What should you consider when heating a greenhouse with your own hands?
Before choosing a heating option, you will have to study this issue from different angles.
It must be taken into account that for obtaining a winter or early spring harvest of crops growing in the ground, it is much more important not air heating, but soil heating.
The climatic zone of the site and the method of growing crops are taken into account: winter or early spring. If this is the south of Russia, it is quite possible to get by with coolants that heat only the air space, because polycarbonate retains heat better than glass or film.
The area of the structure plays an important role; the heating method and the number of heating units directly depend on this. It is necessary to reject some types of heating that are impractical and expensive for a small area, since they are unprofitable and will not pay for themselves.
Heating a polycarbonate greenhouse with your own hands in winter will be budgetary (you won’t need to hire craftsmen), but a labor-intensive process, sometimes expensive in terms of purchasing materials. In order for heating to be as economical as possible, the structure will need to be insulated. Installing equipment yourself requires compliance with all safety measures.
Basic rules for installing a subsurface heating circuit in a greenhouse with your own hands
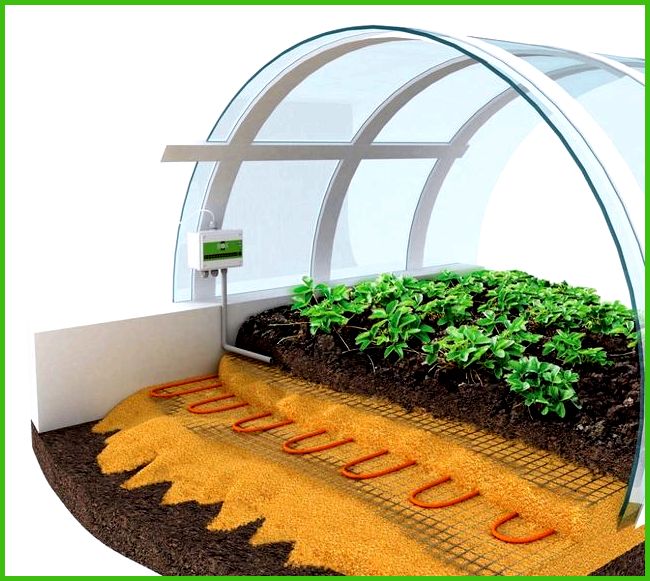
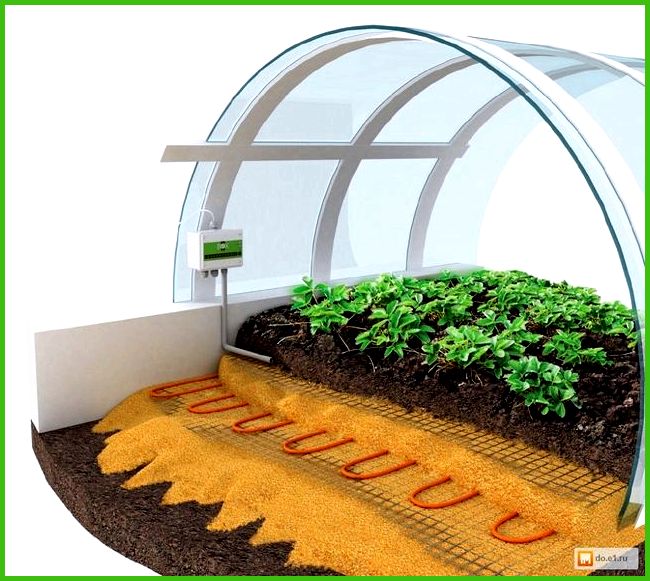
- For subsoil heating, it is better to use high-quality cross-linked polyethylene pipes placed directly in the ground, and if the soil heating circuit is equipped with an automatic control unit, it is possible to provide temperature conditions corresponding to different stages of plant development, which will significantly increase productivity.
- The structure of the soil heating circuit in a greenhouse resembles a “warm floor” system. The pitch of laying plastic pipes is at least 0.3 m; this must be taken into account if you install such a system with your own hands.
- To prevent heat from escaping into the ground, a layer of thermal insulation made of a material that does not absorb moisture (for example, polystyrene foam) is needed; for additional waterproofing, a polyethylene film is laid on top of the thermal insulation layer.
- Polyethylene pipes for heating the soil are laid in a cushion of sand (washed and compacted) about 10–15 cm thick, which will promote uniform heating of the soil and prevent the soil from drying out.
- The thickness of the layer of fertile soil to be filled must be at least 30–35 cm.
In conclusion, it should be noted that installing a water heating system with your own hands is not so easy; it will require certain labor costs and skills. But all the costs will be more than repaid when, in the middle of winter, you will be delighted with flowers or fresh vegetables from your own greenhouse. We recommend that you learn about the option of infrared heating for a greenhouse.
| Print Click Print or CTRL+P to print the page | 2.5 Rating 2.50 (2 Votes) |
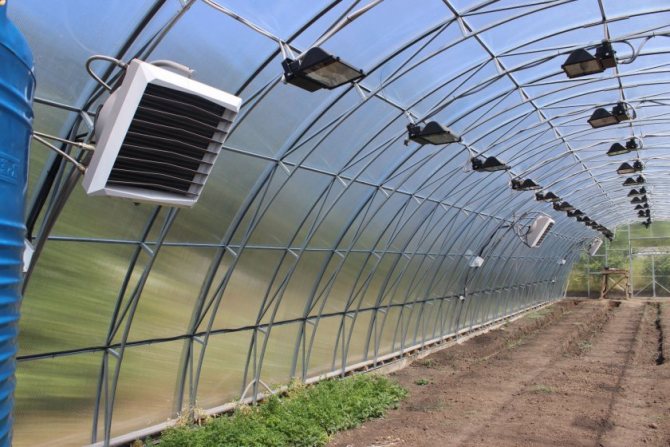
Infrared heaters as one of the best options for heating
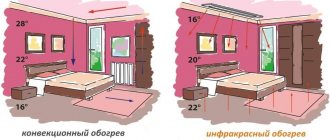
Infrared lamps have their own peculiarity that allows them to be considered a worthy and economical heating option: their heat spreads to plants and water containers, since the thermal elements they emit affect the liquid medium. Greenhouse walls, shelving, equipment, and other objects do not absorb the heat of infrared radiation.
Heating a polycarbonate greenhouse with infrared heaters has a number of advantages:

increase in yield up to 40% due to the complete absorption of heat generated directly by the plants;- with the help of regulation, you can create different temperature zones inside one room, which allows you to grow crops with different heat needs;
- heaters simultaneously serve as heating and lighting devices;
- they have a silent operation mode, without emitting odors and gases;
- the directed action creates the most comfortable conditions for the plants - they heat up, and the space around them remains cool.
The heat emanating from infrared (IR) heaters reaches a soil depth of 60-70 cm, which has a positive effect on the development of the root system of plants.
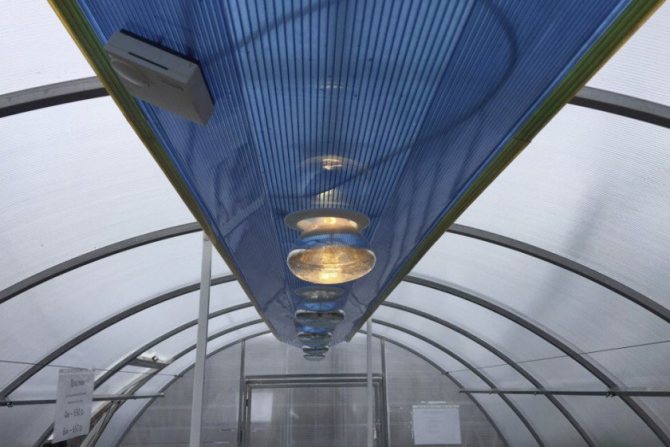
Using infrared heaters in polycarbonate greenhouses, they do not require additional thermal insulation. The presence of good sealing allows even the coldest areas to be heated evenly; they simply will not be there. With top heating, the lamps are suspended from the ceiling; if it is necessary to provide bottom heating, they are installed under shelves or racks on metal, specially prepared elevations.
The lamps must be placed at a distance of at least 1 m from the plants. As the seedlings grow, the lamps are raised to maintain the required distance.
A few tips to help you use IR more economically

