gates. Centrifugal force is used to press them against the stator surface.
Due to the eccentric location of the rotor, during its rotation the plates are constantly in contact with the wall of the housing part, first entering the inside of the rotor and then leaving it. Because of this, the liquid is first pumped into the mechanism and then comes out under pressure.
The positive displacement rotary piston pump can be axially piston or radial piston. Inside this mechanism there are working parts that play the role of pumping fluid. Most often these are plunger or piston elements. Axial piston pumps are characterized by the presence of reciprocating movements located parallel to the axis of rotation of the mechanism. For radial piston pumps, this movement occurs radially.
Axial piston rotary pumps have swash plates or swash plates located in the axial direction. Axial piston-type pumps with an inclined block remain quite popular. To transmit torque in such devices, a connecting rod located in the inner part of the pistons is used. Using this scheme, it is possible not only to reduce the size of the pump itself, but also to improve the dynamics of acceleration and deceleration.
A manual rotary pump is used in the process of pumping fuel and lubricant materials. Most often, this pump is made of cast iron. There is also a rotary barrel pump, made of aluminum, designed for pumping gasoline. Pumps that separate oil into separate reservoirs are easy to use. Despite the affordable cost, these pump options are characterized by a high level of reliability and long-term operation.
Dynamic type rotary pumps are based on the dynamic principle of operation. By rotating certain types of elements, kinetic energy is generated, which supplies pressure for pumping liquid. Depending on the principle of operation, these pumps are vortex and vane. The rotary vane pump does not have a self-priming function. Among the varieties of vane pumps we note:
- devices of centrifugal, radial, diagonal and axial type;
- with a spiral, ring or guide drive;
- depending on the type of liquid, single-flow and double-flow.
Rotary vortex pumps are open star-shaped and closed, having a peripheral channel. Depending on the flow of fluid, vortex pumps are single- and multi-stage.
Depending on the scope of use of pumping equipment, these devices are divided into feed, circulation and condensate pumps.
Rotary pumps (gear) are designed primarily for pumping viscous liquids (condensed milk, cream, sour cream, ice cream mixture, etc.). They come with external and internal gearing.
Rice. 1. Diagram of rotary pumps (gear): a, - with external gearing: 1 - housing; 2 - gears; b - with internal gearing: 1 - body; 2 - gears; 3 - protrusion in the body.
The working body of a rotary pump with external gearing (Fig. 1, a) consists of two gears 2, enclosed in a housing 1, which is two combined cylinders. One of the gears is driving and is fixed to the working shaft. When the gears rotate in the direction indicated by the arrows, the spaces between their teeth will be filled at the bottom with liquid coming from the suction pipe. At the top where the teeth mesh, fluid will be forced out of these gaps and into the discharge pipe. A rotary pump with internal gearing (Fig. 1, b) also consists of a pair of gears 2 located one inside the other. At the top right, the teeth of these gears mesh, and on the opposite side they are separated by a fixed crescent-shaped protrusion 3, which prevents fluid from leaking from the discharge side into the suction side. When the pump operates, fluid coming from the suction line fills the gaps between the gear teeth, then is transferred to the outlet into the discharge pipe, where it is squeezed out by the meshing teeth. In gear pumps, the suction and discharge pipes are interchangeable: changing the direction of rotation of the gears also changes the purpose of the pipe. The theoretical performance of the pump is equal to the number of volumes of liquid transferred by gears from the suction to the discharge pipe per unit time. In fact, the performance due to the reverse flow of liquid into the pump through leaks is less than theoretical. As the pump wears, the end clearances between the gears and the housing walls increase and the volumetric efficiency decreases. The size of the end gaps should be 0.01-0.03 mm. A hole is made in the depths of the cavities so that the liquid is not squeezed between the tooth and the cavity. Gear pumps are manufactured with bronze bodies and gears with external teeth made of stainless steel. The drive is carried out directly from an electric motor or through a gearbox.
