The size of the insulation layer
The materials with which it is planned to insulate the facade of a wooden house are selected depending on the preferences of the owner or on what technology was chosen (wet method, ventilated facade or subsequent finishing with siding). But the thickness of the layer is determined based on the climatic conditions of the region in which the building is located. The table shows the average thickness dimensions of the insulators used.
| Region | Optimal size of insulation layer, cm |
| Leningrad region | 10 |
| Moscow region | 10 |
| Novosibirsk region | 15 |
| Sverdlovsk region | 10 |
| The Republic of Mordovia | 10 |
| Samara Region | 10 |
| Republic of Tatarstan | 10 |
| Krasnodar region | 5 |
| Volgograd region | 10 |
Help from the "façade"
If your region is not in the table, ask in the comments, we will definitely answer you!
Types of wood for ventilated facades
Facade cladding is made from various types of wood:
- Soft conifers (spruce, pine, cedar, etc.) are easy to process, inexpensive, and contain resin that prevents rotting.
- Larch is distinguished by its ability to resist rotting at high humidity. The material is strong and durable.
- Heat-treated wood is natural wood kept at a temperature of 185-230°C. Useful properties of thermowood are durability, aesthetic appearance, moisture resistance, biostability. The thermowood part retains its shape and size in all weather conditions. Manufacturers make thermowood from soft and hard wood.
- Decorative species from the tropics are valued for their attractive appearance. They have high density and specific gravity, so they require a reinforced frame. The cost of exotic wood is high.
The most common methods of insulation
When choosing insulation for the walls of a house, you first need to take into account its thermal insulation characteristics. In addition, an important factor is the tendency of the material to “slip”. Different installation technologies imply special requirements for thermal insulation.
The structure of wall insulation is similar to a layer cake. The structure consists of several layers:
- Thermal insulation material;
- sheathing (not required when installing a wet facade);
- vapor-permeable moisture-protective membrane or reinforcing mesh (depending on the chosen technology);
- finishing layer of facing material.
useful in work
The technology of insulating walls using the wet method is what professionals call pie. The thermal insulation material is glued to the facade using adhesives, then treated with decorative plaster.
Wet facade
The design called a wet facade (pie) requires the use of only dense materials, since subsequent plastering of the surface will be impossible when using Ursa rolled fiberglass wool, which has a low density of 11 kg/m3.
Ventilated facade
The technology of insulating walls using a ventilated method is usually used in the construction of shopping centers or high-rise residential buildings; in private construction, an analogue of this technology is siding, but more on that later. Ventilated facades are usually installed with mineral wool insulation. A special frame (sheathing) is organized and the cladding is attached to it. It is worth noting that the choice of cladding is very large. From heavy stone to lightweight modern aluminum composite material.
The basic principle is the circulation of air between the insulation and the facing layer. Thus, the dew point from the insulation leaves with the rising currents.
It is important to know
Failure to comply with technical requirements when installing a ventilated facade leads to dire consequences. For example, if there are no special gaps between the vertical posts of the profile necessary to compensate for temperature deformation, the system will “bend”, the facing layer will be damaged, and accordingly the money will be wasted.
Siding finishing

This method of wall insulation can be called the most common, since it is inexpensive, and all the work can be done with your own hands. In fact, it is very similar to the ventilated method, the difference is that there are no lugs for air inflow and outflow. Ventilation is carried out through special openings located in each panel. Materials can be used of any density; the insulation can be firmly fixed to the wall using lathing.
Installation of cladding
After installing and fastening the waterproofing, cladding panels or slabs of the selected material are installed on the facade frame. The market offers a large number of different finishing materials for cladding ventilated facades on a wooden base, as well as products that imitate the appearance of a wooden surface.
Each of the materials has its own advantages and disadvantages, which it is advisable to familiarize yourself with before purchasing products.
Natural wood materials usually differ from ventilated wood-look facades in their natural mineral qualities.
Natural wood does not prevent the evaporation of moisture, has excellent visual characteristics, and thanks to modern processing technologies, it can last for a very long time, and atmospheric conditions and other adverse factors will have only a minimal effect on the condition of such coatings.
Fastening the cladding of a ventilated facade is carried out using various clamps, self-tapping screws and other products available on the market in a wide range.
There are open and hidden options for installing cladding. Open ones are easy to use, while hidden ones are more expensive, however, the latter will not interfere with the overall appearance of the house.
