Hello our dear readers. We, as always, are glad to welcome you to the pages of our blog.
So we finally waited for the first snow. Of course, he made some people happy, but others were saddened. At current energy prices, utility bills can drive anyone into depression. There is only one way out - insulation.
But in order to decide what is best to dress your home in, you need to know well the pros and cons of different insulation materials, and there are, to put it mildly, a lot of them on the modern market. Try to figure out which one suits you and which one doesn’t.
I myself have repeatedly encountered similar questions, and therefore, in order not to get confused in the future, I got myself a small notebook where, as a cheat sheet, I wrote down the main properties of the insulation materials known to me and the materials that are mistakenly classified as them. Today I am ready to share these notes with you. Read on.
Pros and cons of polystyrene foam as insulation

Expanded polystyrene is a lightweight gas-filled product made from polystyrene and its copolymers. The main advantage is its low cost. Today it is the most budget-friendly of all high-quality thermal insulation materials.
Besides:
- Expanded polystyrene is not afraid of moisture, so it can be used not only for interior insulation or working with facades, but also, most importantly, for thermal insulation of foundations. Here polystyrene foam is almost irreplaceable.
- Expanded polystyrene has a very low specific gravity (25-45 kg/m3), which means that its use ultimately leads to savings in building materials that could have been used to strengthen foundations, floors or rafter systems.
- Expanded polystyrene has outstanding thermal insulation characteristics. Its thermal conductivity, depending on density, is 0.032-0.035 W/mC, which is twenty-three times less than that of brickwork. In other words, one centimeter of polystyrene foam will replace 23 cm of brick.
The disadvantages of polystyrene foam as insulation mainly relate to its dubious environmental performance. Thus, even with slight heating, the product releases styrene, a very toxic substance that can not only worsen the functioning of a person’s internal organs, but even change his blood composition.
And as a result of the combustion of foam plastics, in general, phosgene is formed, a gas used in the First World War as a weapon of mass destruction.

