- home
- Construction and renovation
- Plumbing
>
>
⬎
Polypropylene pipes and fittings are widely used by plumbers of various levels and home craftsmen. This is not surprising - installation does not require expensive equipment, all work is relatively simple to master. Currently, these pipes are used in water supply, both cold and hot water, and heating. Often risers in apartment buildings are made of polypropylene.
There are also quite a few opponents of this technology. There are reasons for this - various leaks in PPR pipes are far from uncommon, emergency services workers know about this phenomenon firsthand.
To be fair, it is worth noting that problems arise mainly due to non-compliance with installation technology and incorrect selection of the type of pipes. It is also worth noting low-quality pipes and components - due to the great popularity of polypropylene, it began to be manufactured in almost every basement.
In this material we will look at the correct choice of polypropylene pipes for a specific situation, soldering technology and other important aspects.
Types of polypropylene pipes
In this review we will consider PPR pipes for water supply and heating; various thin-walled, summer cottage options will not be considered. All pipes are divided into three main types, characterizing the reinforcing material. Different manufacturers may have additional layers, but in general, this does not change the main purpose of the material.
The data is based on VALTEC products; figures for other manufacturers may differ.
The first is polypropylene without a reinforcing layer
.
It is used in cold water supply systems and has the highest coefficient of linear thermal expansion. And although the manufacturer claims compliance with service classes according to GOST 32415-2013 - 1, 2 (hot water supply 60°C, 70°C), in general, unreinforced pipes are recommended for use only in cold water supply (my personal opinion). In cold water, the pipe is guaranteed to maintain a pressure of 20 bar; with hot water, the operating pressure decreases - 12 bar for a temperature of 60 °C and 8 bar for 70 °C.
The numbers are valid for pipes marked PN20 (more on this below). This type of pipe is often produced with a lower operating pressure. The pipes have a linear coefficient of thermal expansion of 0.00013/1°C. This means that when the pipe temperature increases by 1 degree Celsius, a 1 m long pipe will become 0.13 mm longer. Not much at first glance, however, if you use a pipe in a hot water supply of 70 °C and take into account cooling to 15 °C, the change in length over a three-meter segment will already be 21.45 mm. This is one of the reasons not to use these pipes in hot water supply.
The second is with a reinforcing layer of PP-FIBER fiberglass
. Used in hot water supply systems, they have a lower linear expansion coefficient. May be marked PN20 and PN25. These pipes can be safely used in hot water supply, up to a water temperature of 90 °C; the maximum permissible operating pressure at this temperature is reduced to 6 bar.
The coefficient of linear expansion is 0.000062/1°C - half that of unreinforced pipes. Despite the smaller expansion, it is not worth neglecting during installation.
The third type - with a reinforcing layer of aluminum PP-ALUX
. Used in hot water supply and heating systems, they are marked PN25. These pipes have the lowest coefficient of thermal expansion and greater resistance to pressure at high temperatures. Suitable for use with liquid temperatures up to 95 °C. In addition to pressure and temperature, the aluminum layer prevents oxygen diffusion. Diffusion of oxygen into pipes is a phenomenon undesirable for heating systems. This phenomenon will not be considered in more detail within the framework of this article.
The coefficient of linear expansion of 0.000031/1°C is two times less than that of fiberglass and four times less than that of unreinforced polypropylene. The data is valid for continuous reinforcement of pipes with aluminum, when stripping before soldering is not required.
Watch a video about aluminum reinforcement:
Regardless of the type of reinforcement, all pipes are marked with a maximum operating pressure - PN15, PN20, PN25; this alphanumeric designation characterizes resistance to pressure in bars. For example: the PN20 marking says that the pipe can be operated at a pressure of 20 bar. Also, the marking indirectly indicates the maximum operating temperature, because unreinforced pipes above PN20 are not found (at least for now). By the way, there are also lower PN values, but their use is recommended in systems without pressure.
An older system for designating the working pressure of pipes - SDR - is the ratio of diameter to wall thickness; the lower this number, the thicker the pipe.
The thickest PN25 is equivalent to SDR6. If you look at the table, SDR is not always the same as PN. You need to focus primarily on PN and, if possible, choose a lower SDR. Table of permissible pressures and temperatures of various types of polypropylene pipes
| Reinforcement type | Class PN | SDR Ratio | Operating pressure | Application area |
| PPR 100 | PN20 | 6.0 | ХВ-20 bar 60 °C-12 bar 70 °C-8 bar | Cold water supply, use in hot water with a pressure not higher than 8(70°C), 12(60°C) bar is allowed |
| PP-FIBER | PN20 | 7.4 | ХВ-20 bar 60 °C-13 bar 70 °C-10 bar 90 °C-6 bar | HW, HW, underfloor heating 70 °C, radiator heating 90 °C |
| PP-FIBER | PN25 | 7.4 | ХВ-25 bar 60 °C-14 bar 70 °C-11 bar 90 °C-9 bar | HW, HW, underfloor heating 70 °C, radiator heating 90 °C |
| PP-ALUX | PN25 | 6.0 | ХВ-25 bar 60 °C-14 bar 70 °C-11 bar 95 °C-9 bar | HW, HW, underfloor heating 70 °C, radiator heating 95 °C |
To display the table, use a screen resolution of at least 601 pixels in width!
*Data given for VALTEC pipes.
Classification and technical characteristics
Types of polypropylene pipes are divided into single-layer and multi-layer. The classification of polypropylene pipes is more complex and is divided into chemical composition, structure and diameters. The area of use and the overall service life of the products depend on all these parameters.
Single layer products
According to the manufacturing method and material, single-layer polypropylene pipes are divided into several types:
Type 1 – PPH. Material – homopolypropylene. High levels of hardness and resistance to bending, combined with low resistance to high and low temperatures, determine their scope of application: homopolypropylene communications are widely used in cold water supply and ventilation systems.
USEFUL INFORMATION: How to replace the valve axle box if the mixer malfunctions
Type 2 – PPB – polypropylene block copolymer. An improved chemical structure with a polyethylene additive improves the heat resistance and flexibility of the material. This type of product is used for the installation of underfloor heating systems, cold water supply, ventilation and sewerage; it is not suitable for hot water supply due to the large thermal expansion of the material.

Type 3 - PPR - random copolymer of polypropylene, they are also called polypropylene pipes and are designated PPRC. It is distinguished by increased resistance to high temperatures and the effects of acids and alkalis, and is even stronger than metal-plastic. A product made from such a material is universal, and its scope of application is very wide, but its main purpose is heating systems. Polypropylene pipes have the following technical characteristics:
- absolute environmental friendliness;
- slight thermal expansion;
- high melting point (+170 °C);
- ability to withstand temperature changes at maximum values up to +130 °C;
- frost resistance;
- high constant operating temperature (90°C).

Type 4 – PPS – special low-flammable polypropylene, capable of withstanding temperatures up to 95 ° C in constant operating mode.
[smartcontrol_youtube_shortcode key=”types of polypropylene pipes” cnt=”4" col=”2" shls=”true”]
Brands of single-layer pipes
Single-layer polypropylene products can be divided into several categories, differing in their technical characteristics and permissible operating pressure.