Want more information on the topic? Check out these articles:
Until recently, in our country, facades were most often…
Wooden facades are a classic technology for finishing the exterior of houses. Modern construction technologies make it possible to obtain durable and efficient wooden facades, which have replaced traditional log houses.
The following are used as finishing materials for modern wooden facades:
Board for timber;
Lining;
Wood siding;
Planken;
Block house.
A board under timber is used to imitate the facade of a house made of timber. The shape is flat on the front and back sides, but due to the different shapes of the edges it can give a different appearance.
Facade with board under timber
Lining is used for wooden facades with relief shapes (convex, concave, wavy, etc.). The use of lining often requires its additional processing to ensure resistance to environmental factors. It is connected according to the tenon-groove principle.
Wooden siding is a modern type of lining, manufactured using special technology using heat-treated wood and having special grooves for securing the planks. The classic installation of siding is carried out with an overlap, unlike lining, although today there are many types of siding with similar lining profiles.
Wood siding facade
Planken (facade board) in appearance resembles a regular board with rounded or beveled edges. It is mainly made from larch and has a wide range of applications from facade cladding to the construction of fences.
Planken facade
Block house is a special type of wooden cladding that imitates a wooden frame. It has grooves and tenons for connecting individual panels and securing them to the building frame using metal clamps.
Facade from a block house
In addition to the use of various types of finishing materials, there are two main types of wooden facades - ventilated and lightweight.
Ventilated wooden facades are fixed to a special profile beam with a thickness of 200-260 mm, which allows insulation (mainly mineral wool) to be laid between it. To improve moisture removal, the supporting beam has holes or grooves to form an air gap and allow air to pass not only in the vertical, but also in the horizontal direction. It is also possible to use systems with galvanized or aluminum profiles.
Hinged ventilated wooden facade (planken cladding)
Lightweight wooden facades do not have an insulation system, and the wooden finish plays more of a decorative role than a functional one. In this case, the cladding is fixed to a supporting beam no more than 10-15 mm thick.
Often this solution is used for cladding balconies, gables, and decorative parts of the facade.
When finishing a frame house with wood, we use a ventilating gap between the wall of the house covered with MDVP slabs and the facade itself. In this case, the ventilation gap has several functions.
— removal of excess moisture from the frame wall if it appears. This is a mandatory element for Isoplaat and Steico slabs. Steam can freely escape from the wall and not condense in the insulation layer.
— direct “ventilation” of the wood used in the installation of the facade. This allows the wooden facade to go without repair for many years.
The facade itself can be either horizontal or vertical. In addition, you can combine both of these options to highlight individual elements of the house not only with color, but also with texture. The main condition for a ventilated gap is that its width is sufficient to ensure natural ventilation of the facade. The gap itself is mounted using horizontal or vertical slats or bars (the use of 100*25mm boards is also allowed), the thickness of the slats depends on the height of the house and the minimum value can be 25mm. A 50mm gap is used when the wall height is more than 7 meters. The ventilation gap should be open at the bottom as well as at the top of the wall for free air circulation.
The board for the facade is usually dry and calibrated; the profile can be different.
1.Installation with vertical boards.
First option
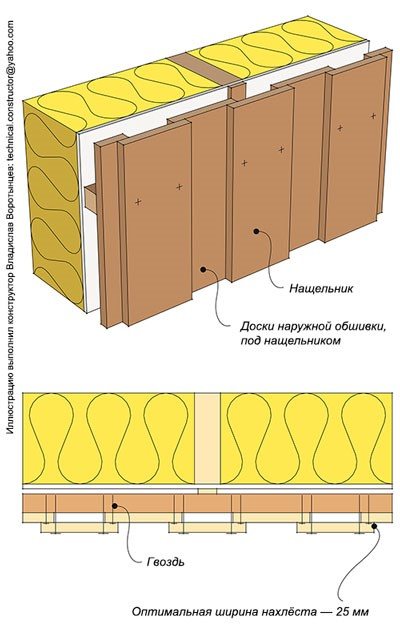
Made from boards 120-170mm. minimum thickness 20mm. As the width of the board increases, its deformation can be very significant; for this reason, for widths greater than 150mm, a board with a thickness of 22mm is used. In this case, the flashing does not have to be the same size as the outer cladding board; it can be either narrower or wider. It is necessary to attach the flashing to the sheathing bar, bypassing the outer sheathing board. This will avoid cracks on the facade when the geometry of the boards changes depending on humidity and weather conditions.
