Structure of foil thermal insulation material
Thermal insulators of this category provide a double structure in the form of a base coated with foil. The front surface of the substrate is made of aluminum foil, the purpose of which is to reflect thermal energy. Mineral insulation or polymers are used as the base. The fibrous or bubble structure of the foil substrate under a heated floor allows you to create a reliable barrier against heat loss, since due to the air gap in the composition, the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material is minimized.
Advantages and disadvantages
Foil floor underlay is highly efficient in terms of energy saving. Among the advantages of using this product, the following points are also noted:
- the height of the floor structure does not increase, since the thickness of the foil sheet varies between 2-10 mm;
- the material is easy to install, even novice craftsmen can do it;
- insulation with a reflective layer has noise-absorbing properties;
- the substrate with foil is able to withstand constant high temperature loads in the range of up to +90°C and above;
- a separate category of resources with a reflective coating is suitable for installing any type of heated floors;
- on the surface of most models of foil insulation, markings are made to simplify the process of laying elements of the heating structure;
- Some modifications of the material are equipped with an adhesive layer to facilitate installation work.
Foil for heated floors is an energy saving solution
Among the disadvantages, note the high cost of the most effective types of foil insulation under heated floors. For example, multifoil is sold at a price of €5 m². Another disadvantage: mineral substrates with a metallized surface should not be used when installing heated floors. This is because, under the influence of high temperatures, toxic compounds are released from the material.
Using foil for heated floors: pros and cons
A cable-based heated floor heats up to a certain temperature. The temperature of the water floor depends on the temperature of the water circulating in the pipes. Heat transfer is determined by the throughput of the substrate on which it is laid.
Foil laid under a warm floor does not greatly increase the heat transfer of cables and pipes. If the floor is concrete, then when pouring the screed, the concrete will tear this gasket. Heat transfer will not increase. Under a wooden floor, provided that there is a layer of air there, the effect will be no more than 2%.
In order to understand the useful life of foil materials under a concrete screed, conduct a test. Pour a small layer of concrete mixture onto the layer and leave it for a couple of days. Dried concrete can be easily wiped off with a rag; it quickly corrodes the metal and the foil layer underneath will be destroyed.
Having considered all the options for using and installing building materials, we can say that using foil under a warm floor will not bring significant savings.
Types of thermal insulation with foil
They produce many models of insulators with a reflective coating, which differ in the characteristics of the base and are used in various construction and finishing works.
Polyethylene foam
Polyethylene sheets of foam structure with a heat-reflecting surface belong to the category of the best products for thermal insulation. The solution is actively used when arranging heated floor structures for both water and cable systems. Foamed polyethylene has high elasticity and strength properties. The material does not react to a humid environment, is resistant to biological threats, and easily withstands the aggressive effects of chemical compounds.
The front side of the polyethylene foam lining for heated floors is covered with lavsan film with a metallized layer. The outer surface with reflective properties promotes uniform distribution of thermal energy, and the foam-like base with air micro-cells prevents the leakage of warm currents into the concrete screed.
Expanded polystyrene with foil
Expanded polystyrene backing is also considered one of the most popular thermal insulators used under heated floors. The operating temperature range of the product varies from -180°C to +180°C. Expanded polystyrene is highly inert to chemical influences and prevents the formation and proliferation of microorganisms.
Basalt insulation
Basalt wool, as a recognized leader among thermal insulators, has enormous potential. The product has a low thermal conductivity coefficient, easily tolerates temperature changes, and has an operating range from -200°C to +700°C. Basalt insulation with a foil surface is non-flammable and easy to install. However, the material is not suitable for underfloor heating systems, since under these conditions there is a high probability of the formation of compounds harmful to health.
Minvata
Mineral insulation with a metallized layer has exceptional thermal insulation abilities, and also belongs to products of a low fire hazard class. Moreover, due to the presence of individual components that form toxic substances when heated, mineral wool is strongly not recommended for laying heated floors. Basically, mineral wool with a reflective coating is used in the arrangement of industrial areas.