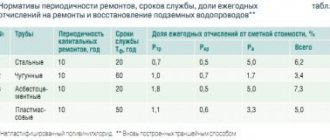
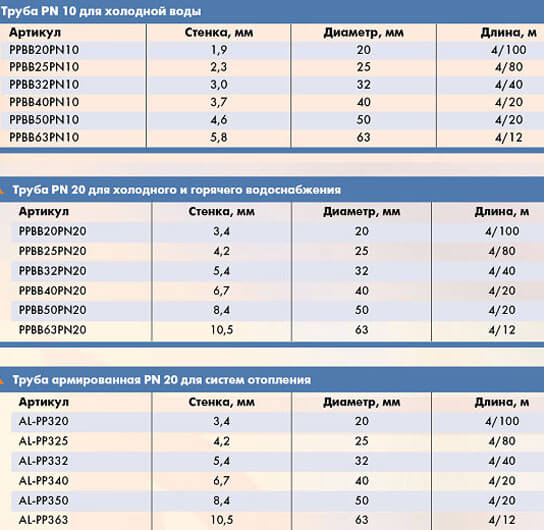
- PN10 is a thin-walled model, designed for cold water supply (up to 20 °C), installation of heated floors (up to 45 °C), as well as for a ventilation system.
The dimensions of polypropylene products of this type are presented in the table:
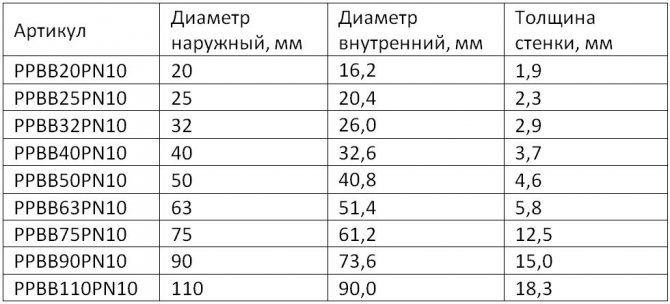
- PN20 is a universal type of product intended for cold and hot water supply (up to 80°C).
For convenience, the parameters of the product of this brand, including the outer and inner diameter and wall thickness, are presented in the table:
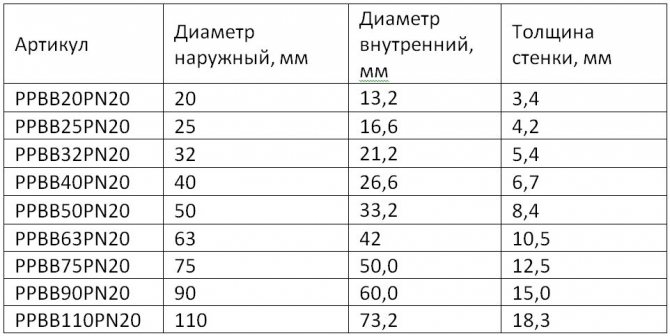
- PN16 is an intermediate model. Used less frequently than others, intended for cold and hot water supply (up to 60°C).
Multilayer polypropylene pipes
As is clear from the name, this type of pipe has 3 layers firmly bonded to each other. The middle layer may consist of aluminum foil, polyethylene or fiberglass. This product is marked PN25.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Connecting a water filter to the water supply: installation procedure
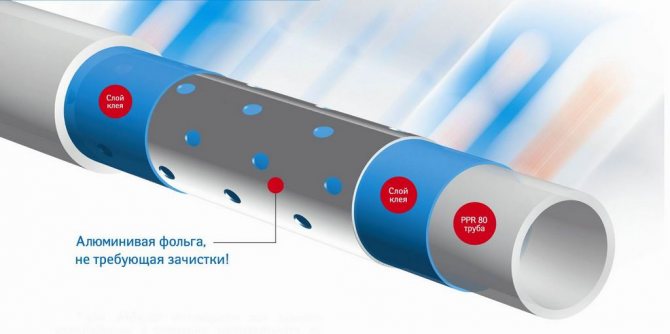
Models with aluminum core
Polypropylene pipes reinforced with aluminum Pn25 are used primarily for installation of heating system wiring, although they are also used for laying cold and hot water supply systems. Polypropylene products of this class are the most popular among plumbers.
The aluminum layer in the PN25 pipe can be smooth or perforated. As practice shows, a smooth aluminum layer is not very convenient, since it needs to be cleaned before welding so that the aluminum does not come into contact with water or other media that will be transported. The perforated layer in PN25 products is more practical: it is a mesh with holes into which molten polypropylene flows during the welding process, which makes the bond more reliable and safe.
Products with a polyethylene layer
Polypropylene pipes with an internal polyethylene layer have many disadvantages. For example, when welding, only the outer layer is connected to the fitting, which means that the inner layer will come into contact with the transported media.
[sma[smartcontrol_youtube_shortcode key=”reinforced polypropylene pipes” cnt=”2" col=”2" shls=”true”]
Glass fiber reinforced pipes
The most prominent type of product in this classification is glass fiber reinforced polypropylene pipes. A visual feature of this type of product is the tinted layer with fiberglass - this is done so that it can be distinguished from other types. There are many advantages to such products:
- due to the internal fiberglass layer, the pipeline elements become more rigid and turn into a monolithic structure;
- the coefficient of thermal expansion is almost 2 times less than that of non-reinforced products;
- high strength;
- ability to retain its properties at high temperatures;
- protection from water hammer;
- best throughput.

The markings of polypropylene heating pipes of different diameters are presented in the table:
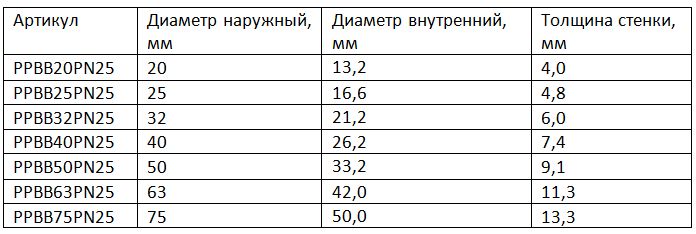
The type of product PN25 must be selected for a specific type of water supply or heating, taking into account the characteristics of operation. When choosing, you need to consider the following technical characteristics:
USEFUL INFORMATION: Do-it-yourself pipeline: methods of connecting PVC pipes
Application of different types of pipes in practice
Despite the data given in the table above, it is worth clearly distinguishing the scope of application of each type of pipe. This is not the absolute truth, this is my humble opinion. And although the manufacturer allows the use of their pipes almost everywhere, I look at things with a realistic look. After all, you need to have a good margin of strength and temperature, as in Soviet times, in order to be confident in the quality of the work performed. So…
Polypropylene for water supply
Any of the pipes described in the table above are suitable for cold water supply. For hot water, I strongly recommend using polypropylene with reinforcement, both fiberglass and aluminum. I generally refrain from using unreinforced products, even for cold water. After all, the cost of pipes with reinforcement is not much more expensive.
Polypropylene for heating a private house
All characteristics are suitable for pipes of all types of reinforcement. The pressure and temperature in your own, individual system are low and you don’t have to worry about a pipe breaking. However, it is better to look towards PN25 fiberglass or aluminum.