To increase the efficiency of the devices, they are placed in a checkerboard pattern, which then leaves fewer areas without heating. The method is used if necessary to heat the entire area of the structure.
If it is necessary to provide heat to a certain area, the units are distributed directly above it.
A quality product cannot have a low price. Responding to an offer to purchase a profitable infrared heater can turn out to be a waste of money.
Heating for a polycarbonate greenhouse should, first of all, be comfortable for the plants, so you should not raise the lamps too high to heat the area more; the seedlings then receive less heat.
The industry produces IR heaters that run on liquid fuel, electricity, and gas. To minimize heat losses, it is better to place energy carriers closer to windows and doors.
Heating greenhouses using water heating
One of the available heating methods, easy to use, with high efficiency. Using water heating, not only the soil is heated, but also the air, which does not dry out, the conditions in the greenhouse become as comfortable as possible for the crops growing there. Such heating provides a good ventilation system.
Water heating of a polycarbonate greenhouse is provided by different types of fuel:

household waste;- firewood;
- coal;
- peat and other suitable material.
The pipes are made from galvanized iron sheets; they heat up quickly and transfer heat well. In addition, you will need a boiler, an expansion tank, and a circulation pump that creates forced water pressure in the system.
The boiler can be isolated from the main area, protecting the plants from smoke entering the greenhouse; its high concentration can poison the seedlings. In this case, the efficiency decreases, because heat also comes from the boiler, heating the air in the greenhouse.
It is important to provide the water system with anti-corrosion protection so that it does not quickly fail due to high humidity.
Electric cable heated floor
The heating cable or heating mats for a greenhouse should have a power of 75–100 W/m kV.
Technically, installing electric heating is simpler and cheaper than running a warm water floor in a greenhouse. But this type of heating is much more expensive to operate.

Cable floor
Installation of electric cable heating of soil in a greenhouse is carried out in the same way as a water circuit:
- A pit with a depth of 50 cm is prepared, insulation is laid on the bottom, but in this case, waterproofing made of thick PVC film must be laid.
- Then everything is exactly the same: a layer of sand, a mesh, a cable, another layer of sand and a protective mesh.
Important! The depth of the heating circuit is always calculated depending on how the soil will be processed while growing plants and how deep gardening tools will penetrate into the soil.
After installation, all that remains is to connect the cable and thermostat to the control unit and set the required heating parameters.
Using gas equipment to heat a greenhouse in winter
If it is possible to heat the greenhouse with gas, this option can be an excellent solution in 2 options:
- connect the heating system to the main gas line;
- use liquefied gas in cylinders.
The first method is possible if the greenhouse is attached to the house; such heating becomes very economical and convenient, its supply is stable and uniform, unlike heating with a wood-burning stove.

Gas heating of a polycarbonate greenhouse located at a distance from the house can be successfully used using cylinders, gas guns, and other devices, but such a heating system is suitable for small areas.
When planning to heat a large area with gas, you will need an expensive project, expensive equipment and its installation, and the gas itself does not cost a penny now. Taking into account the fact that blue fuel is constantly rising in price, such heating becomes unprofitable for the gardener.
When using burners, it is necessary to observe safety; when burning them, there should be no flammable or wooden objects nearby; a high-quality ventilation system is necessary. Access to the burners should always be free so that they can be turned off if necessary. Gas equipment requires regular preventative checks.
A small amount of combustion products serves as natural nutrition for plants, but with poor ventilation, when the concentration of carbon dioxide is exceeded, crops can become poisoned.
Classification of gas heating systems for greenhouses
Gas heating equipment varies in type of design and method of operation.
Depending on this, they are divided into 3 groups:
- infrared;

- catalytic;

- convector.

In addition, there are gas-air and gas-water systems. Not every device is suitable for heating a greenhouse, so you should consider the most appropriate systems to use for such premises.
- Namely:
- heaters with open burners;
- convectors;
- systems operating on gas with infrared burners.
Open burner heaters
Designs of this type consist of a thermostat, as well as two burners - the main one and the pilot one. The devices operate by connecting to a gas cylinder or portable gas heater (you can, for example, use TAG-50).
The essence of the work is that the heated air rises to the top of the building, and, having cooled somewhat, falls into the plant growing zone, thereby creating optimal microclimatic conditions.

