Sometimes you can come across complaints from owners of private houses that the pressure in the heating system drops.
The problem may occur after some action, at the beginning of the heating season, or it may become periodic, without any apparent reason.
Troubleshooting is the main task from which the “healing” of the system begins. This is what we will do.
Installation of a water heating system for a private house
We are not talking about atmospheric or open type systems, when the movement of the coolant flow is caused only by the rise of water to the height of the expansion tank.
Good pressure is built up only in closed systems with a sealed expander and circulation pump.
Proper arrangement of elements and their calculation is the key to the correct functioning of the system.
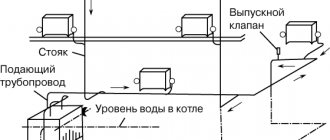
Water heating circuit
The heating boiler is located at the beginning. Then there are pipes and radiators, then an expansion tank (traditionally it is placed in front of the boiler, although a closed tank can be at any point), and then a circulation pump. The location of the pump behind the tank, in front of the boiler, is most optimal and prolongs its longevity.
The norm for a private heating system is a pressure of about 1.5 - 2 Atm.
Pressure increase due to expansion tank

What is the reason and what can be done if the pressure gauge shows high pressure?
The problem may lie in the expansion tank.
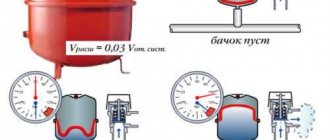
- Membrane damage. When heated to the maximum set temperature in the heating system, the liquid increases in volume by approximately 4%. This excess volume enters the expansion device, compensating for the pressure in the system.
If the membrane is damaged, the liquid will completely fill the volume and initially the pressure in the system will drop. When you open the make-up tap and add water to the system as the temperature increases, the pressure will become higher than rated.
How to determine that the membrane is damaged - when pumping air, the pressure drops, excess liquid comes out through the hoses that connect to the system. A new tank is needed.
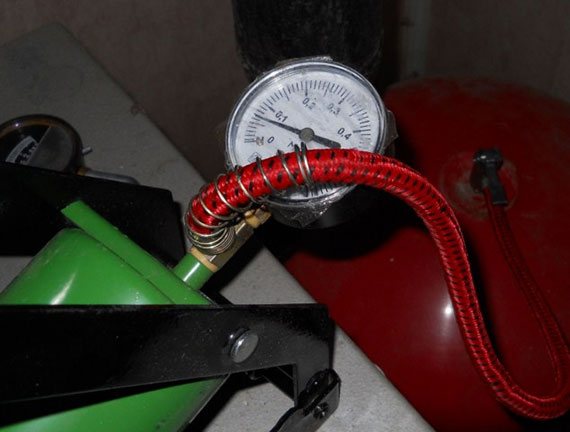

Pump the pump until you see that the water is not flowing. Then you need to bleed the air and pump it up again to the value specified in the boiler manual. Unfortunately, not all manufacturers indicate the pressure of the expansion tank of their products in the instructions; for example, it is not indicated in the instructions for the Immergaz heat generator.
Water hammer causes high pressure in a gas boiler, what to do in this case? In some double-circuit boilers, the compensation tank is located immediately after the circulation pump; when it is turned on, the pressure rises sharply, then also drops sharply.
How can you reduce the influence of the pump and remove excess pressure - the expansion tank is mounted on the return pipe, and the pump is installed in series after the tank, in front of the boiler.
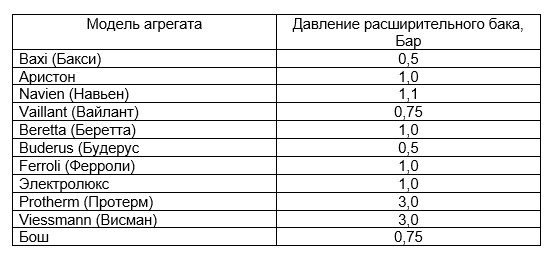
The working pressure of the compensation tank of some 24 kW models is shown in the table.
Why does the pressure drop in the heating system of a private home?
There can be many reasons for a drop in pressure, let's consider the most likely of them.
There is air in the system
Air disrupts circulation, leads to overheating of some areas and cooling of other areas, wears out the pump and leads to the formation of scale on the internal walls of the pipeline. The pressure also drops in an air-filled system.