Against this background, the vapor permeability of the insulation may not be noticed, but this is also a rather serious disadvantage. It is precisely because of this property that polystyrene foam is not recommended for use on “breathing” walls and it is strictly forbidden to insulate wooden structures with it, the material of which has not been kiln dried.
Conclusion: Polystyrene foam can be used as insulation only in cases where during operation it will not be exposed to high temperatures, and the surfaces it insulates are already vapor-tight.
How to choose insulation?
Floor insulation
We insulate the floor
The decision to insulate the floor is sometimes driven by the desire to have a more constant temperature at home. When choosing insulation for the floor, comparing the characteristics of various materials, preference is given to the one that can withstand the considerable pressure exerted on it. In this case, its compression performance will be important.
Well, an indispensable requirement is the ability to maintain insulating qualities, even when exposed to heavy loads and moisture.
Types of wall insulation
Insulation for house walls
Thermal insulation for this category is completely different, moreover, its type depends on the specific place of application - outside or inside the house.
For outdoor use, it is considered ideal to use basalt mineral wool, which is characterized by its ability to hold its shape and durability. Even during long-term use, it does not thin out, does not cake or become compacted.
Insulation from the inside of the structure is carried out based on the possible insulating layer: the layout features do not always allow it to be made sufficiently voluminous.
A more modern way is to use paint with a ceramic base. Its layer can be small, and the tightness conditions are much easier to maintain.
Ceiling and its insulation
Mineral wool for ceiling insulation
For ceiling insulation, mineral wool is constantly in high demand .
This is not at all surprising: it can be quite simply laid out in the interfloor ceilings or in the rafter frame, in the quantity required for this. During operation there, nothing threatens it, thereby ensuring the initially high quality of insulation.
If we neglect the unique qualities of wool and the ease of its installation, then other suitable means for thermal insulation could be sawdust with clay or ordinary slag. However, these substances have not found widespread use due to their high cost and rather complex installation process.
Mineral wool
This name combines several different subtypes of thermal insulation materials of this type. These are slag, stone and glass wool. This insulator is made by processing metallurgical alloys or melts of various rocks: a special synthetic binder is introduced into the resulting glassy fiber.
>
The material produced in this way has excellent sound and heat insulation qualities, moreover, it is not flammable and therefore does not pose a fire hazard. But a huge part of the wonderful qualities of insulation can be irretrievably lost when it gets wet. This should be taken into account.
Stone wool
Stone wool
This is a fibrous material that is sold in the form of rolls and portioned slabs, and has an extremely low thermal conductivity.
The highest quality product is made from rocks called gabbro-basalt. This non-flammable material is used with equal success in the construction of private facilities and the construction of various industrial facilities. The wide range of uses is also explained by the possibility of its use at extremely high temperatures, reaching one thousand degrees.
The insulation's complete immunity to fire is complemented by its excellent resistance to moisture. This is a hydrophobic material, the peculiarity of which is that it does not absorb water, but repels it.
This ensures that the insulation remains dry even after a long period of time. This, in turn, will allow her to maintain her high performance qualities. The unique properties of basalt wool allow it to be used even in boiler rooms, baths and saunas, where high humidity and high temperature are combined . Strength in this case is not directly dependent on the density of the material.
This is a fairly soft material, but at the same time has a sufficient margin of strength. Its structural stability is determined by the special arrangement of the individual component fibers - chaotic and vertical. The material has high anti-corrosion properties.
It can coexist quite peacefully with concrete and metal, without the occurrence of various kinds of chemical reactions. High biological stability provides it with immunity to various biological pests: damage by insects and rodents, the occurrence of fungal diseases, the development of rot and mold.
The basalt insulation passed the combustion test, but the organic insulation burned out
Basalt rock is the main raw material for the production of this type of wool . Treatment with formaldehyde resins gives the material a sufficient level of strength, and the modern technologies used guarantee the complete elimination of harmful phenols at the stage of material production.
The final product reaching the consumer is a harmless and environmentally friendly material with high insulating qualities.
It is actively used for insulating floors of residential and industrial premises, for thermal insulation of roofs and facades, including as external insulation.
Glass wool
This fibrous material is made from a mass of molten glass. Based on it, two types of insulation can be found on sale - soft mats rolled into rolls and hard slabs.
The product is characterized by high strength and excellent elasticity. As in the previous case, recycled formaldehyde resins are used as a coupling or binding agent.
Although not all the wonderful properties of basalt wool are inherent in its glass counterpart, it has its own special qualities. It has high plasticity, which significantly facilitates the stages of working with it, and allows you to significantly compress the material when laying it. But during operation, glass wool can cake and lose its original shape. Glass fiber is highly hygroscopic and can accumulate moisture from the external environment, accumulating it in its thickness.
Styrofoam
We insulate a frame house with polystyrene foam.
Foam is a fairly hard, shape-holding board material widely used for thermal insulation of roofs, walls, floors and ceilings: both outside and inside. It is based on foamed polystyrene foam granules.
It goes on sale in slabs 1 by 2 meters, with different thicknesses: from two centimeters to half a meter. Its characteristics can vary noticeably, which is why the material is selected strictly individually in each specific case.
Depending on the manufacturing process, two different types of foam can be obtained using virtually the same raw materials:
- A porous plastic is a porous substance whose individual cavities communicate with each other. They are further divided into mipore, polyvinyl chloride foam, polyurethane foam and polystyrene foam;
- foam directly - the contents of individual granules in it do not come into contact with the environment and neighboring cavities.
Expanded polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene in the form of bricks
Expanded polystyrene is a material that belongs to plastics with a cellular structure, has almost all the qualities necessary for thermal insulation, it:
- easy;
- hard;
- not afraid of water;
- biological infections.
- But due to its low fire resistance, it is recommended to use it at temperatures no higher than 150 degrees.
To improve this quality, special flame retardants are added to the insulation at the production stage. The symbol “C” is added to the name of such a material, and it is called self-extinguishing. The performance qualities of polystyrene foam have made it a fairly popular material.
Sprayed polyurethane foam
Spray on the wall
It is a foam material that can be applied by spraying through a special apparatus. It contains polyisocyanate, polyester polyol and various additives.
The adhesive properties of the material allow it to be safely applied even to vertical surfaces. It has excellent adhesion to concrete, plaster, roofing felt, metal, and gas silicate blocks.
The material is quite successfully used for insulation:
- internal;
- external walls;
- flat and pitched roofs;
- ground floors;
- foundations;
- basements;
- joints between structures.
Ecowool
This cellulose insulation is made from cardboard and paper waste. Its properties are actually determined by the substances included in its composition. In addition to the usual recycled cellulose, some foreign manufacturers also use hay, cotton waste, and sawdust. 81% of the material consists of carefully processed cellulose, while 12% is a mandatory antiseptic.
The missing 7% comes from specially added flame retardants. Insulation fibers contain lignin, which becomes sticky when humidity increases. All elements included in the insulation are non-toxic, absolutely non-volatile and harmless to health. Cellulose insulation is resistant to combustion and rotting, and has excellent sound and heat insulation properties.
Ecowool can retain approximately 20% moisture while maintaining its performance properties. The material releases moisture to the outside and dries quickly, maintaining all its performance qualities. The disadvantage of ecowool is the difficulty of manually applying it to the surface, as well as the impossibility of arranging a “floating floor” due to its inherent softness.
Penoizol
Another name for the material is urea foam. This is a modern material with high sound and heat insulating characteristics, which is a cheap insulation material. This is a cellular organic foam with particularly low density and low thermal conductivity. The material has high fire resistance, resistance to microorganisms, and a low price. It is easy to process, its air content reaches 90%.
Insulating the attic with foam insulation
The tests carried out demonstrated the capabilities of the material. It turned out that the time of its operation, as the middle layer of a frame structure, is actually unlimited. Tests of its fire resistance showed that the material can be safely classified as low-flammable.
This is the only thermal insulation material of a polymer nature that is not at all suitable for self-combustion. Its fire resistance index places it in the G2 flammability subgroup.
domsdelat.ru
Pros and cons of mineral wool as insulation