Technical characteristics of gear pumps NRM-2 NUK-10 Capacity, l/h 250-2000 10000 Pressure, m of water. st 20 25 Gear meshing internal external Power, kt 0.6 2.8 Number of revolutions per minute of the electric motor 930 950 gears 930 92 Diameter of pipes, mm 36 75 Dimensions, mm length 475 910 width 295 750 height 285 560 Weight, kg 52 335
The performance of the NRM-2 pump is regulated by turning the cover, which changes the volumetric efficiency of the pump. VNIMI research has established that a more stable performance of a gear pump is obtained when it operates on a viscous fluid. The efficiency of the pump is very low compared to the efficiency of piston pumps and is close to the efficiency. centrifugal pumps.
Pump operation
Pumps are installed on foundations, and mobile pumps are installed directly on the floor without fastening. The pump suction line should be as short as possible. However, if the pump and tank or apparatus are fixedly fixed, then there must be at least one branch (elbow) in the line, since a straight section of pipe between two fixed pipes cannot be installed due to the need for axial movement of the pipe to both pipes when screwing up the connections . Before starting the pump, you need to make sure that the pump is cleaned and assembled correctly. After turning on the switch and making sure that the pump moves correctly, open the valve on the suction line completely. The valve on the discharge line of the centrifugal pump is opened enough to have the required capacity. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the seals, especially if the pump operates on a viscous liquid or provides a high suction height, i.e. if a vacuum is created in the pump. In this case, through a leaky seal, air will enter the pump and be worked into the product, which is unacceptable. Therefore, suction lines under vacuum and pump seals must be assembled in such a way that a complete seal is ensured. To do this, the suction line connections must be in good working order, with good rubber gaskets and carefully tightened. The pump seal must be packed, lubricated with animal fat or oil, and properly tightened. If the seal is overtightened, the shaft heats up and the seal fails. When installing the pump, you must strive to ensure that the liquid flows into it by gravity, that is, the pump is under the fill. This can prevent or reduce the possibility of vacuum formation in the suction part of the pump. When installing pumps for suction, it should be borne in mind that the suction height depends on the temperature of the pumped liquid:
Liquid temperature, °C 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Suction height, m theoretical 10.2 10.1 9.9 9.5 9.0 8.3 7.1 5.5 3.2 0 practical 6 5 4 32 1 0 — — —
We recommend reading
- Technical characteristics of Renault Duster Renault Duster 2l 143 l where is it assembled
- Why does German Gref's family need their own school?
- President and Chairman of the Board of Sberbank of Russia German Gref
- Mercedes-Benz introduced the new ML-Class W166 New Mercedes ML
Review of popular models
It is impossible to give a clear name of the model of the best among superchargers without a clear segmentation according to their operating conditions. Therefore, the rating of heating circulation pumps represents the competition between brands and the key features of the equipment they offer.
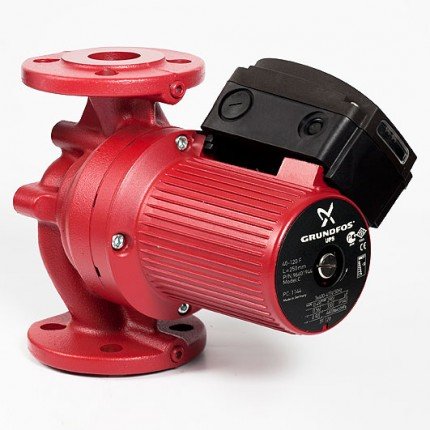
Grundfos UPS
One of the most popular and high quality
types of pumps. A company with roots in Denmark ensured maximum reliability using stainless liners, ceramic bearings, and turbine wheels made of composite materials. Glandless rotor pumps have the following features:
- low energy consumption, from 45 to 220 W;
- very low noise level (up to 43 dB) and vibrations - you can understand that the pump is working only by placing your hand on it;
- wide temperature range from 2 (-20 for some models) to 110 degrees Celsius;
- simple installation;
- unpretentiousness, lack of maintenance;
- durability, service life is at least 10 years.
Grundfos UPS pumps are very compact and lightweight. Their disadvantages include high price,
up to 2 times higher than competitors. However, the popularity of the products of this brand suggests that their characteristics justify the price tag.