Where can air come from in heating:
- falls during repair work;
- when filling the system with new coolant;
- is released from the water over time (two to three years may pass before all the oxygen leaves the liquid);
- the operation of automatic air vents is disrupted;
- There's a leak somewhere.
Release mechanisms, or air vents (Maevsky valves) must be installed in all problem areas - on radiators, at the highest points of the pipeline, where there are slopes and loops. When filling the system, the bleeding procedure must be repeated several times. Sometimes, to completely remove the air from the battery, you need to shake it slightly.
Automatic air vents are a very convenient thing, but whimsical. Ideally, they should deal with the purest water. Since there is no such thing, it must be equipped with a filter, but this does not guarantee the absolute serviceability of the device. It needs to be cleaned or replaced periodically. Otherwise, relying on it, you may encounter air jams that “came from nowhere.”
When replacing heating radiators in an apartment, you need to know the pressure in the heating system of a multi-storey building in order to be sure that the selected batteries will withstand the load.
We will discuss the purpose and operating principle of the air valve for heating here.
The Lemax gas boiler is popular in Russia. Following the link we will analyze its device and technical characteristics.
Coolant leak

Another common cause of pressure drop can be a leak. Water can seep out at joints, taps and in places where any fittings are installed.
A visual inspection is a search for traces of water on the floor, corrosion on batteries and pipes.
But this method may not give results, even if there really is a leak (it is especially difficult to notice small leaks on plastic pipes).
There are more effective ways to find a defect - look at the heating with a thermal imager or conduct a test using air pressure. Both of these methods are only available with the use of special equipment.
The identified leak must be eliminated - the damaged section of the pipe is replaced with a new one, the sealant (FUM tape) in the connections is replaced, and the connections are tightened more tightly.
Turn off the pumps and take static pressure measurements. If the indicators drop, there is a leak somewhere! If the static pressure is normal, you need to look for the cause in something else, for example, in the pumps themselves.
Circulation pumps and boiler
You can find out which pump is faulty by turning off all the others one by one and taking pressure gauge readings each time.
If the pumps have been running for a long time, their seals will become damaged over time (must be replaced).
The suction passage in the pump may be clogged. It needs to be cleaned, and installing filters will help avoid relapse. The impeller could have jammed (the reason is the same lime deposits). Or the bearing has collapsed (to prevent this, the pump must be disassembled and cleaned in the summer).
The source of the problem may also be the boiler heat exchanger. If it is clogged with scale, microcracks have appeared, or there was initially a manufacturing defect, this is a reason for serious repairs.
Application of aluminum batteries

Gas formation is one of the disadvantages of aluminum radiators and a possible cause of pressure drop.
Water, in contact with aluminum, causes an oxidation process, which results in the release of hydrogen.
This is typical only for new radiators - when the entire internal surface goes through the oxidation process, gas evolution will stop.
Extender problem
Closed type expanders come in two types:
- balloon;
- membrane
Both options contain a rubber part inside (a horizontal membrane, or in the form of a bag, in a balloon). Over time, it may become covered with microcracks. The rubber does not break through, but stretches. Because of this, the ratio of the volumes of the two chambers changes, and this affects the functioning of the entire system.

Expansion tank in the heating system
Another weak link is the nipple, which over time can begin to leak air.
If it is determined that the problem is in the expander, the whole thing or some parts need to be replaced.
The volume of the tank is calculated based on the total volume of the system, taking into account the coefficient of thermal expansion and the efficiency of the tank itself (specified in the documentation). Antifreeze will require a larger tank. See the formula here.
Lack of size will result in excess water having nowhere to go, and excess volume will cause a drop in pressure.
Preventing the formation of air jams
Preventative measures against the occurrence of air locks are as follows:
- Pay attention to the correct installation of pipes and connections of heating devices. Many problems are caused precisely by mistakes made at this initial stage.
- To prevent air locks, proper commissioning of the equipment is necessary, before which it is important to first check all components and connections.
- Before putting devices into operation, check them for functionality. Using a compressor, you need to apply a pressure level that is ¼ higher than its normal operating value. If it does not weaken within 30 minutes, then everything is in order and the system is ready for operation. If the pressure drops sharply, then leaks are possible, which should be promptly identified and repaired before starting operation.

