Advantages and disadvantages of floor-standing models
Floor radiators are connected to the general heating system and installed on legs
A floor-standing radiator unit can be installed on special legs or built into the floor surface, mounted like a plinth. Compared to standard options, they have several advantages:
- compactness – small-sized products do not clutter up the space;
- high heat transfer coefficient of models made of cast iron, bimetal, aluminum;
- laconic appearance - suitable for any interior design;
- several color options - standard batteries are made in white, but manufacturers paint them according to the RAL catalog, playing with different textures;
- ease of installation - installation work is reduced to connecting to the heating system or screwing into the floor;
- efficient heating of a room where there is a large window;
- Possibility of installation next to walls.
The disadvantages of floor heating radiators include the need to organize floor wiring and the difficulty of finding the right model in offline stores. Disadvantages also include low price compared to classic options and heating using convection technology.
The floor-standing device can be combined with a classic battery near the wall or under the windowsill.
Features of choosing a device for heating a home

If you need to save space, choose plinth radiators
When purchasing a heating device, there are several factors to consider:
- Material of manufacture. Aluminum ones are lightweight and compatible with any coolant. Bimetallic ones are less susceptible to corrosion, and cast iron ones have the highest heat capacity.
- Construction. Sectional options are easy to match to the window parameters due to the ability to remove or add elements. Panel heats up quickly and is easy to install. Tubular ones are resistant to pressure fluctuations and can withstand loads of up to 20 atm.
- Dimensions and characteristics. The height of floor-standing devices is from 14 to 50 cm, and the length is up to 2 m. They are designed for pressure up to 15 atm. and water temperature up to 110 degrees.
- Heating method and shape. Water batteries are heated by coolant and are equipped with temperature regulators. Electric ones can work together with the “warm floor” system, and combined ones operate from the heating line and the electrical network.
For installation in the bathroom, it is better to choose baseboard modifications, which will save up to 40% of fuel.
Brief list of manufacturers
To make your choice easier, we suggest familiarizing yourself with the most well-known manufacturers of convectors; their products have positive reviews from numerous consumers.
Brand name Technical parameters
| Verano | Manufactured in Poland, can be with natural or forced convection. The thickness of the aluminum radiator plates is 0.22 mm, the steel frame is coated with zinc-magnesium. The diameter of the main copper tubes is 15 mm, body dimensions are from 100×50 mm to 200×100 mm. It is equipped with aluminum, wooden or stainless steel gratings. |
| Kermi | They can be with or without fans, the depth of the box is 18–35 cm, the width is 9–20 cm. It is used as additional heating of the room, installed near entrance doors and stained glass windows. The small installation height allows the devices to be mounted on thin interfloor ceilings. |
| Mohlenhoff | German convectors for in-floor installation. They can have radial and tangential fans, and there are electric heating options. Depth 7–19 cm, width 18–41 cm. A wide range of models makes it possible to increase the scope of use of the equipment. Maximum pressure 16 atm., working pressure 10 atm. They can function in one- and two-pipe heating systems. |
| Jaga | The box is made of galvanized steel, width 14–42 cm, depth 6–19 cm. Manufactured in Belgium, small dimensions significantly expand the scope of use. They can have natural or forced ventilation of the heat exchanger. Service life is at least 30 years. |
| Kampmann | Hi-End devices operate with forced or natural ventilation. Manufactured in Germany, the company was founded in 1972. Depth 9–20 cm, low noise fans. The heat exchanger has aluminum fins and can withstand temperatures up to +120°C. |
| Minib | Produced in the Czech Republic, they have a reduced height (from 5 cm), which allows the devices to be installed on thin flooring bases. The box is made of stainless steel. They have a wide selection of decorative grilles. |
| Heatmann | During manufacturing, the most modern technologies are used, due to which the efficiency is significantly increased. Convectors are manufactured in Germany, the frame is made of powder-coated galvanized steel. Width 10–42 cm, depth 8–20 cm. A wide range of sizes allows consumers to choose the best option, taking into account the size of the room and the specific installation location. There are options with natural and forced ventilation of the heat exchanger. |
| Itermic | The devices are manufactured by a domestic company, the casing is made of galvanized steel, there are options with and without fans. Depth 7–19 cm, width 20–40 cm. Heat exchanger tubes are copper, aluminum lamellas. The thickness of the lamellas is 0.5 mm, the diameter of the tubes is 16 mm. Designed for working pressure 15 atm., pressing pressure 25 atm. There is manual or automatic control of operating modes. |
| Varmann | They are widely used in Europe and our country, the casing is made of galvanized steel, and electric heater options are available. They can work both for heating and cooling a room with natural or forced convection. Depth 9–20 cm, width 14–37 cm. |
| Polvax | The manufacturer is a Polish company; they may have one or two heat exchangers, which increases heating performance. Housing made of alloy sheet steel, depth 7–34 cm, width 18–38 cm. Tube diameter 22 mm, coolant temperature up to +90°C, operating pressure 10 atm. |
We recommend: Brick stove for home (115 photos): DIY installation instructions, stove drawings
Each company produces a wide range of equipment according to technical characteristics, which makes it possible to find the most suitable convector option, taking into account the maximum number of different factors.
Specifics of floor batteries