Multifoil
Multifoil heat insulator is a fabric whose structure provides many air chambers under an aluminum coating. The base of the product is made of polyethylene and polypropylene film. The presence of an air-bubble layer under the reflective plane ensures that heat loss is reduced to a minimum. Multifoil is not afraid of high humidity, has a high potential for thermal insulation properties, and helps to increase the efficiency of heating equipment.
Multifoil for heated floors
Folgoizolon
Folgoizolon has high moisture resistance characteristics, is not afraid of significant mechanical loads, and can easily withstand changes in ambient temperature. Foil substrates of this category are actively used in underfloor heating systems when arranging luxury-class housing in Moscow. Folgoizolon is also used in the construction of baths and saunas, since the material is inert to moisture. The key disadvantage of folgoizolon is considered to be the high cost of the product, but due to its high performance characteristics, the material arouses genuine interest among consumers.
Let's take a closer look at some types of synthetic substrates
- cross-linked polypropylene foam. It consists of sheets with a thickness of 2 to 20 mm. It has sufficient rigidity and elasticity so as not to deform under pressure. It has excellent thermal insulation and sound insulation characteristics. Due to its resistance to heat, it is used as an insulator for building heating elements and as a substrate for infrared and film heated floors. But it is not without drawbacks - it is highly flammable;
- extruded polystyrene foam. Plates with thickness from 5 to 200 mm. It has the lowest thermal conductivity properties among similar products, is resistant to chemical influences, resistant to mold and bacteria, has high compressive strength, and is also not afraid of moisture. It is considered one of the most environmentally friendly materials among synthetic types of insulation. Many experts consider this material optimal and recommend using it as a substrate when installing both water and electric heated floors. However, the material is not without drawbacks - without fire retardant impregnation it has flammable properties. Not all brands of this material are resistant to chemical solvents;
- foil underfloor heating (isolon, folgoizol, polyethylene foam). Inexpensive lightweight material, thickness from 10 to 50 mm. It is a foamed synthetic roll material with many closed pores on one side and covered with foil on the other side. It is resistant to fungi and bacteria, and is not afraid of water, like all synthetic materials. Moderately flammable. However, it has a significant drawback: it does not have much elasticity and quickly collapses under pressure, which reduces its service life to several months. Experts do not recommend using this material as floor insulation;
- polystyrene foam boards with bosses. 20mm or more thick. They come with or without a thin polystyrene coating. Designed for water floors, but recently they have also been used for electric floors. Convex elements (bosses) are needed to fix water pipes or other heating elements between them. During installation, the bosses may break; the heating element is poorly fixed between them without additional fasteners. Therefore, it is more advisable to use coated slabs. In this case, you can walk on them; no additional fixation is needed. This type of insulation has good thermal insulation properties, does not rot, does not wrinkle, and absorbs sound well.
We recommend: How to turn on underfloor heating?
Regardless of which underfloor heating the customer chooses, it must meet modern requirements: be environmentally friendly, durable and perform the functions assigned to it.
- Related Posts
- How is carbon heated flooring installed?
- How to lay heated floors over wooden joists?
- How does the underfloor heating calculator work?
- How to make a dry heated floor?
- What is good about Valtek pipe for underfloor heating?
- How to check a heated floor?
Criterias of choice
When choosing foil mats for laying a heated floor system, take into account the following material characteristics:
- ability to reflect thermal energy;
- coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- resistance to high temperature loads;
- noise absorption properties;
- reaction to a humid environment;
- environmental Safety;
- fire hazard class;
- ease of installation.
An equally important criterion for choosing a heat flow reflector under a heated floor is the cost of the product. Thus, polyethylene foam with aluminum coating is sold in the affordable segment, as is polystyrene foam heat insulator with a reflective surface. To construct a substrate made of multifoil or foil-isolon, you need to pay a significant amount. Basalt mats or other types of mineral insulation are inexpensive, but products in this category are not suitable for heated floors due to their composition.
Selecting a substrate by type of base
You need to choose the substrate carefully, since not only the operation of the heated floor, but also the atmosphere in your home depends on it. Therefore, when purchasing insulation, professionals advise paying attention to the following points and making a choice based on the parameters listed below.