Polypropylene for central heating
Here, you should still consider, first of all, installation with metal or other pipes rather than polypropylene. Because in Russian realities it is possible to exceed all permissible water temperatures in the central system. The same can be said about pressure, especially in multi-story buildings.
Polypropylene can be used only if there is confidence that in a particular riser, in winter, in severe frosts, the coolant temperature does not exceed 95 °C. I have often encountered very hot risers and I am not sure that it was not more than 100 degrees. And if the decision is still made, use only pipes with aluminum reinforcement.
Laying pipes on the street
One of the features of PPR pipes is that when water freezes in it, the pipe does not burst, but expands. When the water thaws, the pipe returns to its original state. I myself have witnessed this phenomenon many times. Moreover, frozen water pipes are very difficult to break by mechanical force, this is subject to a quality choice.
Polypropylene is perfect for laying pipes in a personal plot or country house. You couldn't imagine better material!
Pipe diameters
Standard diameters of polypropylene pipes: 20 mm, 25 mm, 32 mm, 40 mm and more... The standards use the outer diameter, while the inner (useful) diameter depends on the SDR ratio. Very conditionally, they are considered equivalent to metal pipes: 16 mm metal (1/2) - 20 mm propylene, 20 mm metal (3/4) - 25 mm propylene, 25 mm metal (inch) - 32 polypropylene. 32 metal (inch and 1/2) - 40 mm polypropylene.
I called the equivalents very conditional due to the fact that for metal pipes the internal diameter is taken into account as a standard, while for PPR the external diameter is taken into account. For example: a metal pipe “1” (inch) has an internal diameter of 25 mm, an equivalent polypropylene 32 mm has an internal diameter of about 21 mm (depending on the SDR parameter). In other words, if we use 32 mm polypropylene to replace a 25 mm (inch) metal pipe, then the effective internal diameter will become narrower. This should be taken into account when there is absolutely no need to narrow the diameters of the pipes.
In connection with what was written, I compiled the following table:
Table of standard diameters of metal and polypropylene pipes
| Steel water pipe GOST 3262-75 | Polypropylene pipe, useful equivalent | |||
| Thread diameter in inches (nominal size*) | Inner diameter, mm | Outer diameter, mm | Outer diameter, mm | Inner diameter(SDR 6.0), mm |
| «1/4» | 8 | 13,5 | — | — |
| «3/8» | 10 | 17 | 20 | 13,2 |
| «1/2» | 15 | 21,3 | 25 | 16,6 |
| «3/4» | 20 | 26,8 | 32 | 21,2 |
| «1» | 25 | 33,5 | 40 | 26,6 |
| «1 1/4» | 32 | 42,3 | 50 | 33,4 |
| «1 1/2» | 40 | 48 | 63 | 42 |
To display the table, use a screen resolution of at least 601 pixels in width!
*Some dimensions in inches do not match the numbers in millimeters, so the clearance is conditional. In order not to be misled, it is worth taking these numbers for granted.
As we can see from the table, for example, half-inch 1/2 pipes are replaced without narrowing by 25 PPR, and not by 20, as is customary in most cases. This means that it is not at all necessary to change 1/2-inch iron pipes to 25 polypropylene; it is quite possible to get by with a size of 20 mm. But you should understand that the useful diameter will narrow. And if you consider that thinner pipes can be used in the water supply system, SDR 7.4, for example, then the internal diameter will almost not narrow.
Catalog with sizes and prices including VAT
- for cold water
- for hot and cold water
- for heating reinforced
- from 29.44 rubles per meter
Number of reviews: 0Polypropylene pipe Tebo PN10 for cold water supply
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 030010102 20×1.9 29.44 29.44 030010103 25×2.3 43.99 43.99 030010104 32×3.0 73.86 73.86 030010103 40×3.7 114.68 114.68 030010106 50×4.6 185.25 185.25 030010107 63×5.8 284.29 284.29 030010108 75×6.8 386.42 386.42 030010109 90×8.2 532.06 532.06 030010110 110×10.0 815.57 815.57 030010111 125×11.4 1299.08 1299.08 030010112 160×14.6 2038.92 2038.92 - from 27.18 rubles per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Polypropylene pipe Fora PN10 for cold water supply
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 026010102 20×1.9 27.18 27.18 026010103 25×2.3 40.60 40.60 026010104 32×3.0 68.19 68.19 026010105 40×3.7 105.88 105.88 026010106 50×4.6 163.18 163.18 026010107 63×5.8 254.49 254.49 - from 34.90 rub per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Polypropylene pipe Fora PN20 for hot and cold water supply
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 026010202 20×3.4 34.90 34.90 026010203 25×4.2 58.86 58.86 026010204 32×5.4 99.08 99.08 026010205 40×6.7 152.30 152.30 026010206 50×8.4 250.59 250.59 026010207 63×10.5 390.47 390.47 - from 48.18r per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Polypropylene pipe Fora PN25 reinforced with fiberglass (no stripping required)
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 026010402 20×3.4 48.18 48.18 026010403 25×4.2 69.16 69.16 026010404 32×5.4 117.52 117.52 026010405 40×6.7 179.31 179.31 026010406 50×8.4 275.86 275.86 026010407 63×10.5 442.92 442.92 - HIT from 48.74 rubles per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Tebo PN20 polypropylene pipe reinforced with glass fiber (no stripping required)
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 030010402 20×3.4 48.74 48.74 030010403 25×4.2 74.92 74.92 030010404 32×5.4 124.28 124.28 030010405 40×6.7 194.24 194.24 030010406 50×8.4 295.74 295.74 030010407 63×10.5 458.27 458.27 030010408 75×12.5 650.51 650.51 030010409 90×15.0 916.15 916.15 030010410 110×18.3 1384.52 1384.52 - HIT from RUR 38.95 per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Polypropylene pipe Tebo PN20 for hot and cold water supply
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 030010202 20×3.4 38.95 38.95 030010203 25×4.2 66.22 66.22 030010204 32×5.4 110.49 110.49 030010205 40×6.7 171.47 171.47 030010206 50×8.4 279.62 279.62 030010207 63×10.5 438.07 438.07 030010208 75×12.5 605.85 605.85 030010209 90×15.0 902.95 902.95 030010210 110×18.3 1367.04 1367.04 030010211 125×20.8 2000.08 2000.08 030010212 160×26.6 3369.06 3369.06 - from 54.17 rubles per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Millennium PN20 polypropylene pipe reinforced with glass fiber (no stripping required)