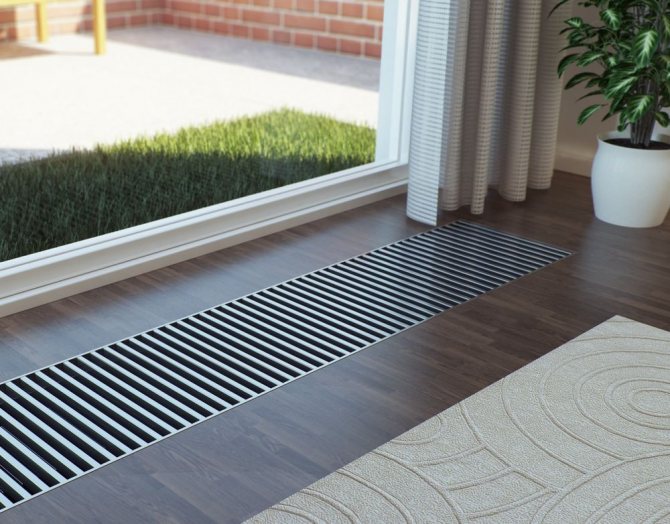
Low radiators are installed under panoramic windows
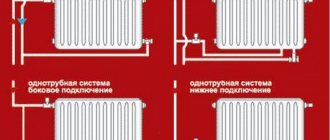
Floor batteries replace conventional ones if you want to open the space without masking the facade. A center-to-center distance of 20 cm will emphasize the panoramic type of glazing. The devices are connected to the main line using a floor or side method, depending on the pipe outlet. To control the intensity of heating and temperature conditions, rooms can be equipped with thermostat valves and taps.
In combination with panoramic windows, the heaters look beautiful and neat. Thermal output depends on the number of sections and is comparable to standard ones with a center distance of 0.35 m.
Operating principle
As a component of a water heating system, floor-standing units function as follows:
- Heating the coolant in the boiler room to the required temperature.
- Supplying water through pipes and filling batteries.
- Heating of the case.
- The supply of thermal energy to a room through radiation or convection.
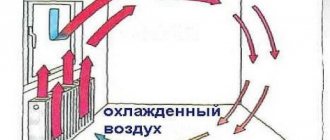
Only panel and sectional batteries operate according to the radiation principle, which consumes up to 80% of the total power. Heat waves are directed perpendicularly or in two directions at an angle.
Models with a ribbed tube radiator transfer heat using the principle of convection. Heated air moves in the room towards the ceiling and displaces cold air.
Differences between a convector and a radiator
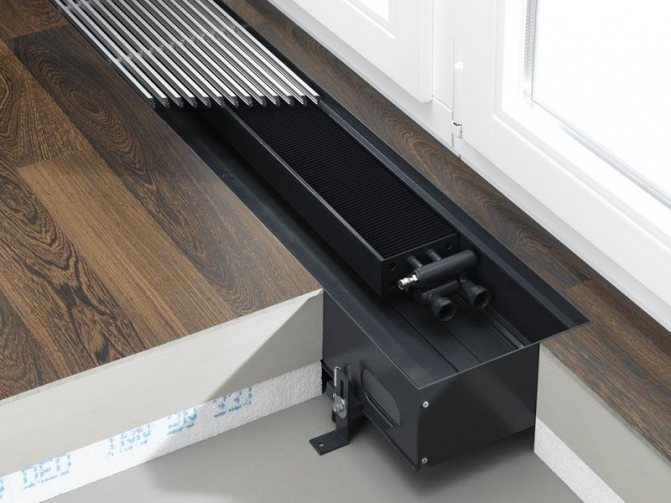

Radiators run on water or antifreeze
Related article: Flexible floor profile: installation and how to use
The difference lies in the amount of heat transferred. The convector is capable of transferring more than 70% of the heat, and the radiator is much smaller.
Both radiators and convectors use water or antifreeze as a coolant.
The choice depends on the characteristics of the material used to create the heating device. The device of each model includes:
- heat exchanger;
- box;
- decorative lattice.