Mineral wool is a fibrous material made from molten glass, slag or some rocks. The main advantages of this product include its relatively high environmental safety and non-flammability, the disadvantages are a sharp decrease in technical characteristics even with a slight increase in its humidity.

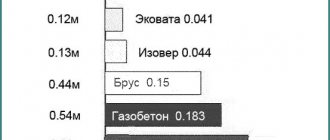
When compared with foam plastics, mineral wool has a thermal conductivity coefficient close to them (0.035-0.039 W/mS), but this is only for material from the conveyor, when the humidity of the product is zero, subsequently these indicators will increase to 0.044-0.05 W/mS .
A distinctive feature of mineral wool is its high vapor permeability, which is why it is used for insulating wooden and frame houses, buildings made of aerated concrete and other “breathable” materials.
Pros and cons of polyurethane foam as insulation
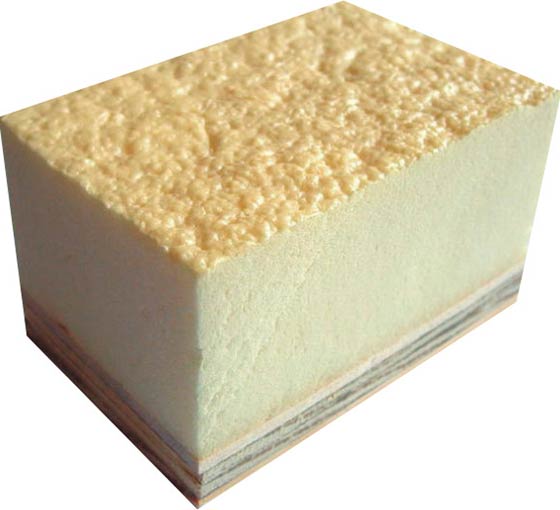

Polyurethane is a heterochain polymer, which was originally developed as an analogue of rubber, and today its foamed product is successfully used as insulation.
If we take only the physical and technical characteristics, then this heat insulator will leave behind both polystyrene foam and mineral wool (unlike the first, it breathes, and from the second, it is not afraid of water), but it has a number of its own shortcomings that cannot be ignored .
The first is the cost of the issue. Polyurethane foam is traditionally considered one of the most expensive heat insulators; moreover, its independent spraying is excluded. You will definitely have to hire specialists, and they will see whether they will come or not.