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 10328ML 20×2.8 54.17 54.17 10330ML 25×3.5 82.83 82.83 10332ML 32×4.4 130.00 130.00 14149ML 40×5.5 194.83 194.83 10334ML 50×6.9 312.00 312.00 10335ML 63×8.6 483.33 483.33 10336ML 110×15.1 1781.50 1781.50 10337ML 75×10.3 664.50 664.50 - from 40.50r per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Polypropylene pipe Millennium PN20 for hot and cold water supply
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 10302ML 20×3.4 40.50 40.50 10305ML 25×4.2 74.83 74.83 10308ML 32×5.4 115.67 115.67 10310ML 40×6.7 184.67 184.67 10311ML 50×8.4 286.17 286.17 10312ML 63×10.5 453.50 453.50 10313ML 75×12.5 676.50 676.50 10314ML 90×15.0 1028.17 1028.17 10315ML 110×18.3 1512.83 1512.83 - from 66.12 rubles per meter
Number of reviews: 4
Polypropylene pipe FD-plast PN20 for hot and cold water supply
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 2722 20×3.4 66.12 66.12 2723 25×4.2 107.35 107.35 2724 32×5.4 185.05 185.05 2725 40×6.7 286.58 286.58 2726 50×8.4 454.12 454.12 2727 63×10.5 709.51 709.51 2728 75×12.5 1023.82 1023.82 2729 90×15.0 1496.74 1496.74 2720 110×18.3 2329.35 2329.35 2651 125×20.8 3121.97 3121.97 2652 140×23.3 3695.51 3695.51 2653 160×26.6 5127.82 5127.82 - from 63.18 rubles per meter
Number of reviews: 4
Polypropylene pipe Millennium PN25 reinforced with fiberglass (no stripping required)
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 14152ML 20×3.4 63.18 63.18 14153ML 25×4.2 90.30 90.30 10353ML 32×5.4 143.50 143.50 14154ML 40×6.7 218.33 218.33 10355ML 50×8.4 337.44 337.44 10356ML 63×10.5 540.50 540.50 10357ML 75×12.5 767.33 767.33 10358ML 90×15.0 1395.50 1395.50 10359ML 110×18.3 2128.50 2128.50 - from 52.73 rubles per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Polypropylene pipe FD-plast PN20 reinforced with aluminum inside (required trimming)
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 2641 20×3.4 52.73 52.73 2642 25×4.2 74.18 74.18 2643 32×5.4 110.90 110.90 2644 40×6.7 373.54 373.54 2645 50×8.4 253.62 253.62 2646 63×10.5 385.48 385.48 2647 75×12.5 464.86 464.86 - from 72.58r per meter
Number of reviews: 10
Polypropylene pipe FD-plast PN20 reinforced with glass fiber (no stripping required)
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 2590 20×3.4 72.58 72.58 2591 25×4.2 108.43 108.43 2592 32×5.4 178.12 178.12 2593 40×6.7 274.28 274.28 2594 50×8.4 434.89 434.89 2595 63×10.5 663.51 663.51 2596 75×12.5 921.82 921.82 2597 90×15.0 1399.97 1399.97 2598 110×18.3 2353.35 2353.35 2599 125×20.8 3395.05 3395.05 2600 140×23.3 4391.82 4391.82 2601 160×26.6 6067.82 6067.82 - from 107.88 rubles per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Polypropylene pipe FD-plast PN25 reinforced with aluminum (mandatory stripping)
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 2732 20×3.4 107.88 107.88 2733 25×4.2 56.89 56.89 2734 32×5.4 243.72 243.72 2735 40×6.7 354.42 354.42 2736 50×8.4 502.85 502.85 2737 63×10.5 857.57 857.57 2638 75×12.5 1229.89 1229.89 2639 90×15.0 1756.18 1756.18 2630 110×18.3 3441.10 3441.10 - from 78.28r per meter
Number of reviews: 2
Polypropylene pipe FD-plast PN25 reinforced with glass fiber (no stripping required)
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 8630 20×4.1 78.28 78.28 8631 25×5.1 115.51 115.51 8632 32×6.5 202.74 202.74 8633 40×8.1 303.35 303.35 8634 50×8.4 466.43 466.43 8635 63×12.7 713.82 713.82 8636 75×15.1 1085.20 1085.20 - from 36.28r per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Polypropylene pipe Kalde PN10 for cold water supply
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 3202tbe200010 20×1.9 36.28 36.28 3202tbe250010 25×2.3 55.18 55.18 3202tbe320010 32×3.0 139.09 139.09 3202tbe400010 40×3.7 173.86 173.86 3202tbe500010 50×4.6 216.95 216.95 3202tbe630010 63×5.8 346.21 346.21 3202tbe750010 75×6.8 744.57 744.57 3202tbe900010 90×8.2 1020.48 1020.48 3202tbe1100010 110×10.0 1503.50 1503.50 - from 71.06 rubles per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Kalde PN20 polypropylene pipe reinforced with glass fiber (no stripping required)
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 3202tfr200020 20×3.4 71.06 71.06 3202tfr250020 25×4.2 96.00 96.00 3202tfr320020 32×5.4 160.25 160.25 3202tfr400020 40×6.7 241.89 241.89 3202tfr500020 50×8.4 360.57 360.57 3202tfr630020 63×10.5 582.81 582.81 3202tfr750020 75×12.5 842.84 842.84 3202tfr900020 90×15.0 1640.32 1640.32 3202tfr110020 110×18.3 2418.91 2418.91 - from 49.89 rubles per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Polypropylene pipe Kalde PN20 for hot and cold water supply
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 3202tbe200000 20×3.4 49.89 49.89 3202tbe250000 25×4.2 86.17 86.17 3202tbe320000 32×5.4 139.84 139.84 3202tbe400000 40×6.7 216.95 216.95 3202tbe500000 50×8.4 352.25 352.25 3202tbe630000 63×10.5 550.30 550.30 3202tbe750000 75×12.5 805.04 805.04 3202tbe900000 90×15.0 1120.26 1120.26 3202tbe1100000 110×18.3 1676.61 1676.61 - from 96.76r per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Polypropylene pipe Kalde PN25 reinforced with aluminum (mandatory stripping)
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 3202tbf200000 20×3.4 96.76 96.76 3202tbf320000 32×5.4 291.78 291.78 3202tbf400000 40×6.7 364.35 364.35 - from 75.59 rubles per meter
Number of reviews: 0
Polypropylene pipe Kalde PN25 reinforced with glass fiber (no stripping required)
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 3202tfr900000 90×18.1 1674.34 1674.34 3202tfr200000 20×4.1 75.59 75.59 3202tfr110000 110×22.1 2494.50 2494.50 3202tfr250000 25×5.1 99.02 99.02 3202tfr320000 32×6.5 164.79 164.79 3202tfr400000 40×8.1 251.72 251.72 3202tfr500000 50×10.1 407.44 407.44 3202tfr630000 63×12.7 623.63 623.63 3202tfr750000 75×15.1 874.59 874.59 - from 48.89r per meter
Number of reviews: 2
Polypropylene pipe FD-plast PN10 for cold water supply
vendor code Size Price Quantity Sum 2702 20×1.9 48.89 48.89 2703 25×2.3 71.82 71.82 2704 32×3.0 123.82 123.82 2705 40×3.7 196.12 196.12 2706 50×4.6 289.51 289.51 2707 63×5.8 461.51 461.51 2708 75×6.8 651.51 651.51 2709 90×8.2 957.97 957.97 2700 110×10.0 1506.28 1506.28 2661 125×11.4 1944.74 1944.74 2662 140×12.7 2392.43 2392.43 2663 160×14.6 3159.51 3159.51
Shown 1 to 20 of 20 (total 1 pages)
Pipe fittings (couplings)
Fittings for polypropylene pipes are more often called couplings. Couplings are either collapsible or non-dismountable. Based on my experience, I recommend using non-separable ones; fewer components means higher reliability.