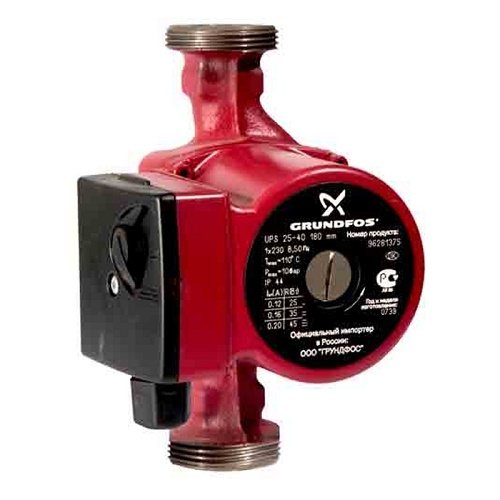

Pump Grundfos UPS 25/40
Products from this brand are considered the most reliable. Only proven and simple solutions are used in their design and electronic circuits. The pumps are characterized by:
- efficiency;
- simple power adjustment;
- reliability, durability - cast iron housing, turbine wheel made of polypropylene, bearings made of metal graphite, stainless shafts;
- operating temperature from -10 to 110 degrees Celsius;
- protection against voltage surges and surges;
- ease of installation.
Wilo Star-RS pumps are compact, lightweight and maintenance-free
. Their price is also higher than that of competitors, but lower than that of the leader in the rating. Users note that at the highest speed the pump begins to make noise over time.
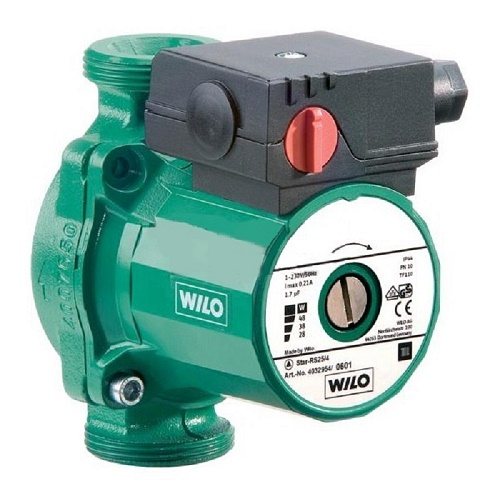

Pump Wilo STAR-RS25/4-130
The Compass series is a reasonable choice, a strong mid-ranger with attractive characteristics and cost. The pumps are distinguished by:
- efficiency;
- simple speed switching circuit;
- small dimensions;
- fairly low noise level up to 65 dB;
- rich equipment and easy installation;
- fault tolerance due to the absence of complex technical solutions and the use of reliable materials;
- low price.
The manufacturing company has an extensive service network, but users note that the pumps of the Gilex “Compass” series break down extremely rarely.

Pump Gilex "Compass" 25/60
DAB VA
A series of pumps from an Italian manufacturer is an optimal balance of characteristics and price.
They are not able to offer record performance, but they are reliable and adapted to the realities of domestic energy networks. The devices are characterized by:
- three-stage speed adjustment;
- simple installation using a quick-release connection;
- two types of mounting dimensions: 130 and 180 mm;
- noise level up to 70 dB;
- affordable price.

Circulation pump DAB VB 55/120
Kinds
The fluid pressure is created by the rotors on which the blades are attached. Most often, the design of a heating circulation pump involves one rotor, but you can find an option with two. An important operating condition is the absence of air in the system.
According to the design and design of the working part, the pump can be with a wet rotor or a dry one. Those with a wet rotor are specially designed so that it and the impeller are in the pumped medium. Changes often affect the design of the housing, made in such a way that liquid enters through existing technological gaps, its constant movement cools the motor and lubricates moving parts.

Wet rotor
Circulation pumps equipped with a wet rotor do not have an oil seal or a sliding mechanical seal. The rotor is completely located in the pumped medium, which provides cooling and lubrication of parts. As the rotor rotates, water constantly passes through the sleeve. The best effect is observed if the pump is positioned horizontally, then air pockets do not form inside the wet rotor.