A significant disadvantage of the installation is the combustion of a large amount of oxygen inside the greenhouse, which can negatively affect the condition of the vegetation. To establish proper gas exchange, ventilation must be adjusted. You can get by with a basic exhaust system.
Gas convectors
This type of equipment usually consists of:
- housing - its main function is to protect the room from open fire, so it is made of heat-resistant materials;
- heat exchanger - its main task is to heat the air in a short time, due to the release of its own heat obtained as a result of heating by fire;
- gas burner - consists of an ignition and main part, located inside the heat exchanger;
- combination valve - provides pressure regulation;
- combustion product removal systems;
- thermostat - controls the microclimate by maintaining the set temperature at a constant level;
- automation systems - responsible for analyzing the operation of the entire system as a whole, eliminating emergency situations (turning off the gas supply in the event of a malfunction).
Regarding combustion product exhaust systems, gas convectors are divided into fireplace and parapet. In the first option, air masses from the room enter the heat exchanger, and combustion products are discharged through a vertical chimney to the street. This exhaust system is typical for a conventional oven.
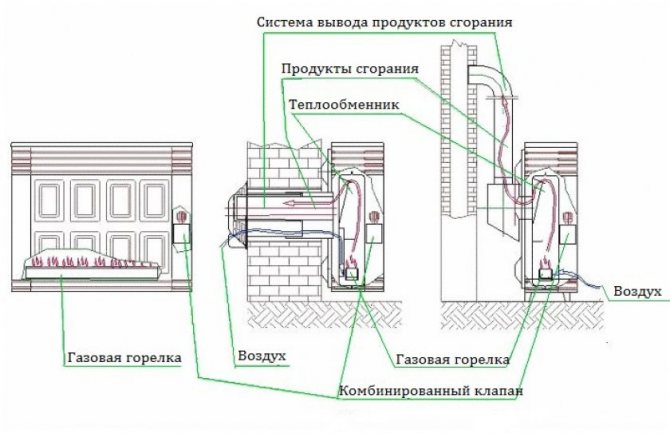
Parapet convectors are more environmentally friendly in this regard. Air and combustion products are taken in through a coaxial pipe laid through the outer wall. The pressure in the pipe is maintained by a built-in fan.
The essence of the device’s operation is the same as in the previous version, but is carried out using automation. Due to the fact that cold air concentrates in the lower part of the building, as well as near windows and doorways, it is more advisable to install it in close proximity to these areas.
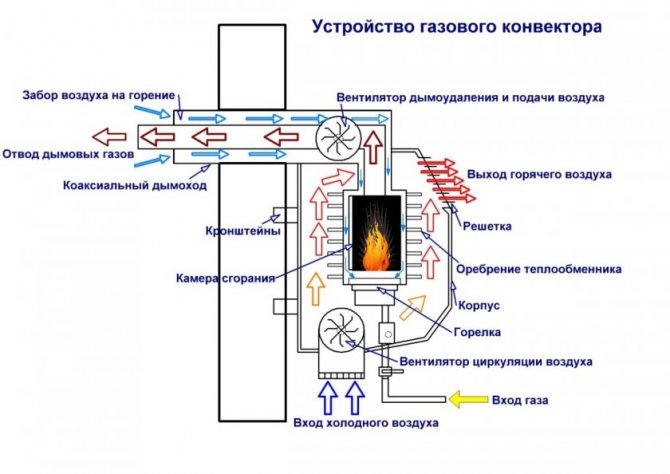
A household heat generator of this type is well suited for installation in a room with a gas supply system. For example, in a greenhouse attached to a house or intended for the production of products on an industrial scale.
Gas heaters with infrared burners
This type of structure was specially developed for heating large areas. At a room temperature of +10°C, by installing it, you can warm up the air to +25°C in a short time within a radius of 6 m from the device.
This device consists of:
- cylindrical body with a built-in gas cylinder;
- stand with a hose connecting the cylinder to the burner;
- a mesh with a large cross-section and a cylindrical shape, to which the manual control panel is attached;
- hood of a gas burner operating in low pressure mode.
Heating a polycarbonate greenhouse with a potbelly stove
Sometimes, when thinking about a heating system for a greenhouse, the owner does not have the opportunity to invest a lot of money in this matter; he considers the option of purchasing or manufacturing a potbelly stove. These types of units are popular among greenhouse growers as a budget-friendly and effective way to protect plants from the cold.