The second minus can only open again during a fire. Despite the fact that polyurethane foam burns rather poorly, during this process it releases hydrocyanic acid, which is a very strong poison.
Conclusion: PPU is a fairly high-quality insulation material, but there are also cheaper methods of thermal insulation.
Insulating walls - an inexpensive way
If the house has a facing side, then a ventilation gap must be provided between the facing and the wall so that the condensation formed on the wall can evaporate, and the ecowool layer can dry and release the accumulated moisture.
This method of insulation involves the use of cheaper wind protection - windproof roll materials, which do not prevent the evaporation of moisture from the insulation, but do not protect the house well from direct wind.
The construction of walls when using less expensive materials is as follows, starting with the outer layer:
- if this is provided for by the building design, the first layer of the wall is facing (it is installed on a vertical sheathing);
- Next, it is necessary to organize a ventilation gap that allows condensation to roll off and ensures drying of the insulation;
- then there is a layer of windproof material that covers the entire area of the wall;
- load-bearing wall structure;
- a layer of ecowool, the installation of which was carried out using the dry laying method;
- vapor barrier film with low vapor permeability or kraft paper;
- the last layer is plywood, chipboard, OSB, lining, gypsum board or any other finishing material.
This method of insulation requires less cost, but the facing materials should be selected correctly so that they successfully withstand the effects of side winds.
Pros and cons of doronite as insulation
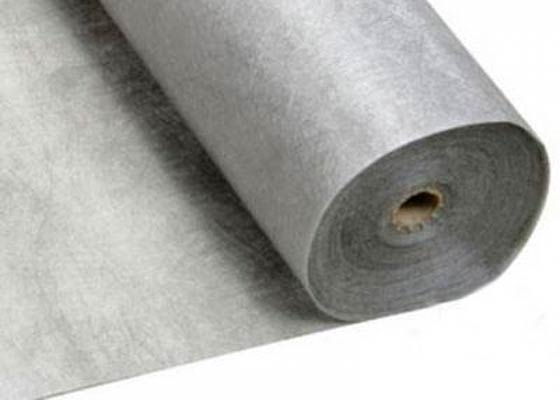