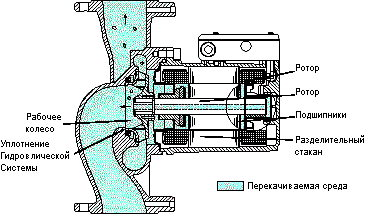
The fact that all parts of the heating circulation pump are constantly in liquid not only lubricates the moving parts, but also absorbs vibration noise, so they are practically silent. To check its operation and the correct rotation of the rotor, use a special device or visually by opening the rear plug. The absence of noise during operation allows them to be widely used for individual heating. In addition, the design of pumps equipped with a wet rotor can be conventional - for heating systems, and special - for hot water supply, where the possibility of mineral deposits is taken into account.
Dry rotor
In such cases, the liquid does not wash the rotor or lubricate the moving parts. The main advantage of this type is the ability to pump a larger volume of liquid. The advantage is manifested in installing engines of higher power. In addition, the device comes with a solid shaft on which a motor with impellers or with a coupling is installed - here it is possible to replace the electric motor or install another one with larger parameters.
To prevent water from entering, a mechanical seal or oil seal is installed between the pump and the electric motor. When rotating, a thin film of water appears between the surfaces. Due to the pressure created inside the pump, the film additionally seals the rotating parts. The main material in the manufacture of rings is agglomerated coal; sometimes, under difficult working conditions, the seal is made of ceramics or stainless steel.
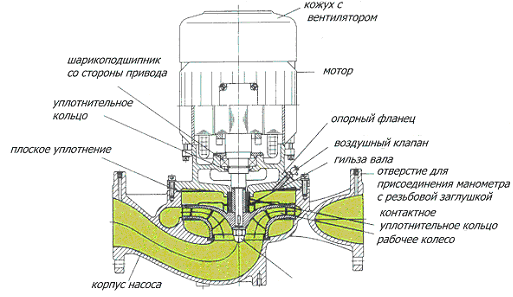
According to the design, the circulation pump device comes with a flange motor connection and a coupling connection. If the pipes (suction, pressure) are located on the same axis, then this is a direct-flow design, which allows them to be installed directly in the line. A frame is provided for mounting. In addition to attaching the pump and electric motor to the frame, it is itself installed on the foundation.
How to choose a heating circulation pump
When selecting circulation pumping equipment, you should take into account such a parameter as the power of the unit.
Many owners of private houses, when choosing such equipment for their heating system, try to buy the most powerful model. Such an installation will cost more, and besides, it will make a lot of noise during operation, despite the fact that the owner will not need to use its power to the maximum. In order not to spend extra money and purchase a good pump, it is necessary to calculate the power of the equipment. which will be enough for your home. When performing them, the following parameters are important:
- pipe diameter;
- coolant temperature;
- coolant pressure level;
- boiler performance;
- throughput.
You also need to know about the number of liters of water that can pass through the heating system within one minute. You should also calculate the amount of water required for the radiator and heating system rings to operate normally.
The length of the pipeline is also an important factor on which the power of the circulation pump depends. Typically, 10 meters of pipeline requires half a meter of pumping pressure.
To calculate the coolant flow, it is necessary to equate its parameters to the boiler power. For example, if the installation power is 25 kW, then in this case the coolant flow will be at the level of 25 liters per minute. If the heating system has a battery power of 15 kW, then for its normal operation it will require 15 liters of water per minute. As the diameter of the pipeline decreases, the resistance that occurs when the coolant moves increases.
Calculation of circulation pump flow for heating
Any circulation pumping equipment has a number of indicators by which the performance of the installation is determined. The main parameter is the pressure flow. It is reflected by the equipment manufacturer in the technical passport.
When calculating the flow rate of the heating pump, use the following formula:
where N is the boiler power;
t1,t2 is the temperature leaving the heat source and located in the return pipeline.
The pressure of the heating pump is calculated in a similar way. Based on European standards, 100 watts of equipment power is needed per 1 square meter of private building.
Performance calculation
First, we take the value of the required heat for heating equal to 70 - 100 W per 1 square meter of room area. Next, we carry out the calculation using the formula: the required pump performance is equal to the power of the entire heating system, multiplied by 0.86, and divided by the difference in coolant temperatures at the inlet and outlet.
In standard writing, the formula looks like this:
Q=P×0.86/(Tf-Tr)
Where:
- P - boiler power in kW,
- Tf – output temperature, (for example 90 C)
- Tr – return temperature.