The operation of water heating networks is characterized by two main parameters - temperature and coolant flow. But there is a third value that often attracts the attention of residents of apartment buildings and private buildings - the pressure in the heating system. The main question is what it should be like for the normal functioning of all heating devices - radiators, heated floors, and so on. Since there is no clear answer, we decided to explain the essence of the problem within the framework of this publication.
How to prevent air from entering the heating system?
It is very difficult to completely avoid air getting into the system, but you can minimize the problem and learn how to easily and quickly remove traffic jams:
- It is necessary to monitor the serviceability and tightness of all joints, shut-off valves, etc.
- Before starting the system, air is pumped into it using a compressor at a pressure 20% greater than the working one. Measurements from the pressure gauge are taken at the beginning of the test and after 20 minutes. If the indicator has not changed, there are no leaks, the system is sealed. A leak will be indicated by the pressure gauge needle, as well as a characteristic whistle. To finally make sure that the leak has been found, lubricate it with a thick soap solution.
- The system must be filled with cold water and smoothly. After filling, the air is released several times using air vents and Mayevsky taps. Each time after draining, water is added to the system.
- It is recommended to use stainless or bimetallic heating radiators.
- It is also advised not to change the coolant too often. A fresh portion of water always contains oxygen impurities.
- To bleed air, install air vents in all problem areas and use them regularly. Or equip radiators with automatic devices and monitor their serviceability.
The adaptation period of the system, during which it is necessary to bleed air and add water again and again, is several days.
Options for solving the problem
To solve the problems described above, you can use the following recommendations:
- Leak in the heating system.
In this case, thermal imaging examination will help, during which system defects are identified. Using a thermal imager, you can easily detect leaks that cannot be seen with the naked eye. The leak itself is eliminated depending on its characteristics: the connections are tightened and sealed or the unit in the system is replaced. - There is a rupture in the expansion tank or the nipple is leaking air. The first thing you should try is to replace the nipple itself
. If there is no result from such manipulation, then change the tank. - Cracks in the heat exchanger in the boiler.
To eliminate this problem, you will have to use the services
of specialists
or monitor the operation of the gas boiler for a long time and identify the liquid entering it.
Next, seal the discovered area
. - Air in the system
. This problem requires a more scrupulous approach, more on that below. - The coolant drain valve
is not closed tightly. It is worth checking the tightness of the tap and tightening it if necessary.
Important: it is best to diagnose a gas boiler and its operation in the presence of a specialist who can ensure safety and prevent an emergency.
Preparing water for the heating system

The higher the hardness of the water, the worse it is for heating - scale leads to overgrowing of the gaps in the pipes, damages the boiler heat exchangers and kills the pumps.
Cleaning the system from scale is an extremely difficult task that takes several days. It’s easier to make an effort once to properly prepare the coolant for heating.
Soft water is not available everywhere, but hard water can be softened at home before adding it to the system. For this purpose, special filters – softeners – are purchased.
There is also no need to try too hard when softening water, because soft liquids have higher acidity, and this leads to the release of carbon dioxide and corrosion of metals. Antifreezes containing glycol also have high acidity. Additives - inhibitors (silicates, amines, phosphates and others) help reduce its harmful effects.
Good acidity: 8.5 – 9.5 pH.
Recipe: You can mix tap water with distilled water in a 1:1 ratio.
Pre-chlorinated water needs to sit for several hours.
After mixing, the resulting liquid must be boiled (to remove oxygen from it).
Do not use chemical additives to soften water.
Their use destroys seals, and when heated, processes occur that are destructive even for metals.
Every homeowner should know what the pressure in the heating system in a private home should be. This directly affects the performance of the heating circuit.
See the following review for the types of electrolysers and their purposes.
So, if the pressure fluctuates or is consistently low, the search for the problem should begin by inspecting the pipeline for leaks. Then check the performance of the pumps by measuring the static pressure. In order not to encounter the problem again, you need to install air vents everywhere and spare no effort in preparing the coolant with an optimal pH.
Problem with the boiler: flooded through the drain
NNN wrote: The discharge from the safety valve should be into the sewer, and not onto the floor or into a bucket.
definitely!!! Here is a list of general requirements for installing domestic natural gas boilers, taken from a related resource. It contains mandatory and recommended standards.