Doronite is one of the types of geotextiles, which is mistakenly accepted by some as insulation. However, this is just a separation film, which, although used in a heat-insulating cake, does not have any significant heat-retaining properties.
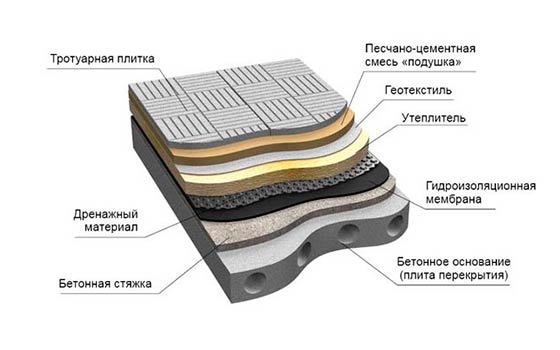
Conclusion: To the question: “Can dornite be used as insulation,” there is only one answer: “Definitely not”!
When is a ventilation gap still necessary?
So, if you are thinking about whether a ventilation gap is needed in the facade of your carcass house, pay attention to the following list:
- When wet If the insulation material loses its properties when wet, then a gap is necessary, otherwise all work, for example, on insulating a home, will be completely in vain
- Steam Permeation The material from which the walls of your home are made allows steam to pass through into the outer layer. Here, without organizing free space between the surface of the walls and insulation, it is simply necessary.
- Preventing excess moisture One of the most common questions is: is there a need for a ventilation gap between vapor barriers? If the finish is a vapor barrier or moisture-condensing material, it must be constantly ventilated so that excess water is not retained in its structure.
As for the last point, the list of similar models includes the following types of cladding: vinyl and metal siding, profiled sheets. If they are tightly sewn onto a flat wall, then the remaining accumulated water will have nowhere to escape. As a result, materials quickly lose their properties and also begin to deteriorate externally.
When answering the question of whether a ventilation gap is needed between the siding and OSB (from English - OSB), it is also necessary to mention its need. As already mentioned, siding is a product that insulates vapor, and the OSB board consists of wood chips, which easily accumulate residual moisture and can quickly deteriorate under its influence.
We suggest you read: The best way to insulate the ceiling in a bathhouse and how to do it correctly: do-it-yourself insulation
Let's look at a few more mandatory points when clearance is a necessary aspect:
- Preventing the formation of rot and cracks The wall material under the decorative layer is prone to deformation and deterioration under the influence of moisture. To prevent rot and cracks from forming, just ventilate the surface, and everything will be fine.
- Preventing condensation The material of the decorative layer can contribute to the formation of condensation. This excess water must be removed immediately.
For example, if the walls of your house are made of wood, then an increased level of moisture will negatively affect the condition of the material. Wood swells, begins to rot, and microorganisms and bacteria can easily settle inside it. Of course, a small amount of moisture will collect inside, but not on the wall, but on a special metal layer, from which the liquid begins to evaporate and be carried away with the wind.
In what other cases will you need a ventilation gap between the wall and the decorative covering:
- The material of the decorative layer promotes the formation of condensation.
- The wall material under the decorative layer can deteriorate from moisture (rot, cracks, etc.).
Otherwise, all the moisture that will condense on the inner surface of the corrugated sheet will be absorbed, which will be destroyed as a result.
In the case of a ventilation gap, moisture, of course, condenses on the inner surface of the profiled sheet - this is metal. But it does not have direct contact with the surface of wooden walls. And the air current that is present in the ventilation gap carries away this moisture in the form of steam and removes it from the space between the decorative layer and the wall.
Consider which of the above cases is yours and choose whether you need a ventilation gap or not. See what kind of wall material you have.
- Question: Good afternoon, dear gentlemen! Please tell us how best to decorate the outside of a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks (ECB), what façade would be appropriate here, what materials can be used?…
- Recently, people have begun to give preference to wooden houses. The first thing that attracts this natural material is its environmental friendliness. In addition to this, the tree is very good...
- This page shows a sectional view of a frame wall along with insulation, which is mounted between the frame posts. Simply put, a frame wall in cross-section looks like this...
- If you look at the history of the construction of residential buildings in cold regions, insulating walls with sawdust began to be practiced not so long ago. Sawdust as wall insulation during construction...
- The simplest design of the walls of a frame house is vertical posts connected by upper and lower frames and tied with jibs for additional structural rigidity. When using slab…
The ventilation gap in a frame house is a point that often raises many questions among people who are involved in insulating their own home. These questions arise for a reason, since the need for a ventilation gap is a factor that has a huge number of nuances, which we will talk about in today’s article.
The gap itself is the space that is located between the sheathing and the wall of the house. A similar solution is implemented using bars that are attached on top of the wind barrier membrane and on the external finishing elements. For example, the same siding is always attached to bars that make the facade ventilated. A special film is often used as insulation, with the help of which the house, in fact, is completely wrapped.
Many will rightly ask, is it really not possible to just take and attach the sheathing directly to the wall? Do they just line up and form an ideal area for installing sheathing? In fact, there are a number of rules that determine the necessity or unnecessaryness of organizing a ventilation facade. Let's figure out whether a ventilation gap is needed in a frame house?
We suggest you read: How to plaster a stove so it doesn’t crack
Pros and cons of foil insulation as insulation

Another dubious insulation is foil insulation. Made from foamed polyethylene, it, of course, has a good thermal conductivity coefficient, but due to its insignificant thickness it cannot serve as the main insulation. Used in a heat-insulating cake as a hydro or vapor barrier. He copes with this task excellently.

Pros and cons of sawdust as insulation
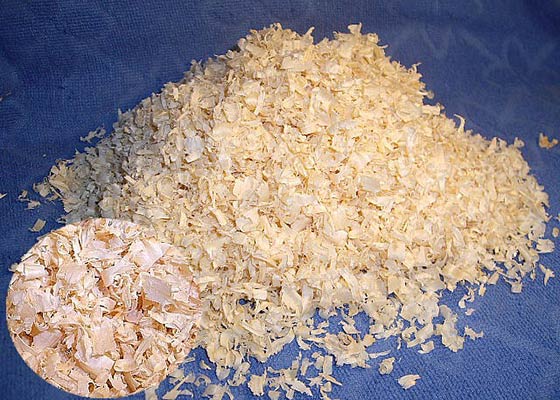

Sawdust is a secondary product of wood processing, each fragment of which has the same thermal insulation properties as in ordinary wood, but the mass itself, due to its loose structure, has much better performance.
The advantage of such insulation is obvious. There is an unquestionable environmental friendliness and low cost of the product (you can often get it for free), but you will also have to tinker with it a lot.