It is recommended to use couplings and pipes from the same manufacturer, but this is not a necessary condition. Since the outer diameters of all pipes are fixed standard, couplings from other manufacturers will fit without problems. However, it is worth remembering that the manufacturer declines all responsibility for pipe leaks if components from other companies were used.
.
An important point in choosing couplings is compliance with the permissible pressures with the pipes. If a PN25 pipe is used, then the coupling must have the corresponding designation. Very often, sellers in specialized plumbing stores do not indicate this fact and sell PN20 couplings for a PN25 pipe.
It is worth adding that it is better to try to take high-quality fittings from global brands. The fact is that in a good fitting, at the junction of the metal and polypropylene, there is an O-ring. It is possible to see this ring only by sawing the coupling lengthwise.
What does this ring do? Not so often, but it does happen that when the coupling is of poor quality, water is forced between the iron and the plastic. You can’t call it a leak; it usually squeezes out a few drops in ten to twenty minutes and after a few hours the leak becomes clogged. But sometimes the leak does not stop the next day, so the unit has to be replaced. And considering that the soldering point is disposable, replacement can bring a lot of hassle. In general, do not skimp on couplings and fittings!
Watch a video about combined polypropylene fittings:
Fittings for polypropylene pipes
The connection of polypropylene pipes to each other is carried out by welding on special welding machines. But the installation of a pipeline is impossible without the use of fittings of various types. The use of such connecting elements allows you to create engineering systems and structures of almost any complexity.
Manufacturers of polypropylene pipes produce the following types of fittings:
- Couplings and adapters - designed for joining pipes of the same or different diameters (respectively), used to connect metal and polypropylene pipelines.
- Angles 45, 90 ° of various configurations - used to change the direction of the pipeline without deforming the pipes, can be equipped with metal threads. Some elements allow joining pipeline sections with different diameters.
- Tees and crosses (distributing elements) are designed to create branches from the main pipeline line. Modifications with metal threads and different diameters are available.
- Bypasses are used to organize communications in the presence of obstacles along the pipeline path.
- Taps and valves (shut-off elements) - provide control of the flow of the working medium; they can be threaded or threadless.
- Plugs—used to temporarily close a section of pipeline, available with or without threads.
- “American” is a coupling with a union nut; it is in demand in cases where individual elements of the system are to be disconnected, as well as for connecting a section of a pipeline made of metal pipes.

Polypropylene taps
When using plastic pipes, it will be more aesthetically pleasing to use taps coated with polypropylene. This is usually what inexperienced plumbers think about. In fact, it is better to use regular brass taps with a transition to polypropylene through a coupling.
The fact is that taps filled with plastic have lower reliability. The faucet consists of two fundamentally different materials (metal and plastic), with different densities and thermal expansions. Due to different properties, problems often arise in the form of leaks or breakdowns. Global manufacturers recognize the shortcomings of polypropylene cranes and are working on the mistakes, but it is too early to say with complete confidence about reliable cranes of this type.
A much more reliable solution would be a brass tap with two threaded couplings. The coupling also contains two materials, metal and plastic, but these parts are stationary, unlike a tap.
In addition to reliability, there is also an aesthetic side to using conventional taps: the tap can be rotated along its axis and given a more even position. The sealed plastic tap cannot be turned on the pipe; you need to do the soldering very clearly the first time; the soldering can only be corrected by soldering in a new tap.
In addition, conventional cranes are, as a rule, smaller in size, and the range of products is much wider.
Just like brass, polypropylene taps come in two types: valve and ball. Please note that ball valves can only be used in two positions: open and closed, adjustment is not allowed.
All manufacturers say so. However, on this score, in the process of working as a plumber, a different opinion was formed...
The above is true for expensive, high-quality products, but in our realities, as a rule, we have to deal with budget faucets. So, if we compare two budget products, a valve and a ball valve, the ball wins in terms of reliability, even with constant adjustment. Although the valve is specifically designed for regulation, it fails very quickly. This opinion has been formed over many years of work. These considerations are valid both for brass shut-off and control valves, and for products filled with polypropylene.
About leaks, fistulas and other reviews about polypropylene
On professional construction forums, many horror stories are told about polypropylene leaks. The climax is a video where a man breaks pipes on a comb like dry rods. Any novice plumber or home craftsman will immediately disown this technology. What can I say, experienced craftsmen are confused by such arguments.
The reason for such defects, oddly enough, is savings on pipes and components. Currently, many products are sold from “basement” factories, for which technical descriptions cannot be found. Please note: if you decide to use a PP-ALUX pipe, for example, from a little-known manufacturer, the data in the pressure and temperature table above does not necessarily apply to your brand. No one exempts you from studying technical documentation from a specific pipe manufacturer.
It follows from this that many “plumbers” do not bother studying the characteristics of pipes. And this can lead to errors in soldering and installation. By the way, despite the simplicity of the technology, it must be performed with due care, observing the soldering temperature and other nuances. I have seen a lot of pipes soldered by “shabashniks” - in the vast majority of cases, the soldering was done with overheating, the pipe was incorrectly selected for a specific task.
I had to dismantle a lot of plastic pipes and I didn’t come across the horror stories described on the Internet. The pipes, after 5-10 years of operation, were in excellent condition; no cracks or destruction of the material were observed from the inside. Most often, the places where the leak occurred were poorly soldered connections, despite the fact that a properly soldered connection is much more reliable than the pipe itself. In simple terms, it’s hard for me to imagine such “hand-assed” installers. Nevertheless, there are a lot of such installers - they showed the technology, and simply said - this is the end of the worker’s qualifications. Hence all the ensuing consequences and problems, as well as the tarnished reputation of polypropylene.
Also, polypropylene owes its tarnished reputation to marketers who are actively promoting cross-linked polyethylene
. By the way, cross-linked polyethylene is not as resistant to high temperatures as it seems from beautiful stories. The job of marketers is to emphasize the advantages and gloss over the shortcomings of their product, and comment on the opposite about the competitor’s product. Everything is simple, just study the technical documentation for both products and everything will fall into place.
We will look at soldering polypropylene separately, but that’s all for now. And once again, I strongly recommend that you carefully select all materials for rough plumbing, beware of fakes and approach the issue thoroughly.
yserogo.ru
Types of polymer pipes
To create a reliable heating circuit, you need to choose the right material. There are different types of plastic.

Each of them has its own pros and cons. Therefore, before purchasing materials for arranging a heating network, you need to study their technical characteristics.
Today, to solve the problem, it is permissible to use structures from:
- Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC).
- Polypropylene (PP).
- Glass fiber reinforced PP pipe.
- PP pipes reinforced with aluminum foil.
- Cross-linked polyethylene.
- Metal-plastic.