No. Name of requirement
- General requirements 1.1 Connection and operation of a gas boiler is permitted subject to the technical conditions of the local gas service and the agreed “Gas supply” project. 1.2 For heating private residential buildings, it is allowed to install boilers with exhaust of combustion products through an external wall and a sealed combustion chamber. For heating residential buildings up to 10 floors high, it is allowed to install boilers with exhaust of combustion products into the chimney in accordance with DSTU B V.B 2.5-33:2007 1.3 There should be no more than two heat generators in one room. 1.4 The selection of the most optimal chimney should be carried out by a specialist. You just need to know that the internal diameter of the chimney must be no less than the diameter of the boiler neck; there should be a minimum amount of various bends and elbows in the path of flue gases; When installing a chimney, it is imperative to take measures to prevent the formation of condensation. An important condition for the uninterrupted operation of gas heating equipment are chimneys for boilers with natural ventilation. To remove combustion products from heat generators, chimneys inside the walls of buildings and structures, attached external and internal ones, and special horizontal channels in external walls can be used to remove combustion products from heat generators with a hermetic firebox. The cross-section of chimneys and the amount of draft must ensure normal operation of heat generators in all operating modes. The combustion products must be removed to a height of 0.5 m above the roof ridge when the chimney is located horizontally no further than 1.5 m from the ridge; at the level with the ridge when located no further than 3 m; not lower than a straight line drawn from the ridge downwards at an angle of 10° to the horizon, when the chimney is located at a distance of more than 3 m from the ridge. In all cases, the height of the pipe must be at least 0.5 m from the adjacent part of the roof, and for houses with a flat roof, at least 2 m. 1.5 Installation of the chimney and gas pipelines must be carried out by a specialized organization that has a license, appropriate permits and approvals. 1.6 Responsibility for the safety, good condition and safe operation of heat generators lies with the owner of the premises in which they are installed. 1.7 The equipment must be stored indoors, protected from dust and moisture, at an air temperature of at least +5 °C. 1.8 Before installation of equipment begins, it is necessary to ensure 100% construction readiness of the boiler room (furnace), including engineering support and internal work. In this case, be guided by both these recommendations and the recommendations of related organizations whose equipment is installed in the boiler room (furnace room).
- Architectural and construction part 2.1 The installation of a gas heating device with a power of up to 30 kW should be provided in a kitchen or specially designated room that meets the following requirements:
- volume (LxWxH) of at least 21 m3 (for the kitchen), 7.5 m3 (for a separate room);
- height (B) not less than 2.2 m. At the same time, the duration of stay of people during the day in the territory of this premises should not exceed 4 hours. 2.2 Installation of a gas heating device with a power from 30 kW to 200 kW should be provided in a specially designated room that meets the following requirements:
- volume (LxWxH) not less than 13.5 m3 (from 30 to 60 kW), not less than 15 m3 (from 60 to 200 kW);
- height (H) not less than 2.5 m. 2.3 Determine the dimensions of the room taking into account the requirements of clauses 2.1,2.2, as well as taking into account the ease of installation and maintenance of the installed equipment. 2.4 The enclosing structures (walls, ceilings) of the boiler room must have a fire resistance limit of at least 0.75 hours. In this case, the limit of fire spread over the entire area of the structure must be zero. Such partitions are made to cover the entire height of the boiler, while the height of the room must be at least 2.5 m, and the walls must be made vapor-gas-tight. 2.5 The walls and floor of a separate boiler room must be fire-resistant and not a source of dust. One of the most optimal solutions for creating and maintaining cleanliness in a boiler room will be tiling the walls and floors with ceramic tiles, as well as coating them with oil paint. Since it is dust that leads to the deposition of contaminants on the burners and in the heat exchanger channels, which largely reduces the performance of this heating equipment. If the room is made of flammable materials, then the wall or floor where the heating boiler is supposed to be installed is made of non-combustible materials or lined with non-combustible materials. 2.6 The window must provide natural light at the rate of 5% of the volume of the room, and be equipped with a window or transom. 2.7 The floor must be waterproofed to a water level of 100 mm (if possible). 2.8 Provide a sewer drain DN50, slope the floor towards the drain. 2.9 Pour a 100 mm high foundation under the boilers, and provide a “reinforced” floor under the water heater tank (if possible). 2.10 Doors with a width of at least 800 mm must open directly outwards. 2.11 Provide installation openings to allow delivery of boiler equipment. 2.12 Pipe passages through enclosing structures should be made in sleeves, and the inputs of all utility lines should be sealed.