The design feature is the absence of gaps between the heat exchanger and the pipe. This helps to increase the functionality of the device, and to increase power in modified devices, several heat exchangers are installed in one housing.
Modern models are equipped with a removable grille and an air damper that allows you to control the heat transfer force. Such compact devices are absolutely fireproof, they do not dry out the air in the room, distribute heat evenly, and are equipped with a thermostat that allows you to regulate the heating temperature.
Underfloor heating radiators are popular due to the fact that they can be used with both autonomous and centralized heating. Moreover, in an autonomous system the working pressure of the convector reaches 8 atmospheres, and in a centralized system – 10 atmospheres.
Types of materials for floor radiators

Aluminum floor radiators have an increased service life
Water floor devices - batteries for heating a house or apartment, are made of several materials.
Aluminum
They are produced using casting technology (casting a solid device) or extrusion (connecting individual parts). They have increased heat transfer, so they heat up quickly. Aluminum batteries are the best option for a home autonomous system. They differ:
- working pressure 5-16 atm.;
- thermal power of one section from 81 to 212 W;
- compatibility with coolant with a maximum temperature of 110 degrees;
- effective at water pH 7–8.
When choosing aluminum modifications, you need to make calculations based on the area of the room and additionally purchase pressure and temperature sensors, and dirt filters.
Bimetallic

Bimetallic radiators are made of two types of metal and are not sensitive to water hardness
Bimetallic heaters are made with a steel inner core and an aluminum body. Due to its insensitivity to the composition of water, the devices can be used to heat an office or apartment.
An anti-corrosion coating is applied to the internal and external parts of the product, preventing the appearance of rust and wear of components. Radiator systems can withstand water hammer and a maximum pressure of 50 atm.
Depending on the materials used, there are designs made of 100% (steel core and aluminum body) or 50% (steel vertical pipes) bimetal. Both types are different:
- operating pressure limit of 18-40 atm;
- thermal power of a separate section from 125 to 180 W;
- maximum coolant temperature from 110 to 130 degrees.
Bimetallic options are lightweight, look beautiful, but are expensive.
Cast iron

Cast iron radiators are characterized by increased heat transfer and aesthetic appearance
They look like cast sections, hermetically sealed to each other. The cast iron type of batteries is suitable for an apartment and is selected according to the total area, number of windows, number of floors, location of rooms.
The design is characterized by high heat transfer, long service life and insensitivity to chemical influences. Cast iron can accumulate and retain heat for a long period. The downside of metal is its heavy weight and ruptures due to pressure changes.
Heaters have the following characteristics:
- maximum pressure limit of 18 atm;
- highest coolant temperature 150 degrees;
- power of one section from 100 to 150 W.
The main advantage of cast iron is wear resistance, which does not depend on the composition of the water.
Types of devices
Devices are divided into electric and water - powered by a circulation circuit.
Electrical
In these devices, the heating element (heating element with plates) is powered from the electrical network. Plugged it in - it was warm. There is no electricity (line failure) - it’s getting colder.
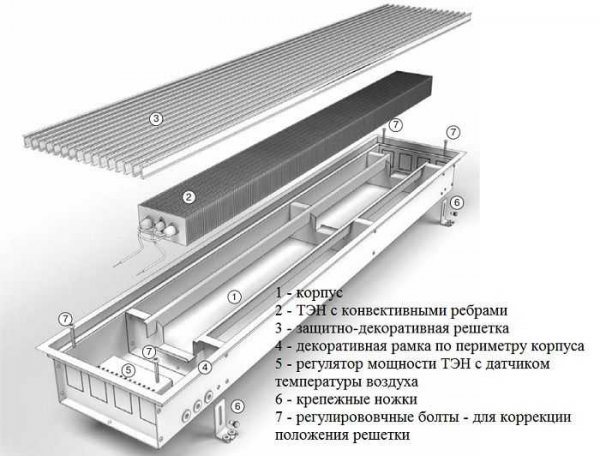
Powered by a circulation circuit
The operating principle of this type of in-floor convectors is the same as that of a classic radiator water heating system: the coolant heated from the boiler (gas, diesel, wood) gives off heat to the air masses.
Undoubtedly, the process of heating the room is lengthened. But you will probably not freeze if the electricity in the house goes out.
Fan coil units
Based on floor-mounted convectors, another type of heater is produced that works not only for heating, but also for cooling. Depending on the installation location, in addition to the internal one, they are also wall, floor and ceiling. The Russian-language name for such a unit is fan coil - from the English fan-coil, which means fan-heat exchanger.
This definition means a combination of two devices working in pairs:
- fan coil itself - a floor-mounted mechanism for influencing air temperature, including one or more heat exchangers;
- chiller - a separately installed unit for cooling the coolant (water) supplied to the fan coil in the summer.
Fan coils are single-circuit (two-pipe) and double-circuit (four-pipe).
In single-circuit units, hot water from the central heating system or antifreeze from the heating boiler is passed through a heat exchanger in winter. In the summer, cold water from a chiller passes through the same heat exchanger - a device that does not use freon or other gas with identical characteristics for cooling.
In double-circuit fan coils, the movement of hot and cold coolants is carried out through separate heat exchangers.