READ MORE: How to fix a tie that was placed on cellophane
It is necessary that the substrate meets the requirements laid down by the heating system manufacturers:
- Water floor - for this design, a foil backing with a reflective coating is used. This mat is inexpensive and is great if you want to save living space, but the type is not recommended for basement floors. For water floors, it is better to take film models; although they are more expensive, they are equipped with increased thermal properties. An excellent solution for a water structure is an extruded foam substrate with bosses; it has improved quality and ease of installation, since the pipes are laid in grooves. Choosing rolled cork or expanded polystyrene would also be a good option.
- Electric floor - foil roll or tile insulation is suitable. The presence of an aluminum reflective layer is not recommended; it is better if it is vacuum deposition. If the height allows for a thicker cake, then it is worth putting polystyrene foam with a foil layer 2 - 3 cm thick. If height is limited, polyethylene foam 2 - 3 mm can be used as thermal insulation.
For the infrared floor model, you can choose chipboard sheets or magnesite slabs, but you will first need to lay foil film.
The lighter the floor covering, the more permissible it is to use an underlay with lower strength.
When installing a laminate, you can use foamed polymer, and when using ceramic tiles, which will be laid on a concrete screed, you need a substrate made of extruded material, which has increased strength.
Under linoleum, only a solid base or an additional thin concrete screed is required.
By type of base
Almost any type of substrate can be laid on both a concrete sub-base and a wooden one.
The only peculiarity when installing on a wooden floor is an increased level of waterproofing and fire resistance.
The choice of damper material depends on the type of decorative floor covering. The more the finish weighs, the greater the strength of the substrate should be:
- Ceramic tile. When arranging the structure, concrete technology is used when the contour is located under the screed.
- Laminate. Considering the weak throughput of the panels, the main criterion for selection is increased heat saving performance. The best option is heat-reflecting materials with low thermal conductivity.
- Linoleum. The coating is laid on top of plasterboard boards, plywood sheets, OSB. Given the large weight of the panels, the requirements for insulating gaskets increase. It is better to give preference to cork or polystyrene foam options.
The most successful design is considered to be one in which the role of the substrate is provided to polystyrene foam. The material is impervious to mechanical and shock loads, has high noise, hydro and thermal insulation. When the environmental friendliness of the product is a priority, you will have to purchase cork insulation, which best meets the requirements of the heating system. Thin polystyrene foam substrates help out when creating structures with minimal thickness.
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of an insulating gasket for heating systems. The efficiency of the system directly depends on the placement of the “water coil” and its compliance with the decorative coating.
When choosing foil mats for laying a heated floor system, take into account the following material characteristics:
- ability to reflect thermal energy;
- coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- resistance to high temperature loads;
- noise absorption properties;
- reaction to a humid environment;
- environmental Safety;
- fire hazard class;
- ease of installation.
An equally important criterion for choosing a heat flow reflector under a heated floor is the cost of the product. Thus, polyethylene foam with aluminum coating is sold in the affordable segment, as is polystyrene foam heat insulator with a reflective surface. To construct a substrate made of multifoil or foil-isolon, you need to pay a significant amount.
The thickness of the reflective layer is also of great importance. If a simple spraying is performed on top of the thermal insulating layer, this causes a low level of efficiency of the substrate. It is worth remembering that the lower the quality of the reflector, the easier and more intensely thermal radiation leaks through it.
Features of installation of foil material
When planning the installation of the products in question, it is worth considering the following points:
- reflective thermal insulation in tiled design is mainly used for heated floor systems;
- a floating screed is constructed on the basis of foil mats and laid between the joists.
Required Tools
To cut and install a heat-insulating substrate with a reflective effect, you must have the following tools and devices on hand:
- scissors or stationery knife;
- roulette;
- aluminum tape.
It is also necessary to prepare the estimated amount of thermal insulation material.
Installation stages
The technology for laying foil under a heated floor involves the following steps:
- Floor slabs are cleaned of debris and dust, if necessary, the base is leveled using mortars, and unevenness, cracks and other surface defects are eliminated.