- Heating and ventilation 3.1 To ensure constant 3-fold air exchange and supply the required amount of air for combustion, install an adjustable supply air louver grille in the outer wall, the bottom at 0.3 m from the finished floor level.
Calculation of hood power: Formula: M = (SxHx12) + 30%, where: M - hood power S - kitchen area H - ceiling height in the kitchen 12 - every hour (according to SES standards) the air in the room where the gas boiler is located should update up to 12 times 30% - the minimum power reserve required for effective air purification.
An example of calculating the hood power: In a room where a gas boiler is installed, the area is 7 sq.m., the ceiling height is 2.5 m. The hood power required for such a room is: M = (7 × 2.5 × 12) + 30% = 273 cubic meters/hour
Note: it is necessary to take into account the fact that 30% of the power reserve is only sufficient if the hood is located directly above the boiler. In other cases, when calculating the exhaust power, you should add another 15% for each turn of the air duct pipe and another 10% for each meter of the air duct. 3.2 The ventilation duct is designed to ensure 3-fold air exchange to the height of the chimney, ending with a protective umbrella. The exhaust hole in the boiler room should be equipped with a decorative grille at a height of the bottom of the hole no lower than 0.3 m from the ceiling. 3.3 Provide a heating system based on heating the supply air and compensating for heat loss. The estimated air temperature in the boiler room is 16°C.
- Water supply and sewerage 4.1 Cold and hot water supply pipelines should be made from “drinking” quality pipes. 4.2 Provide wastewater drainage from the sewer drain into the sewer system. 4.3 Provide for the possibility of replenishing the heat supply system from a pipeline with potable water or after installing water softening (in accordance with the requirements of the boiler and heating equipment manufacturer). To do this, ensure the necessary pressure of the make-up water.
- Electrical supply, electrical lighting, electrical protection 5.1 Electrical supply to the boiler room is carried out from the distribution board of the house or existing electrical networks. It is also necessary to take into account the parameters of the location of the gas pipeline relative to the house electrical network. For example:
- the distance of the gas pipeline from the electrical panel must be at least 30 cm
- from electrical wires that are laid in an open way at least 25 cm
- from hidden wiring about 5 cm. 5.2 Provide artificial lighting 5.3 Run cable routes along the walls and ceiling in trays (if possible). 5.4 Install 2 sockets with a voltage of 220V, 10A, connect a 3x2.5mm copper cable to the boiler from the distribution board through a 16A circuit breaker. 5.5 Install a household gas monitoring and alarm device (SGB 1-2 type alarm) above the gas metering unit, for which provide a 220V, 6A socket. 5.6 Install the outside temperature sensor on the north or north-west side of the house. From the sensor, lay a 2x1.5 mm copper cable to the boiler regulator in a protective pipe. In the boiler room, leave a free end of the cable to the boiler ~2 m; It is prohibited to lay the cable from the sensor with 220V (400V) power cables. 5.7 If the boiler is controlled by a room thermostat installed in a living room (recommended in the bedroom), lay a 3x0.75 copper cable from the device to the boiler. 5.8 Main equipment, automation equipment and power supply equipment should be grounded. 5.9 It is recommended to install a powder fire extinguisher in the boiler room and have a portable lamp with a voltage of no more than 12V. 5.10 Provide lightning protection for chimneys (if necessary). 5.11 It is recommended to install a voltage stabilizer and an uninterruptible power supply.
- Gas alarm 6.1 In the room provided for a gas boiler, a gas alarm must be installed, which will help monitor the microconcentration of carbon monoxide and send a signal to an individual warning alarm system, which, if the required level is exceeded, will shut off the gas supply.
- Start-up requirement 7.1 Have permission to start gas. 7.2 Before starting the boiler, flush all heating systems and remove air. 7.3 Prepare reports: 3-fold air exchange, chimneys, ventilation ducts, hidden work, hydraulic tests. 7.4 Provide gas pressure in front of the boiler burner in accordance with the requirements of the boiler equipment manufacturer. All safety parameters indicating the location of gas heating equipment in centimeters are clearly stated in the installation instructions for each individual boiler model.