Schematic representation of a double-circuit fan coil unit (without a chiller).
Thus, depending on the set mode, the fan drives room air through a hot or cold heat exchanger.
There is no universal scheme for installing a chiller-fan coil system pair; its installation is possible in any room, but the installation project will be tied to specific conditions.
One chiller, correctly selected in terms of power, can be connected to a system of many fan coil units (wall-mounted, ceiling-mounted, in-floor), serving several rooms and even buildings.
This system for ensuring the required temperature in rooms is used mainly in public and industrial buildings, as it is difficult to maintain and expensive.
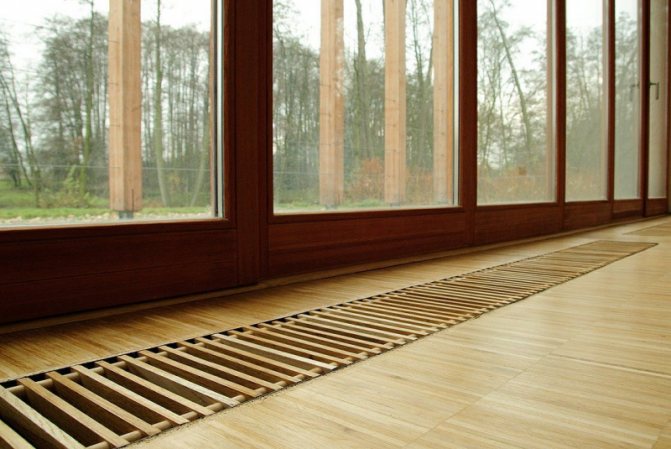
Possible alternatives

An in-floor convector saves space, but is inconvenient to clean
Floor-standing radiators can be replaced with other devices if it is necessary to create an aesthetic design.
Built-in options
The in-floor unit allows heating to be installed in a hidden way. It is installed in the floor, and a decorative grille is used to remove thermal energy, standing flush with the coating. Built-in modifications differ:
- ability to withstand pressure from 10 to 16 bar;
- thermal power from 13 to 100 kW;
- water heating limit from 110 to 130 degrees;
- simplicity of design, light weight and compactness;
- corrosion resistance;
- hidden location - mounted in a doorway or floor covering;
- uniform heating of the room;
- preventing fogging of window structures.
Due to the large installation length and the need to create a niche, it is better to design the location of the sections at the construction stage. The models operate only on the radiation principle, so their heat transfer is minimal.
Skirting convectors
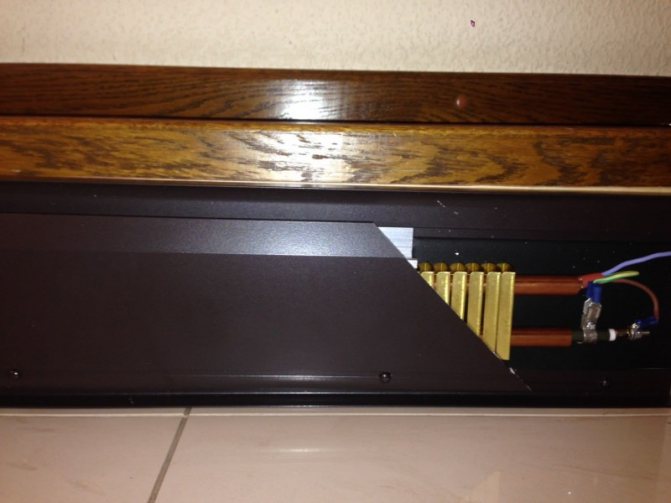

Uniform heating of the bathroom can be achieved by installing baseboard radiators
It is not always possible to install radiators in the bathroom, so you can use warm baseboards. Products differ:
- height from 20 to 25 cm and depth 10 cm;
- efficiency - fuel costs are reduced by 50%;
- thermal power from 50 to 150 kW;
- operating pressure limit up to 16 atm;
- heating the water to 130 degrees;
- protection against overheating thanks to a thermostat;
- ease of installation;
- uniform distribution of heat flows.
Low water floor heating radiators should only be installed by specialists. If the technology is not followed, the wall decoration can be damaged.