If you decide to test whether sawdust can be used as insulation, then you will have to first dry it (preferably chamber drying), treat it with antipyroseptics and slaked lime, and then, so that the insulation remains “airy,” add gypsum to the mixture.
After such manipulations, sawdust, of course, significantly loses its thermal insulation properties, but with a layer of 30-40 cm it can serve as good insulation for floors or attic floors.
Conclusion: Despite the apparent cost-effectiveness, sawdust insulation will not cost you a lot in the end.
Reasons for getting wet insulation on the roof
First: during the installation process, the hydrobarrier or superdiffusion membrane was damaged. That is, the seal of the film is broken with a self-tapping screw or nail. Also, quite often, this occurs due to excessive tension of the hydraulic barrier. According to the standards, it must be installed with a slight sag, so as not to create tension in the material, and so that condensate water can be collected and discharged at the sagging point.
The second reason may be the lack of gluing at the joints of the canvases, which leads to the penetration of condensate moisture by rising wind currents.
The third reason is poor fastening at the junction of chimney and ventilation pipes. It should be noted that the edges of the hydrobarrier must be fixed vertically, upward, to the wall, and a pressure bar must be installed.
The fourth reason may be the use of low-quality superdiffusion membranes, which are often found in cheap segments.

These are the main reasons that occur when working with hydraulic barriers. But water in the insulation can also appear due to poor installation of the vapor barrier.
This happens especially often when wet work is being carried out in the house in the autumn-winter time, and the roof is already insulated. At the same time, the difference in temperatures inside and outside is noticeable, and all the condensation, rushing upward, gets into the insulation if your vapor barrier is not glued, or is not glued tightly at the joints.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Insulating the ceiling of a bathhouse with insulation
Check the tightness of the films until they are completely closed, be sure to glue the joints and abutments to the walls.
Take it out and dry it, or buy new insulation. But you can’t leave it wet in the rafters, as mold may form on the wood.
Remember that only professional builders, or the developers themselves who have thoroughly studied these technologies, should carry out insulation work.
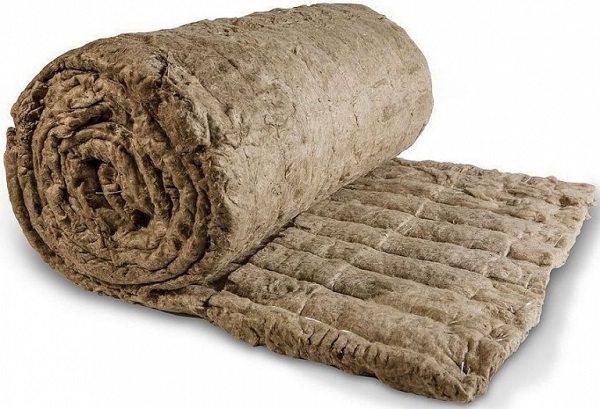

Rock wool getting wet in the attic can be due to at least a few reasons. Due to a leak or damage to the roof, an incorrectly positioned vapor barrier, lack of ventilation or errors in its execution. Regardless of the reason, the result is the same. Mineral wool is wet. Does this type of cotton wool still fulfill its role? How to dry it?
Mineral wool primarily insulates. In winter it protects from cold, in summer it protects from heat. Increases fire resistance, provides sound insulation, thanks to it the house becomes quieter. When choosing mineral wool, you should choose products with increased hydrophobization. These are materials from which moisture evaporates very quickly.
It must be remembered that wet mineral wool cannot be installed. If it happens that the cotton wool gets wet during transportation or storage, you should first unroll it and dry it thoroughly. Only after it has dried can you begin to install it.
Pros and cons of expanded clay as insulation

Expanded clay is essentially clay that has been foamed and fired in this state. The material was developed specifically as bulk insulation. Among its advantages are low cost and environmental friendliness, but in order to compete with the same polystyrene foam this was not enough.

Expanded clay is very afraid of moisture, has twice the thermal insulation properties compared to expanded polystyrene and a higher specific gravity, therefore in private construction it is most often used as a filler for dry screeds, and not as the main thermal insulation material.