Products made from chlorinated PVC are becoming quite popular. The addition of chlorine made polyvinyl chloride structures more resistant to high temperatures. Conventional PVC pipes are not suitable for arranging heating circuits. Because they can only withstand temperatures up to sixty degrees. While CPVC can be used in the construction of networks with media temperatures of up to one hundred degrees.
In addition, this material has a fairly low thermal conductivity. This helps reduce heat loss during coolant delivery to the radiators.
The cost of the structures in question is decent. Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride is more expensive than standard PVC.
Polypropylene structures are the most budget-friendly. Their key disadvantage is their high linear expansion coefficient.
Structures made from this material quickly deform. During the heating season they may sag. These properties negatively affect the aesthetics of the circuit and its functionality. It only makes sense to use such designs if there are no pressure and temperature differences inside the system.
Glass fiber reinforced polypropylene products are many times stronger than standard PP pipes. Moreover, their installation is practically no different from the installation of standard products. The option under consideration is excellent for creating heating systems. It is durable, reliable and practical.
Aluminum reinforced PP structures . They are largely similar in their characteristics to the previous variety. Key advantages include high strength, wear resistance and easy installation. To install these structures, it is necessary, unlike the previous option, to carry out additional work. Before soldering products, it is important to remove the aluminum layer. However, performing this operation is quite simple.
Cross-linked polyethylene is suitable for installing underfloor heating systems and central heating circuits. In terms of its properties, this material is very similar to reinforced polypropylene. Installing a circuit from the structures in question requires special skills and knowledge. In addition, you need to have special clamping equipment. It is necessary to choose products from this material only if the installation of the system will be carried out by highly qualified specialists.
Metal-plastic products
Metal-plastic products are in many ways similar to polypropylene analogs reinforced with aluminum. But the thickness of their walls is less. It is quite convenient to use them to solve the problem under consideration. The main thing is to purchase quality products. Now the market is full of fakes that do not have the proper level of reliability and durability. Over time, such structures begin to deteriorate and delaminate. Therefore, purchase only high-quality metal-plastic materials.
Below we will examine in more detail each of the listed types of materials. You will learn detailed information regarding their main characteristics and properties.
Types of polypropylene products
Technical requirements for PP products are given in the regulatory document GOST No. 52134 “Thermoplastic pressure pipes” dated 2003. According to this GOST, all polypropylene pipes, depending on design features, are divided into 4 categories:
- PN-10;
- PN-16;
- PN-20;
- PN-25.
The differences between the pipes lie in the wall thickness and material structure - PN 10,16 and 20 products are made of composite materials, while PN 25 pipes are reinforced with fiberglass or aluminum. Let's look at each variety in more detail.
- PN-10 - single-layer thin-walled, for cold water supply (operating temperature +20 degrees) and low-temperature heating systems (maximum temperature +450). Withstands pressure of 10 MPa. The internal diameters of PN-10 polypropylene pipes vary in the range of 16-110 mm, wall thickness - from 2 to 10 mm.
- PN-16 - composite, for low-temperature heating and hot water supply. Can be used in systems with operating pressure up to 16 MPa. Temperature maximum +600.
- PN-20 - universal, applicable in heating systems. Withstands pressure up to 20 mPa and temperature up to 800. Dimensions: internal diameter - from 10.6 to 74 mm, wall thickness - from 1.5 to 18.4 mm.
- PN-25 - multi-layer reinforced, designed for high-temperature radiator heating. Withstand pressure up to 25 MPa and heating up to +950. The range of internal diameters is 13.2 - 50 mm, wall thickness - from 4 to 13.3 mm.
The reinforcement layer affects how much pressure a PP product can withstand and provides the product with zero vapor permeability. The absence of diffusion of oxygen into the coolant through the walls ensures that rust will not form inside heating devices (boilers, radiators).
Reinforced polypropylene pipes are less prone to linear expansion than their composite counterparts, since the foil layer acts as a heat insulator that prevents heating of the outer shell, which also ensures that there is no temperature loss by the coolant.
Advantages and disadvantages
One of the key advantages of PP pipes is their durability. Polypropylene products have a service life of 50 years (subject to the operating rules and temperature conditions specified by the manufacturer) in hot water supply and heating systems, and about 100 years in cold water supply.
Let's consider the advantages that polypropylene pipes have:
- The internal walls in contact with circulating water are not subject to the formation of deposits and rust, which guarantees the same throughput, noiselessness and constant water quality at all stages of operation of PP products.
- Reinforced products tolerate pressure drops within 5 MPa without consequences; due to the sufficient elasticity of the material, the polypropylene pipeline does not deform after the coolant freezes in it.
- Polypropylene pipes are extremely easy to install - they are connected by soldering or fittings (compression, threaded and crimp), the installation of which does not require expensive equipment.
- PP pipes have high strength characteristics, crack resistance and resistance to deformation.
- Polypropylene products have an aesthetic appearance that does not change during the operation of the system - there is no need to paint the pipeline.
- Variable sizes of PP pipes allow you to choose products for use both in heating and water supply lines inside the house, and for laying external sewerage.
The only significant drawback of PP pipes is the tendency to linear expansion, which is equally characteristic of all plastic products - when heated, the product increases its size, as a result of which the internal stress in the material increases and, if installed incorrectly, the pipeline can be deformed.
This is not a critical problem as expansion can be mitigated through proper piping design, expansion joints and sliding type retaining clips.
Technical characteristics and markings
Polypropylene products of any standard sizes have the following technical characteristics (according to GOST No. 52134):
- specific density - 0.9 g/cm3;
- maximum temperature leading to deformation +1500;
- resistance to tensile loads - 35 N/mm2;
- yield strength - 25 N/mm2;
- coefficient of linear expansion - 0.15 mm/m;
- nominal heat capacity (at temperature +200) - 2 kJ/kgf;
- nominal thermal conductivity (+200) - 0.24 W/ms.
The marking of polypropylene pipes is unified and does not differ among different manufacturers. The products have the type nomenclature: PPR PN20 20*2 class-5/20 mPa TU No. xxx , in which:
- PPR is a modification of polypropylene used for the manufacture of products (PPR - random copolymer, PPH - homopolymer, PPB - block copolymer). The most common are PPR pipes, in demand due to the increased temperature resistance of the material;
- 20*2 — diameter*wall thickness (mm);
- class-5 - product operation class;
- 20 MPa - maximum working pressure;
- TU No. xxx is a regulatory document according to which the PPR pipe is produced.
In total, there are 5 classes of operation of PPR pipes specified in GOST; they differ depending on the maximum temperature of the coolant. The table shows the temperature range of each class.
How to choose polypropylene pipes? (video)
Scope of application of polypropylene pipes
Depending on the type and design, polypropylene pipes can be used to transport both inert and chemically active liquids. In some cases, these products can be used in the organization of pipelines designed to ensure the operation of hydraulic equipment (up to 25 atm). Based on this, the main areas of application of polypropylene pipes are:
- heating systems, as well as hot and cold water supply;
- production lines for the transportation of chemicals and compounds;
- "warm floor" systems;
- compressor equipment pipelines;
- climate and ventilation equipment;
- irrigation, reclamation and drainage systems.