- Prepare pieces of the reflector of the required length.
- From the corner segment of the surface, they begin to lay the heat insulator close to the wall, with the reflective layer facing up.
- The entire surface of the floor is worked in a similar way, the strips of the substrate are laid joint to joint.
- Assembly seams are processed using aluminum tape to eliminate gaps between the elements of the reflective fabric and provide high-quality heat and moisture insulation.
Installation of foil for heated floors
After laying the foil backing, you can immediately begin installing the heating system.
It is noteworthy that any type of insulation is suitable for water or cable underfloor heating, and when installing infrared systems, only foil backing is used.
When installing heated floors, it is assumed that there is a substrate that contributes to the efficient operation of the system.
It should not be neglected when installing a heated structure, since it has many functions, the main one being the reduction of heat loss.
The most popular type of substrate is foil.
Do you need foil for underfloor heating?
A water heated floor is installed from pipes laid in a concrete screed or in grooves made of polystyrene foam or wood. The surface is heated by the circulating liquid.
When using extruded polystyrene foam to install the system, waterproofing does not need to be used; the material is quite dense and does not allow water to pass through. Reflective insulation in slabs is necessary to ensure that heat rises to the floor surface rather than heating the neighbors' ceiling. You can lay the insulation under the insulation or on top of it.
The advantages of a water floor are that it will evenly heat porcelain stoneware and tiles and save energy.
You can connect it from home radiators. With all the advantages, there is one minus - the risk of flooding due to incorrect pipe connections and poor-quality installation.
Foil for underfloor heating - is it necessary?
A substrate with foil when installing a “warm floor” system is today one of the integral parts of the heating pie. Insulation with a foil layer most effectively saves the heat generated by the heating device and distributes it evenly.
This helps save heat resources, increases the potential of the heating system and the rate of heating the room, which in turn affects the life of the floor.
For your information! It is believed that using foil material in an electric warm cake is not safe, but this is misleading. Today there are many protective and insulating materials available.
The structure of the foil substrate includes a base and a foil. The base can be: basalt, mineral, polystyrene foam, polyethylene. Most of these thermal insulation products have a bubble structure. The surface of the foil for heated floors can be aluminum or metallized.
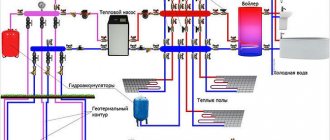
Water heated floor
Works on water heating pipes laid between the ceiling and the flooring. Water is heated in a boiler or boiler and supplied through the heating circuit using a pump.

The cooled water goes back into the boiler and so on in a closed cycle. The built-in heat control system will not allow the floor to heat up above the set temperature.

This type of heated floor is good for individual housing, but is completely unsuitable for an apartment building with central heating. Another disadvantage is that if a pipe breaks or leaks, it is often necessary to dismantle the entire structure.
We recommend: Features of the “combined heating: warm floor and radiators” system
Advantages and disadvantages
As mentioned above, a substrate with a foil surface is an excellent material for saving energy. In addition, foil has a number of other advantages, but there are also disadvantages.
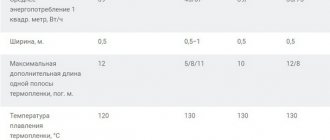
| pros | Minuses |
| Does not affect the height of the floor, since the foil material is only 2-10 mm thick. | High cost is the main disadvantage. |
| It is not difficult to install, so even an inexperienced person can handle the job. | It is not recommended to use a mineral substrate with a metallized layer for heated floors, since toxic substances are released during the heating process. |
| It has soundproofing and waterproofing properties. | Using such a substrate in rooms with high humidity significantly reduces its service life. A foil-coated product is recommended. |
| Withstands heating up to +90 degrees and more. | Dissolves upon direct contact with cement. |
| Most products with foil are equipped with markings, which simplifies the process of laying heating elements. | |
| There are models with a sticky layer, this makes installation easier. | |
| Reduces heat loss and promotes its uniform distribution. |
It should be noted that the foil product is strong and durable if installed and used correctly.