Second option
Option for installing a vertical façade using a strip cover made from a bar. The width of the overlap on each board must be at least 20mm. Each flashing is nailed to the sheathing beam directly, and not through the façade boards. The flashing and external cladding boards can be swapped, i.e. the wide board will be on the outside covering the flashing. In this case, it is important to maintain a minimum distance between the boards of 15-20 mm for ease of painting work. The strips of the flashing must be at least 60mm wide to ensure an overlap of 20-25mm with the sheathing boards.
Third option
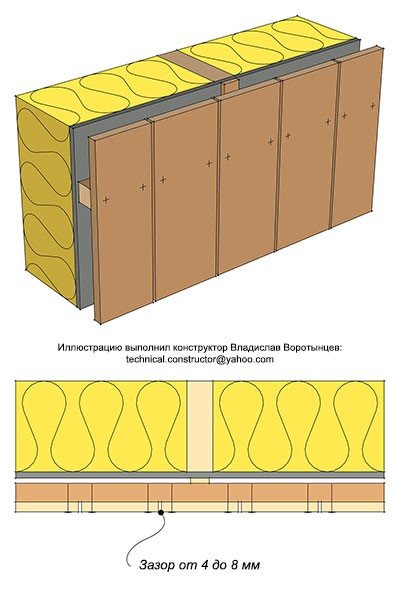
The simplest option is a facade made of rectangular boards with a gap. At the same time, the board protects the cladding of the house from rain, and ventilation of the facade due to the gaps is much more effective. But it should be noted that with a gap more than 8 mm wide, the impact of natural phenomena and ultraviolet radiation can negatively affect the MDVP slabs and the facade sheathing; for this reason, it is recommended to use an additional windproof membrane when installing the facade in this way.
Air access device at the bottom of the wall
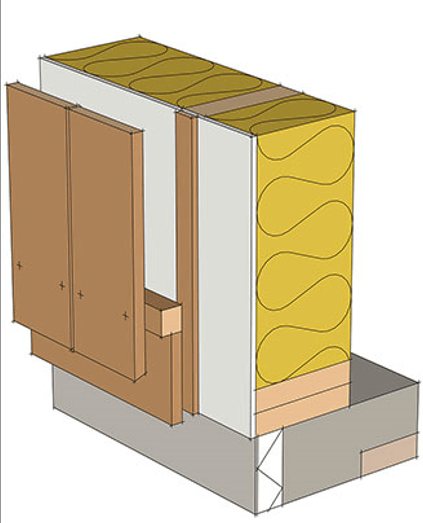
To ensure the safety of the wooden facade, it is necessary to ensure high-quality priming of the boards and sheathing bars themselves. You need to prime the entire surface, both internal and external, as well as the grooves if it is imitation timber. For this reason, priming should be carried out before installation, preferably by immersion in a suitable solution. If the primer is applied with a brush, then this procedure must be carried out at least 2-3 times. Finns usually practice covering painting, i.e. the board is completely covered with paint, hiding the texture of the wood, this ensures greater wear resistance of the facade to natural factors.
For the article, material from frame house designer Vladislav Vorotyntsev was used
Modern building codes, in force since 2000, provide for the construction of energy-efficient buildings. Their rather stringent requirements are determined mainly by considerations of energy saving. Residential buildings that do not meet these standards cannot be built in the city—the state commission simply will not accept them.
In individual low-rise suburban construction, standards do not play such an important role - after all, the house is being built for oneself, and no state commission accepts it. However, it makes sense to focus on these standards if you want to build an energy-efficient house that allows you to save on heating.
What are the requirements for energy-efficient buildings?
If we talk about single-layer, non-insulated external walls, then in order to meet the requirements for heat retention, the thickness of the brickwork must be at least 2 meters, and the thickness of solid wooden walls must be at least 40 cm. It is clear that no one will want to build brick the walls are two meters thick, and wooden walls 40 cm thick are very rare. There is a more rational way to meet the requirements of building codes and save heat in the house without increasing the thickness of the enclosing walls: build multi-layer, insulated walls.