The most accessible design is an old iron barrel, a firebox door is welded to it on the side on one side, a pipe for hot air outlet on the other, a smoke outlet is welded into the upper part of the container.
Pipes are laid around the perimeter or in the central part. Hot smoke passing through the pipes will heat their surface, from which heat radiates.
Heating a polycarbonate greenhouse in winter with a potbelly stove has some features that cannot be ignored:
- to ensure more efficient draft, the chimney is installed at a slight angle towards the exhaust chimney;
- Such heating will be sufficient and high-quality for a small greenhouse area;
- the opening for the firebox is installed on the entrance side to minimize the entry of smoke and ash into the greenhouse;
- if the potbelly stove has legs, a foundation is provided so that during operation there is no accidental overturning or distortion due to one of the legs plunging into the ground;
- This heating method is labor-intensive; you often have to add firewood, since it is impossible to automate such a process.

To further improve heat transfer, the stove itself is coated with clay or lined with refractory bricks, and a water tank is installed above it. When it heats up, it gives off heat and humidifies the air; the heated water can be used for watering plants.
A working potbelly stove must be supervised; the fuel used should not be wet, otherwise heat transfer will decrease and deposits on the pipes will form faster.
Each gardener chooses for himself how to make heating in the greenhouse; the main thing to focus on is providing the plants with a pleasant microclimate, because this is the primary goal. Each of the listed systems has its positive and negative sides.
Heating the soil in a greenhouse 360m2
Reviews:
Alexey Sharapov
writes: how did they solve the issue with the thermal expansion of the PP pipe? If the temperature fluctuates, the pipe will come out of the ground in a couple of months
cucumbers here
writes: I have exactly the same thing)))
Pasha Pavlov
writes: well, how does it warm up? We installed polypr-n under steam, and this is more than 100 degrees, so the pipes were barely warm. Due to low thermal conductivity
Papa Papa
writes: polypropylene has very low thermal conductivity at temperature. coolant 80 degrees. the pipes will be barely warm. It was a waste of money in vain.
Egor Ivanyuk
writes: the effect will be noticeable in the first 2 3 editions, the rest will be cold, it was necessary to survive in a zigzag and it would have been cheaper to put PVC

There is a more original way to heat the soil in a greenhouse - using flue gases from a wood-burning stove. The latter is installed in a deep pit, and the chimney pipe is buried under the beds, after which it goes vertically upward outside the building. The body of the furnace heats the air in the greenhouse, and the flue heats the soil. Below is a diagram of such a combined heating system:

Water heating of soil in a greenhouse, although it requires financial costs, is considered the most reliable, efficient and versatile. Versatility lies in a wide selection of energy carriers, because the coolant can be heated with anything or whatever is more profitable. Here it is important to correctly lay the loops of heating circuits from pipes and organize the maintenance of the required soil temperature.

This method of heating the soil in a greenhouse is considered optimal if it is located near the house. The only difficulty is the need to maintain the water temperature inside the pipes no more than 40 degrees Celsius. Otherwise, the roots of the plants will receive numerous burns, and the above-ground part will begin to wither.
All you have to do is choose the most suitable method of heating the soil in your greenhouse. Consider not only the cost of the heating system, but also the costs of its further maintenance, as well as the possibility of year-round or seasonal cultivation. In any case, your diligence will pay off with a high harvest, and if you are a private entrepreneur, then also with increased income.
The second container is a heating boiler, from which the coolant will flow into the heating system of the greenhouse. To do this, you need to cut a hole in its upper part for connection to the expansion tank, and in the lower part for a drain valve (if desired).