Types of substrates with foil
Currently, a large number of models of insulation with foil are sold; they have different bases and are intended for different construction work.
Watch the video - how different types of substrates work, reflection of thermal radiation, etc.
Folgoizol
Underfloor heating made of foil insulation is most often used for the construction of baths and saunas. After all, the main advantage of folgoizolon is that it is not afraid of water and sudden temperature changes. The service life is long, since the product is not subject to rotting.
The material is environmentally friendly, has enhanced sound insulation properties, and is able to withstand mechanical loads. But due to its high cost, it is practically not used as insulation for residential premises, with the exception of luxury housing.
Basalt insulation
Basalt wool is the leader among insulation materials. It has low thermal conductivity and tolerates temperature changes well, in the range from -200 to +700 degrees. This type is equipped with a reflective surface, does not burn, and the installation process is simple.
Despite the fact that the insulation is not susceptible to heat, it is not recommended to use it in underfloor heating, since heating may release harmful substances.
Minvata
Mineral wool with a layer of foil has excellent thermal insulation properties, in addition, it is fireproof. However, the composition contains components that, when heated, release harmful substances, therefore it is contraindicated for warm systems.
Composition and types of foil material
This insulation consists of two layers. One is the main one and the other is a reflective coating.
The basis is various building materials: polystyrene foam, mineral wool, etc. The reflective coating is aluminum foil. The thickness of the insulation material depends on what material is used as the base.
Today, there are the following types of insulation for underfloor heating, which are based on foil:
- expanded polystyrene;
- foamed polyethylene;
- mineral wool;
- basalt foil insulation;
- foilisolone.

Valtec multifoil
The most popular is expanded polystyrene, which is laid under film floors. This material is characterized by high strength, resistance to all kinds of chemical influences and the ability to withstand temperature changes from -180°C to 1800°C.
There are usually markings on the reflective layer, which makes installation work much easier.
This thermal insulation material is made on the basis of foam plastic, and it is known to be of non-natural origin. This means that it is not at risk of exposure to moisture. Consequently, such thermal insulation can be safely used when installing a water heated floor.
Mineral wool covered with foil is much less commonly used. It is not recommended for use when installing water heated floors; it also does not combine well with electrical systems. When the temperature increases, the insulating material begins to release harmful substances into the air.
Another disadvantage is that mineral wool is susceptible to moisture. However, on the other hand, it is resistant to fire, which is an advantage of such a material. It is rational to use such a reflector when arranging roofs or insulating walls.
Multifoil in its structure has a special air gap between the insulation and the reflective layer. Thanks to this, heat is reflected more effectively into the room, and the heated floor is heated more evenly.
Foamed polyethylene, covered with a layer of foil, is characterized as durable and plastic insulation. It is resistant to moisture, so it is often used to install a water-heated floor system. It is not exposed to chemical influences, does not emit harmful substances, is easy to install and has a long service life.
This thermal insulation absorbs sound well, but does not tolerate ultraviolet rays.
Folgoizolon is used quite often when installing not only heated floors, but also baths and saunas. This is due to its resistance to moisture.
This material is durable, does not decompose, withstands temperature changes well and is environmentally friendly. The disadvantage is the high price.
Choosing a pipe for a warm floor.
What type of thermal insulation is better to choose and why?
When choosing foil material for heated floors, you need to consider:
- heat reflecting properties;
- thermal conductivity coefficient;
- resistance to high temperatures;
- presence of sound insulation;
- environmental safety;
- reaction to moisture;
- prostate in styling;
- fire safety indicators.
Video - ways to reflect thermal energy, how insulation works
The price of insulation for heated floors also plays an important role. For example, polyethylene foam coated with aluminum, or polystyrene foam substrate with a reflective layer, are affordable in cost.
But when buying multifoil or foilisolone, you will need to spend a decent amount. Mineral or basalt type insulation, although inexpensive, is not suitable for warm floors.