Calculation example: house with an area of 100 m. Boiler 10 kW, water output from the boiler - 70 C, return flow - 50 C (20 C difference).
This means we get: 10: 0.86 = 8.6 (70-50=20) = 0.43 m/hour (8600:20). The calculation is quite simple and universal.
Design features of pumps with a wet rotor
Models with a “wet” rotor are characterized by a low level of noise generated. They are of interest from the point of view of domestic use. They are widely used in the installation of autonomous heating systems in private buildings or in small administrative and industrial premises. The pump rotor is located directly in the liquid. They are attractive because they are easy to repair at home. But in order to eliminate the malfunction, you need to know the design features. Therefore, let’s take a closer look at how a circulation pump with a “wet” rotor works.
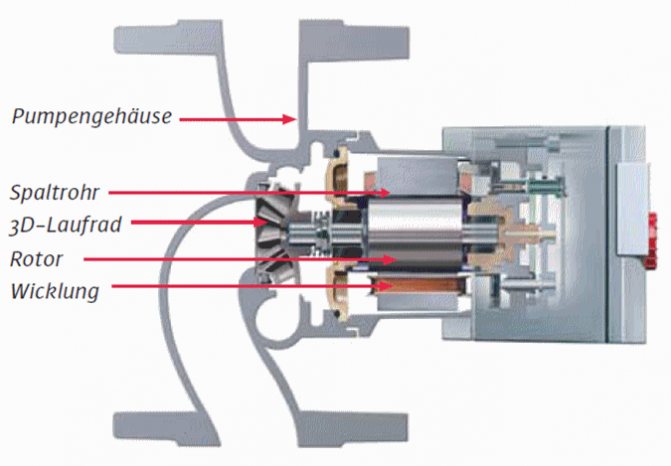
For the manufacture of the body of models for heating, cast iron is usually used, although products are produced in which the body is made of stainless steel (non-ferrous metals, aluminum, bronze, brass). They are used for hot water supply and cold water supply systems. The rotor is placed in a special glass and is rigidly connected to the impeller (impeller). This achieves its isolation from the stator. The peculiarity of the technology is that the shaft can be either metal or ceramic. It is secured in plain bearings (graphite or ceramic). The volute, on which the inlet and outlet pipes are located, is attached to the body using bolts, which are unscrewed with a special key (hexagon) supplied with the product. There is a plug on the front (end) part of the pump; by unscrewing it, excess air can be released. Although it is also possible to automatically remove it during operation. For this purpose, an air vent is located in the upper part. There is a box for electrical connection with an operating mode regulator. When the plug is completely unscrewed, access to the shaft opens, on the end of which there is a slot for a screwdriver. Thus, you can manually scroll if the pump does not start after a long “idle period” (for example, due to salt deposits). Perhaps the only drawback of such pumps is their low efficiency. If for “dry” models it is within 70–80%, then for “wet” models it does not exceed 55%. But at the same time, such a circulation pump design has a number of undeniable advantages:
- the liquid it pumps simultaneously cools and lubricates the parts;
- upon startup, the products automatically remove trapped air;
- The pumps are assembled using a modular principle. Therefore, when repairing, it is enough to replace the faulty part;
- due to low power, they consume little electricity;
- switching of operating modes is provided, which allows you to choose the most optimal one;
- the ability to automatically regulate the start and stop process when using a temperature sensor, which also reduces energy consumption;
- absolute silence in operation;
- does not require maintenance.
The latest models of “wet” pumps are produced shaftless. The impeller (also known as the rotor) rotates on ceramic bearings under the influence of the electromagnetic field created by the stator winding. This significantly simplified the design (no shaft and seals) and increased reliability and durability. Even if small fractions get inside along with the liquid, it will not affect the operation of the pump.
Dry rotor unit and its features
The peculiarity of this type of pump is that it operates without contact with the pumped liquid. The main advantage of such a pump is that such equipment has a very high efficiency, which can reach 80%.
But despite this, such devices have disadvantages:
- Quite a high level of noise emitted during operation;
- Demanding in the pumped medium - there should be no debris or air bubbles.