Material characteristics
The main heat insulators used, the installation of which you can do yourself, are shown in the table:
| Insulation , brand | Density, kg/m3 |
| Styrofoam | 25-35 |
| Foam plastic GOST 15588 | 40 |
| Extruded foam | 32-38 |
| Polyurethane foam | 40-60 |
| Penoplex 35 | 35 |
| Penoplex 45 | 45 |
| Rolled fiberglass wool | 11 — 45 |
| Rockwool brand mineral wool | 37-160 |
| Mineral wool "TechnoNIKOL" | 30-127 |
| Mineral wool “Parok Extra” | 37 |
The specific density coefficient depends on the specific brand of the material . The table shows general values.
Vapor permeability
When insulating a log house from the outside with your own hands, it is necessary to take into account the vapor-permeable characteristics of the wall. The material used must have good characteristics that allow steam particles to escape.
It should be remembered that even if the wet method is used, decorative plaster, as well as adhesive compositions, must be vapor-permeable.
Thermal insulation must be adjacent to the facade, and between it and the wall it is strictly prohibited to install materials that prevent air from penetrating through the insulation boards. This can lead to moisture accumulation and subsequent destruction of the wall.
useful in work
Thermal insulation sheets, in the case of using ventilated facade technology, are strung on brackets pre-fixed to the wall.
There must be a distance of at least 4 cm between the insulation and the decorative material (ventilated gap). It is necessary to ensure air circulation inside the system and removal of condensate outside. In this case, it would be correct to use a vapor-permeable moisture-proof membrane; it will prevent the insulation from getting wet and weathering and will extend the service life of it and the entire wall.
The table shows the average vapor permeability resistance coefficients of the most common heat insulators.
| Thermal insulation | Air humidity more than 70% | Air humidity less than 70% |
| Styrofoam | 60 | 60 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 150 | 150 |
| Minvata | 1 | 1 |
| Polyurethane | 50 | 50 |
| Ecowool | 2 | 2 |
| Expanded clay | 2 | 2 |
Installation of a wooden facade
Ventilated facades are easy to assemble. The owner of the house will install the structure himself, without having much construction experience behind him.
Installation is carried out in stages:
- Installation of the frame - the sheathing is mounted on the wall. The sheathing material is a metal profile or wooden blocks impregnated with an antiseptic.
- Laying a layer of thermal insulation. Mineral wool is the best option because it has high vapor permeability and low thermal conductivity. Mineral wool fasteners - umbrella dowels.
- Laying a waterproofing film that does not allow moisture to pass through from the outside, but removes it from the inside.
- The second sheathing of 4-5 cm thick bars provides the required ventilation gap between the insulation and the facing material.
- Installation of cladding is the final stage, which gives the building a new look.
Important nuances
Without taking into account some nuances that are very important, it will not be possible to create high-quality thermal insulation of a wooden house.
Preparatory work
Before starting work, the walls of a wooden house must be cleaned of dust, dirt, and foreign elements in the form of old decorative cladding. After which it would be best to treat the facade with an antiseptic. This will avoid the formation of fungus and the appearance of insects that destroy the structure of the tree.
The next action should be to inspect the façade for rot. If present, it must be cut out and replaced with an uninfected element. It is best to check all the joints between the logs. The cracks that form over time need to be caulked . Only after this can you begin installing the insulation and sheathing on the wall.
Fixing the insulation

Basically, to insulate a wooden house with your own hands, mineral or glass wool is used. This is due to the vapor permeability of the material, which allows the beneficial characteristics of wood to be preserved. One of its disadvantages, compared to polystyrene foam, is its weight. Mineral wool is heavier, so it would be correct to additionally secure it to the surface. This will prevent the slabs from gradually sliding down and forming unprotected areas. In order to properly fix heat-insulating materials on the wall, special mushrooms are used.
An additional measure when insulating the facade of a wooden house is the thermal insulation of the base and foundation. It is best to install using expanded polystyrene, which can then be covered with finishing bricks or decorative stone. This will prevent freezing of the base of the walls and keep the floor in the house warm.
Selection of insulation and protective film
For the ventilated façade of a timber house, only materials with breathable properties are suitable. The most suitable is mineral wool. It refers to the category of fibrous materials. For such cases, basalt wool and glass wool are used, which are lightweight and soft. The installation technology involves the use of a protective film, which should release steam from the thermal insulation and prevent wind from blowing into the insulation. The film should cover the mineral wool. Wind protection and a diffusion membrane cope best with this task.