Technology for the production of polypropylene products
The production of polypropylene products requires a special production line, the basic equipment of which is an extrusion unit. The equipment used is quite compact; a plant for the production of PPR pipes can be organized in a room with an area of 100 m2.
The manufacturing process of PPR products is implemented using the following technology:
- Raw materials (propylene granules) are loaded into equipment - an extrusion hopper.
- The temperature in the bunker rises to the melting point of propylene, additives and reagents are added to the melt, giving the material the required technical characteristics.
- The molten mass is squeezed out of the storage hopper and passes through the extrusion head (the equipment is equipped with heating elements that maintain the required temperature of the workpiece). When pressed through the head, the material obtains the required shape.
- The workpiece is moved to the calibration wall, where the product is rolled through press rollers and receives the final length and diameter.
- The PPR pipe is placed in a cooling bath in which the plastic hardens.
- The blanks are moved to the cutting line (the equipment used is guillotine and circular saws), where PPR pipes are cut into sections of specified sizes.
- Polypropylene products are marked and packed into manufacturer's packaging.
Investments in opening a plant for the production of PPR pipes amount to about 8 million rubles, the amount includes the costs of equipment, raw materials (100 tons), wages for personnel and rental of premises for the plant.
Manufacturers rating
Products are supplied to the domestic PPR market by a fairly large number of manufacturers, which causes a serious variation in the quality of products. After analyzing consumer reviews and expert opinions, we compiled a rating of the leading manufacturers of PPR pipes, which includes the following companies:
- Valtec
- Ecoplastic
- FV-Plast.
The quality and technical characteristics of PPR pipes from these manufacturers always correspond to what is declared; their products are manufactured not according to specifications, but according to GOST standards, which already says a lot.
The rating is deservedly headed by Valtec, a domestic plant founded by the joint efforts of Russian and Italian engineers. The company produces PPR products with a diameter of 20 to 110 mm; the company's product range includes composite and reinforced (fiberglass and aluminum) products that meet the PN20 and PN25 standards.
trubypro.ru
Features and scope
The invention of the thermoplastic Random Copolymer (PP-R) was a breakthrough in the use of plastics. High temperature resistance and excellent technical characteristics allow the use of products made from this type of plastic in many industries. How unique this material is can be imagined even from the incomplete list of the main advantages of products made from this copolymer:
- high strength;
- low adhesion;
- chemical inertness (polypropylene is absolutely non-toxic);
- low thermal conductivity coefficient;
- good sound insulation;
- ability to withstand temperature and pressure changes over a wide range;
- durability;
- cost-effectiveness of transportation and installation.
Despite their common origin, polypropylene products differ significantly in their properties and performance.
Products of European quality, from an exclusive supplier in Russia! You can buy Aquatherm pipes, as well as piping and fastening systems, on this website https://agpipe.ru
When choosing pipes from this material, be sure to check whether their technical characteristics comply with future operating conditions.
In addition, depending on the application, the pipes may be reinforced with aluminum foil or fiberglass. Depending on this they can be used:
- for water supply (both cold and hot);
- in the agro-industrial complex;
- in underfloor heating systems;
- for heating systems;
- in systems for transporting chemical compounds;
- in pipelines of compressor units.
It would be dishonest to remain silent about the main disadvantage of polypropylene pipes - their coefficient of linear expansion is 0.15 mm/m°C (about 10 times more than that of steel), but this problem is successfully solved by the production of reinforced products. The use of an aluminum armored belt can reduce the thermal expansion of polypropylene by more than five times.
Advantages and characteristics of polypropylene pipeline systems
Technical characteristics of PPR pipe:
- The price of a polypropylene pipe is an order of magnitude lower than that of a metal pipe.
- Light weight. Polypropylene is several times lighter than metal. This facilitates transportation, installation and maintenance of polypropylene water supply.
- Easy to install. Along with the low weight, the significantly simplified connection method adds to the ease of installation work. For this purpose, sleeve welding is used, the implementation of which is measured in seconds. The resulting joints, if all welding and operating rules are observed, can last a long time and reliably, without allowing water to pass through. If you need to fix such a pipe on the wall surface, it will take much less fastening material, and in this case there are much fewer requirements for the base.
- Good elasticity. This property explains the widespread use of polypropylene tubes in the organization of underfloor heating systems, which are characterized by a mass of rotating sections.
- Chemical inertness. Polypropylene products are completely safe for the environment, as they do not emit any harmful chemicals. Thanks to these characteristics of ppr pipes, they can be safely used to organize the supply of drinking water: no toxins enter the liquid during transportation.
- Corrosion resistance. Polypropylene is not afraid of water, so rust or limescale does not appear on it. This makes it possible to avoid applying additional protective coatings, which is required when using metal pipes.
- Stability of original dimensions. During operation of polypropylene pipelines, a decrease in their internal diameter is not noticeable.
- Resistance to changes in operating conditions. The products are able to withstand quite significant changes in temperature and pressure without loss of quality.
- Low thermal conductivity. This allows you to avoid such an unpleasant phenomenon as the formation of condensation during pipeline operation. In this regard, polypropylene pipes are noticeably superior to metal ones.
- Due to the good sound insulation of the walls, the noise of water passing inside the products is almost not felt.
- Easy maintenance. Due to the corrosion resistance, the periodic painting procedure required for metal systems is not necessary in this case. As for repairing or replacing damaged sections of a polypropylene pipeline, this will not take much time.
Thanks to these characteristics, it is not for nothing that polypropylene pipes are called one of the most promising among other products of this type.
Basic physical and mechanical parameters
The Russian standard for “Thermoplastic pressure pipes and connecting parts for heating and water supply systems” (GOST 521343:2003) establishes six operating classes for polypropylene pipes depending on the nominal temperature:
- Application in hot water supply (up to 60°C).
- Application in hot water supply (up to 70°C).
- Use in underfloor heating systems (low temperature - up to 60°C).
- Work in high-temperature floor and low-temperature radiator heating systems (up to 70°C).
- Work in high-temperature radiator heating systems (up to 90°C).
- Application in cold water supply (class designation - ХВ).
Characteristics
- The density of polypropylene is the lowest of all plastics - 0.91 kg/cm2. Despite this, the surface of products made from it has high hardness and wear resistance.
- The mechanical strength of PP-R pipes depends on the time of force application, and since this parameter is associated with gradual heating or cooling, we can speak of sufficient strength for any operating conditions. By the way, the limit value for PPR is 35 N/mm.
- Increased resistance to chemically aggressive environments - surface destruction is possible only when combined with high-temperature exposure to a strong acid.
- Frost resistance – no less than -15°C. Most often, pipes work with coolant at positive temperatures, so even such unexceptional indicators are quite enough.
- The melting point of polypropylene is from 160 to 170°C, depending on the composition.
- Softening point - 140°C.
- The maximum coolant temperature is no more than 120°C.
- Working pressure – from 10 to 25 atmospheres.
- External diameter – from 16 to 125mm.
The bending radius of pipes depends both on their diameter and on the presence and type of reinforcing layer. The maximum parameter is for polypropylene pipes with aluminum reinforcement without perforation.