In this case, “dry” rotor systems are divided into vertical and horizontal (cantilever). In the first, the engine is located vertically, and the pipes are on the same axis. For the second, the motor is in a horizontal position, and the pipes are perpendicular to each other.
Thus, rotary circulation pumps are excellent for pumping various liquids. Depending on what mass will be distilled, you should choose pumps with a dry or wet rotor.
How to choose a circulation pump
Each circulation pump has a set of technical characteristics. They are selected individually for the parameters of each system.
Selecting technical specifications
Let's start with the selection of technical characteristics. There are a lot of formulas for professional calculations, but to select a pump for the heating system of a private house or apartment, you can get by with average standards:

Selecting a circulation pump for heating following these rules is not difficult. Elementary calculations. But it must be said that these figures are statistical averages. If your house at some point differs greatly from the “average” indicators, you need to make adjustments either towards increasing or decreasing technical characteristics. For example, you have insulated your house well, but the power of the previously purchased boiler turned out to be excessive. In this case, it makes sense to choose a pump with a lower capacity. In the opposite situation - the house is chilly in extreme cold - you can install a more efficient circulator. It will temporarily solve the problem (in the future you will need to either insulate or change the boiler).
Model selection
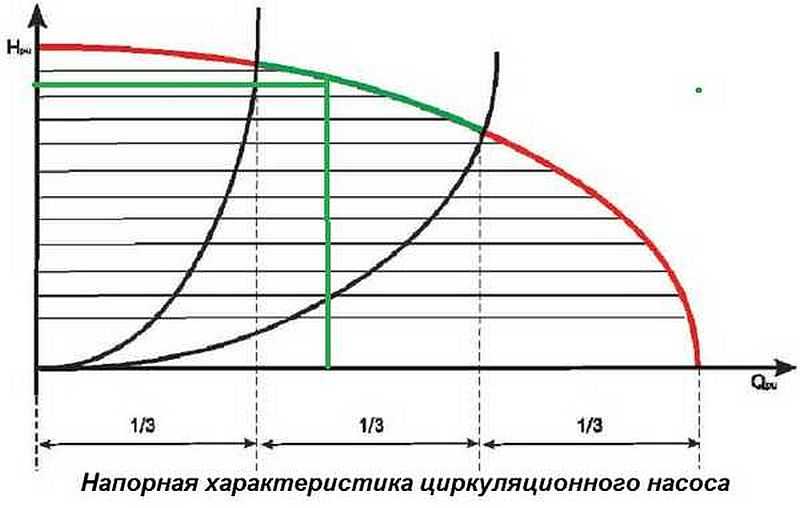
When choosing a specific model, pay attention to the graph with the pressure characteristics of the pump. On the graph you need to find the point at which the pressure and productivity values intersect
It should be located in the middle third of the curve. If it does not fall on one of the curves (there are usually several of them, characterizing different models), take the model whose graph is closer. If the point is in the middle, take the less productive one (the one located below).
What else to pay attention to
In the technical characteristics of circulation pumps there are several more items that are worth paying attention to. The first is the permissible temperature of the pumped medium
That is, the temperature of the coolant. In high-quality products this indicator ranges from +110°C to +130°C. In cheap ones it can be lower - up to 90°C (but in fact 70-80°C). If your system is designed as a low-temperature system, this is not a big deal, but if you have a solid fuel boiler, the temperature to which the coolant can be heated is very important.

It is also worth paying attention to the maximum pressure at which the pump can operate. In the heating system of a private house it is rarely higher than 3-4 atm (this is for a two-story house), but normally it is 1.5-2 atm
But still, pay attention to this indicator.
Something else to pay attention to is the material from which the case is made. The optimal one is cast iron, the cheaper one is made of special heat-resistant plastic
Connection type and size. The circulation pump can have threaded or flanged connections. The thread can be external or internal - appropriate adapters are selected for it. Connection sizes can be: G1, G2, G3/4.
It is also worth paying attention to the presence of protection. May have dry running protection
In circulation pumps with a wet rotor, it is very desirable, since the cooling of the motor occurs due to the moving medium. If there is no water, the motor overheats and fails.
Another type of protection is overheating protection. If the motor heats up to a critical value, the thermal relay turns off the power and the pump stops. These two features will extend the life of the equipment.