In addition, the thickness of the foil layer also plays a big role. In cases where conventional spraying is used on top of the heat-insulating fabric as a reflective layer, the efficiency of the product is significantly reduced. The lower the quality of the reflective surface, the easier it is for heat to pass through it.
For your information! Products that are intended for insulation of walls or ceilings should not be used for heating floors. After all, there they will be subject to mechanical stress, which can lead to the loss of their properties. Therefore, you only need to install insulation intended for the floor.
Also, when choosing a thermal insulation material, it is important to consider that:
- More often, the product in tiles is used for heated floors;
- foil mats are used to make floating screeds; they are laid between the joists.
Laying foil under heated floors
Installation work for installing a substrate on a floor with a heating system includes several stages.
Preparatory activities
When starting to install a backing with foil under a warm floor, you should prepare the tools that will be needed for the work. Need to stock up:
- knife or scissors;
- tape measure;
- aluminum tape.
In addition, you should buy the required amount of the selected type of foil insulation.
Installation on cement screed
Laying the substrate under the heating device is as follows:
- The base is cleaned of dust and debris. If there are uneven spots and cracks on the slab, they are covered with a special solution, which must be dry before installing the backing.
- The reflector is prepared - it is cut to the required length.
- The material is laid from the corner of the room close to the wall, with the reflective surface facing up. Glue is applied pointwise to the base of the mats.
- The following strips are laid out end to end.
- The seams are processed using aluminum tape; this will prevent the formation of cracks, which will ensure high-quality heat and moisture insulation.
Afterwards, you can proceed to laying the heating system and flooring (linoleum, parquet, laminate).
For your information! When installing a cable or water system, you can use any type of insulation: with or without foil, and for infrared - only one with a foil coating.
In addition, when pouring a concrete screed onto a cable or water-heated floor, the quality of the aluminum foil substrate is significantly reduced. After all, when concrete comes into contact with foil, it corrodes it, thereby losing its properties.
Laying on wood
If the base is made of wood, then it is better to take insulation on a self-adhesive film. If you have a regular backing, you can use double-sided tape for fixation.
The working process is as follows:
- The base is prepared: dust and debris are removed. You can sand the surface with a grinding machine.
- To preserve the wood better, it is treated with an antiseptic.
- When the primer has dried, the insulation is rolled out, it usually comes in a roll, and the required size is cut off. The material is laid with the reflective surface up, the protective film is removed, and the insulation is pressed to the floor. The strips are laid at the joint, there should be no gaps.
- The joints are sealed with foil tape.
- The heating elements and flooring material are being installed.
The underlay is a mandatory layer of a heated floor, especially when building a private house or in apartments on the ground floor. And if you use insulation with a foil layer, the system will function much more efficiently.
Types of substrates
The underfloor heating is a flexible flooring that is located between the floor slab and the heating element. The substrate has a number of functions:
- waterproofing - protects the heating element from moisture penetrating from below;
- thermal insulation - prevents heat penetration downwards;
- distributes heat evenly if the heating elements are located at some distance from each other. Thanks to the substrate, heat is distributed evenly over the entire surface;
- removes heat from heating elements, preventing overheating;
- performs a small soundproofing function;
- evens out minor unevenness in the subfloor.
Since the substrate has several purposes, it must meet certain requirements:
- be moisture resistant, that is, not fail if water gets on it;
- be elastic and withstand the pressure of the coating and the weight of the contents of the room;
- be tough and not crumble under pressure;
- be resistant to fungal mold and bacteria.
We recommend: How is the length of a heated floor pipe calculated?
Substrates are:
- mineral;
- natural;
- synthetic;
Mineral types of substrate include fiberglass. It is a rolled material made of fiberglass. Fiberglass does not get wet, does not burn, but has minimal thermal insulation. Used as a contour between the water-heated floor and the coating.
Natural types include cork, jute, and felt substrates. These are easy to use, environmentally friendly materials.

Without special impregnation, they are quickly exposed to destructive biological influences, that is, they become infected with fungus and bacteria, which significantly reduces their service life.
The above types of materials are used as a substrate between the screed and the floor covering, for example, under laminate.