Markings and sizes
Labeling of polypropylene products can include both information about the material and data on nominal pressure and temperature. The letter index means:
- PP – simple polypropylene.
- PP-R – polypropylene random copolymer.
- PP-RC is a random copolymer of type III polypropylene, intended for hot water supply and heating systems.
- PP-RCT is an improved random copolymer of polypropylene.
PP-RC pipes are precisely those products that are used in water supply and heating systems. They are most often used in industry and agriculture.
The letter designation of pipes is PN, and there are four product modifications, depending on the nominal operating pressure for which they are designed:
- PN10 – liquid pressure up to 10 atmospheres. PN10 pipes are used for transporting low-temperature coolant (up to 45°C) in cold water supply or underfloor heating systems.
- PN16 – the allowed pressure in the system is no more than 16 atmospheres, and the operating temperature should not exceed 60°C. Recommended for use in low-temperature heating systems.
- PN20 is the most common brand. Allows transportation of liquid up to 95°C at a pressure of up to 20 atmospheres, due to which it is used both in heating systems and in hot water supply pipelines.
- PN25 – has the lowest coefficient of linear deformation, withstands long-term liquid pressure of up to 25 atmospheres at temperatures up to 95°C.
PN pipes can be either glass fiber reinforced or aluminum foil reinforced. In the second option, it is possible to use both perforated and monolithic tape as a reinforcing layer. In heating systems, it is recommended to install pipes without foil perforation. Such products most successfully resist air diffusion into the coolant.
In everyday life, pipes with an outer diameter of 20, 25, 32, 40 mm are most often used. The main parameters of pipes of the most common brand PN20 are summarized in the table.
Manufacturers and assortment
Many large companies around the world are engaged in the production of polypropylene pipes. The process of their manufacture differs both in technology and in the use of various modifications of material. This is what the rating of polypropylene pipe manufacturers looks like:
- PPR pipes from Banninger Reiskirchen are rightfully considered the best products. For their production, only the highest quality PP-RCT polypropylene (Wefatherm brand) is used. It’s not for nothing that German engineers installed a 10-year production warranty on their products.
- Polypropylene systems from the Czech manufacturer WAWIN Ecoplastik are pioneers in the industry. The quality of the products is practically in no way inferior to pipes from Germany, as is the prohibitively high price, which limits their distribution in our country.
- The well-known company Valtec from Italy. Products are optimal according to quality/price criteria.
- Turkish and Polish manufacturers (TEBO, Vesbo, Pilsa and others).
- Products of Chinese and domestic companies.
Each manufacturer produces a wide range of pipe brands, fully covering all possible consumer needs. As proof, here is the range of the Italian brand Valtec, comfortably located in the middle of our list:
- Valtec PPR PN20 pipe. Installation in water supply systems is allowed. Water temperature - no more than 70°C, pressure with cold coolant - up to 20 atmospheres, with hot fluid - no more than 10 atmospheres. It has no reinforcing layer. According to Russian GOST, it belongs to classes 1,2,XB.
- Valtec PP-FIBER PN20. Can be used in any type of water supply and heating systems with coolant temperatures up to 90°C. The operating pressure is similar to the previous brand. The pipes have a three-layer structure with fiberglass reinforcement.
- Valtec PP-FIBER PN25. Products of this brand are designed for high pressure - up to 25 a in pipelines. The diameter of the pipes starts from 20mm.
- Valtec PP-ALUX. Thanks to the presence of aluminum reinforcement made of solid foil, the pipes are capable of operating in systems with temperatures up to 95°C and pressures up to 10 atmospheres. In cold water pipelines this value is 25 atmospheres.
Of course, with the growth of technical indicators, the cost of products also increases, however, we repeat that the quality of Valtec products is comparable to world brands, and the price is significantly lower.
Pipe selection criteria
When setting up a pipeline system, consumables are usually selected taking into account its internal pressure and temperature.
Composition of polypropylene pipes:
- PN 10. Using this polypropylene pipe, you can organize cold water supply with temperatures up to + 20 degrees, heated floors up to + 45 degrees. Permissible operating pressure – 1 MPa.
- PN 16. The product can withstand hot water temperatures up to + 60 degrees, with a nominal operating pressure of 1.6 MPa.
- PN 20. Tolerates water heating up to + 90 degrees, at an operating pressure of 2 MPa.
- PN 25. This polypropylene pipe is reinforced with reinforcement. With its help, hot water supply and heating systems are equipped up to + 95 degrees, at a pressure of 2.5 MPa.
When using any type of polypropylene pipe, it is best to take connecting elements from the same material. Combination parts of this type are equipped with a nickel-plated pressed-in brass insert, which has internal and external threads. This makes it possible to simply and efficiently organize transitions from the polypropylene section of the pipeline to the metal section.
Recommendations for selection
When going to the store, pay attention not only to the price, but also to the technical characteristics of the product. Select pipes with a small margin based on basic operating parameters.
- Operating pressure. Manufacturers indicate its value for room temperature, therefore, when choosing pipes for the heating system of an apartment, pay attention to PN25 brand products. If you are the owner of a home with individual heating, pipes marked PN20 will be sufficient.
- Temperature. For reinforced pipes, manufacturers indicate a coolant temperature of at least 90°C. You should not overpay for products labeled 95°C - their characteristics are the same.
- Diameter. For risers with a diameter of ¾ inches you will need a pipe with a diameter of 25 mm, and for inch risers - 32 mm. For linear wiring, 20mm products are most often used.
- For heating and hot water supply, choose only reinforced products.
When choosing pipes, remember that their manufacture is a high-tech process. Therefore, do not be tempted by the low price of Chinese products - the slightest violation of technology leads to delamination of pipes during operation. And this is fraught with big troubles.
Even products with the most impressive characteristics from a world-famous company will not be able to fully operate if the installation of the system was initially carried out carelessly and with miscalculations. Pay close attention to this when constructing pipelines from polypropylene pipes with your own hands.
remkasam.ru
Types of fittings used
The pipe line consists of linear elements and connecting elements - fittings, which are installed at connections, transitions from one diameter to another, corner turns and bends of the system.

List of polypropylene fittings used for installation of utilities:
- Connecting couplings. Used for joining two linear segments.
- Angular turns. The wiring at the entrance to an apartment or floor rarely retains its linear configuration. In practice, due to the limited dimensions of the premises, the network is turned by 45° or 90° with bent corner bends.
- Transitions from one size to another. The ends of the adapters are made with different internal diameters, allowing you to create a pipeline from polypropylene pipes with different cross sections.
- Tees and cruciform bends. When several pipes are simultaneously joined in one unit, it becomes necessary to install a connecting tee or cross.
- Contours. When installing a water supply or heating line, it is necessary to route the pipeline around protruding building structures. Contours are installed in breaks in the linear main.
Do-it-yourself stripping for polypropylene pipes without special tools To increase reliability and maximum pressure, polypropylene pipes have a reinforced layer. But it interferes with the formation of a high-quality welded joint. The solution is stripping for polypropylene...
The design of the heating system cannot be completed without the use of an American combination coupling. This threaded part consists of a metal base on one side and a plastic end for welding on the other side. The result is a dismountable connection, convenient for installation work.