Why is it necessary?
A heating circuit with a circulation pump eliminates some of the problems that are typical for the natural type of coolant movement. After all, if the water leaving the radiator is cold, and when it also reaches the outer radiators it is barely warm, then the cold water entering through the return forces the boiler to work at its maximum capabilities. With the slightest design miscalculations or installation errors, the imbalance in temperature becomes even more noticeable, especially when it is necessary to warm up the room quickly, or when the system is first started, which can be seen in the operation of the boiler, in distant registers.
The use of a circulation pump eliminates these disadvantages. First of all, the requirements for compliance with pipe slopes and their flow area are reduced, and all traffic jams caused by temperature differences are eliminated. Heat transfer occurs evenly, the temperature of the coolant at the inlet/outlet of each radiator is almost the same, and the difference between the coolant before entering the system and returning it to the boiler is several degrees, within ten.
The pump greatly simplifies the design of the piping system.
What does this give? Stabilizes the operation of the boiler. If the difference is several degrees, then a smaller volume of gas is spent on heating, and the duty cycle is reduced. For example, we need a coolant temperature of 70. Initially, when the water is cold, the boiler operates at maximum power, but as it warms up over time, the picture changes.
In the spring and autumn months, when the house is slightly cool at night and comfortable during the day, the combined operation of the boiler, automation, and circulation pump can maintain the coolant levels within 40°, which is impossible with natural circulation.
The coolant returns in one pass through the system, having lost only 5°, its temperature is 65°, while in the rooms it is the same, the heat is distributed evenly across all radiators, and the automation turns off the burner according to the programmed indicators.
The next switching on will occur when the temperature drops. This is an economical mode of operation, in which there is no constant heating, but only maintenance of the required temperature parameters. If thermostats are installed on all radiators, then by setting the necessary temperature parameters on each register, for example, in the kitchen, in a warm room on the south side, by lowering them, we will get additional savings.
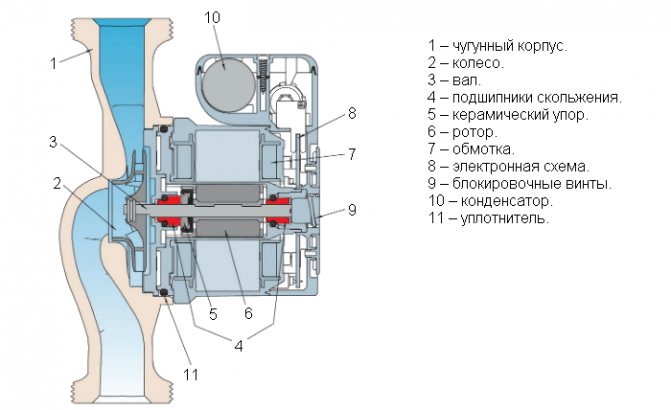
Design
The pump device consists of a cast iron casing in which an electric motor rotates a composite wheel mounted on a shaft. The wheel consists of two disks, between which curved blades are located radially. The coolant enters the wheel through a hole in the lower disk.
In wet running models, all moving parts (including the motor rotor) are in contact with the coolant, which will act as a lubricant/cooler for the ceramic (graphite) end bearings and the rotor itself. In this case, the stator is isolated from the coolant using a metal partition with sealing gaskets.
The design of “wet” pumps is more complex than the design of pumps with a dry rotor, so their cost with equal characteristics will always be higher.
Note! As a rule, circulation pumps have 3 speeds, which are switched by turning the regulator to one of three speeds. At the same time, at minimum speed, the pump consumes approximately 2 times less electricity compared to maximum speed.
Design and principle of operation
All circulation pumps have a centrifugal operating principle. They are built into the pipeline section. Moreover, their inlet and outlet flanges are made of the same diameter for ease of installation. Advantages of the centrifugal design:
- absence of rubbing elements (except for two bearings);
- no more than one sealing gland (and even then, it can be excluded);
- compatibility of the impeller with high rotation speeds of electric motors; (no noisy gearbox).

The centrifugal type is the most commonly used not only in heating networks, but also in other applications. This is a universal general industrial type of pump. It can work for many years without maintenance. The only wearable components are the bearings and seal.